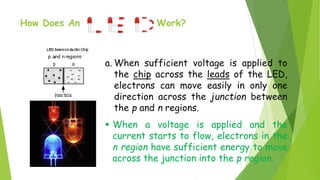
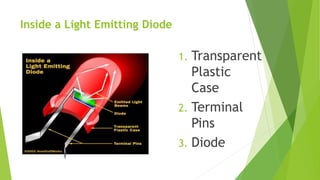
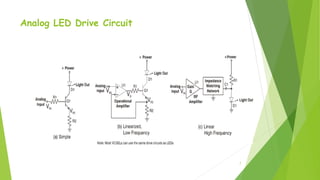
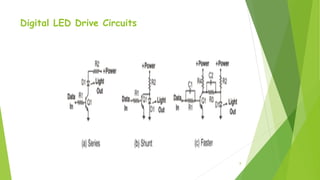
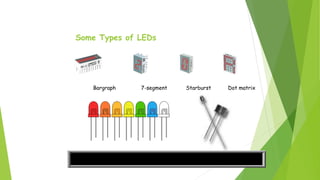
The document provides an overview of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and liquid crystal displays (LCDs), explaining their mechanisms and applications. LEDs are efficient light sources that convert electrical energy into light, while LCDs utilize liquid crystals to modulate light for display purposes. Both technologies are contrasted in terms of power consumption, response rates, and size options available.