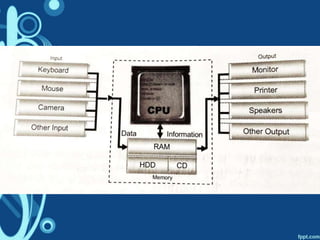
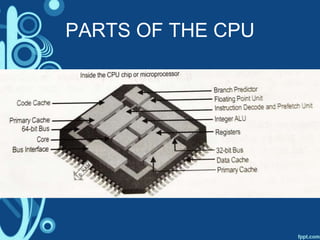
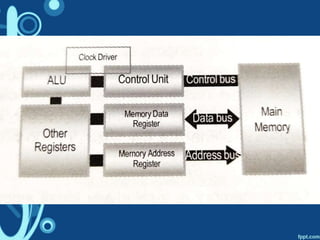
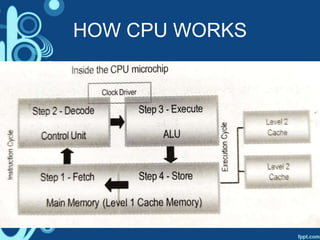
The document discusses how a computer system works by describing the input, processing, and output of data. It also outlines the key parts of a computer that are necessary for it to function, including the central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), output devices, and secondary storage. The CPU is described in more detail, with its main components explained as the control unit, arithmetic logic unit, registers, cache, and buses that connect the various parts.