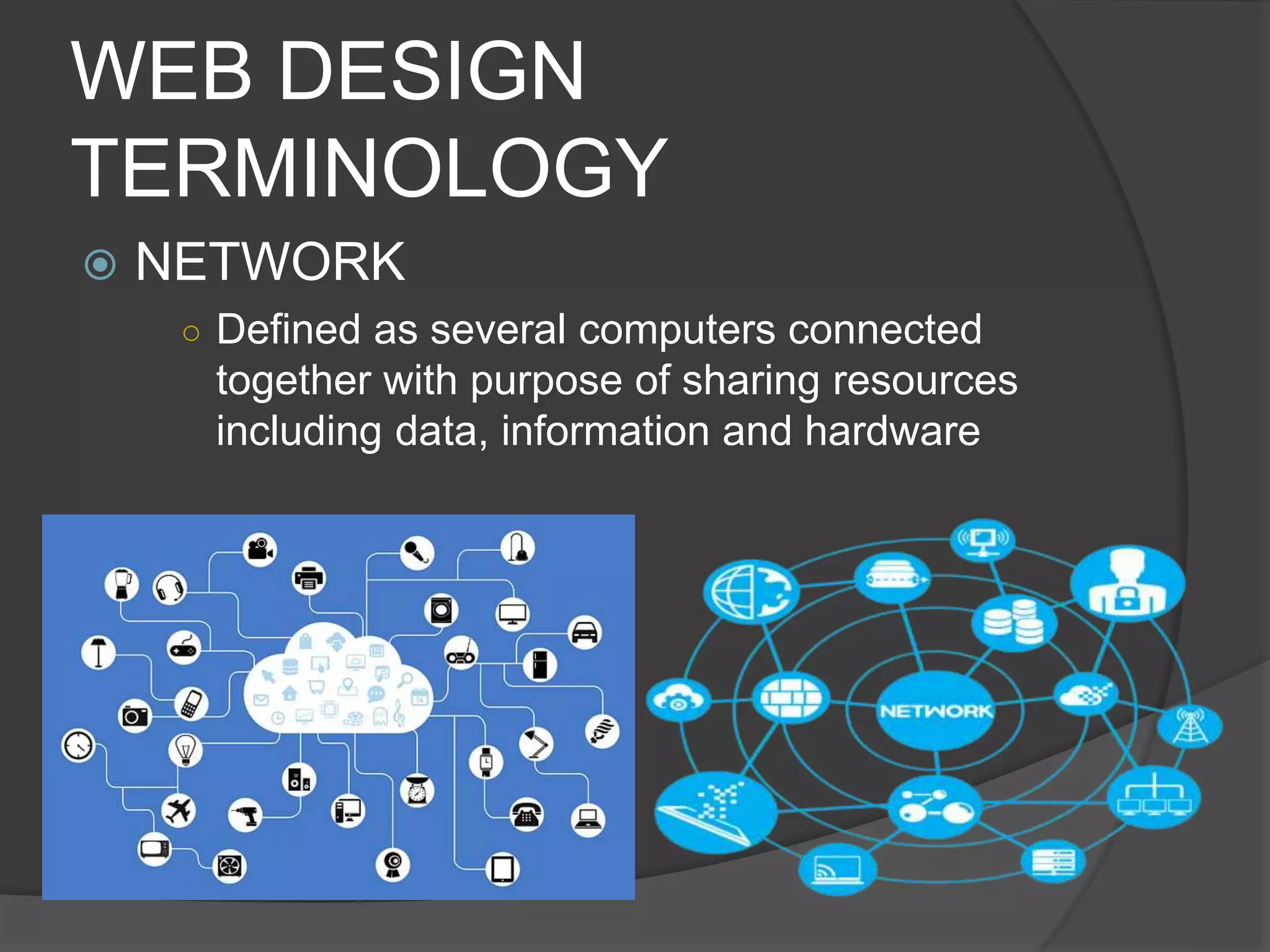
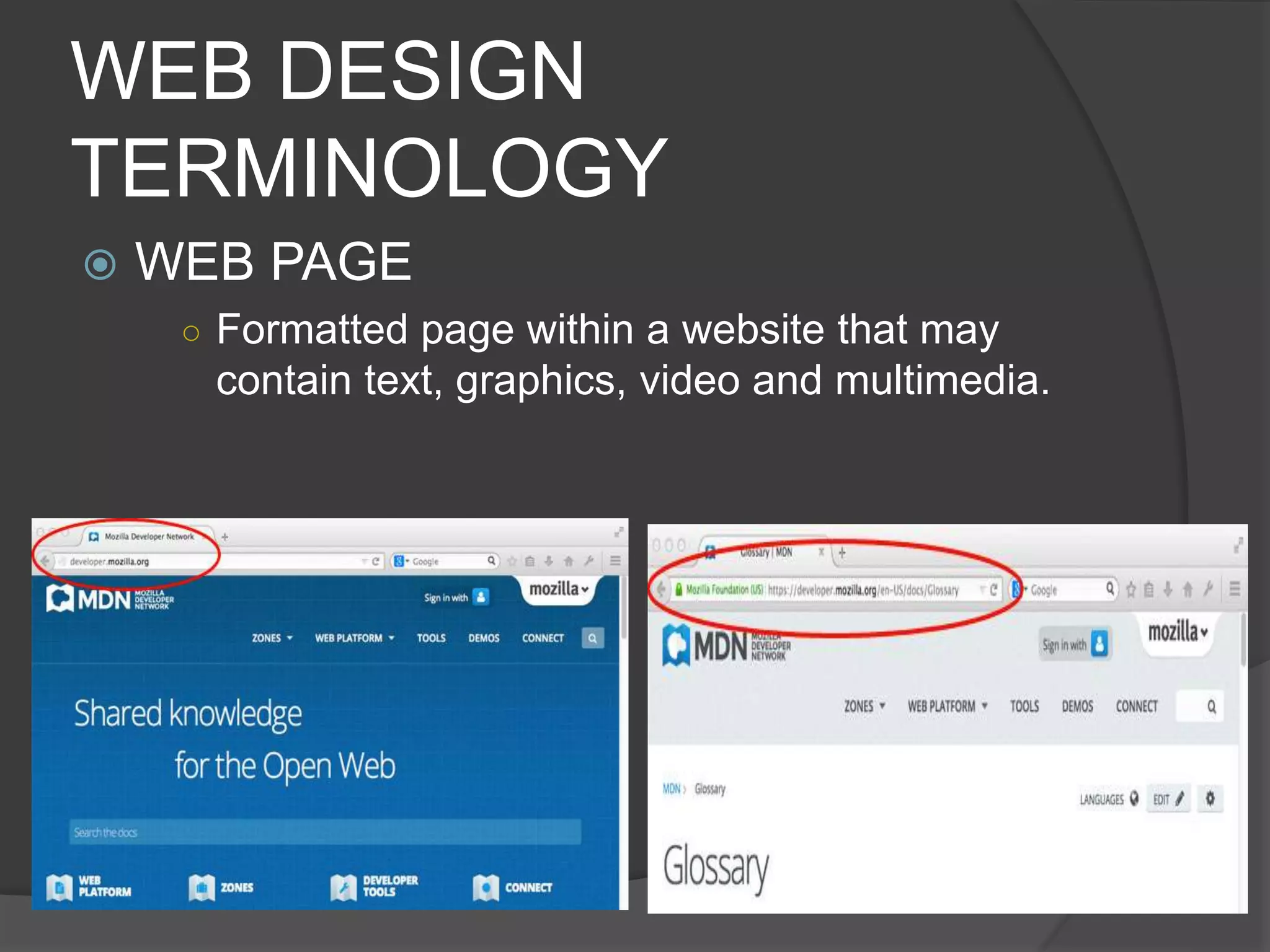
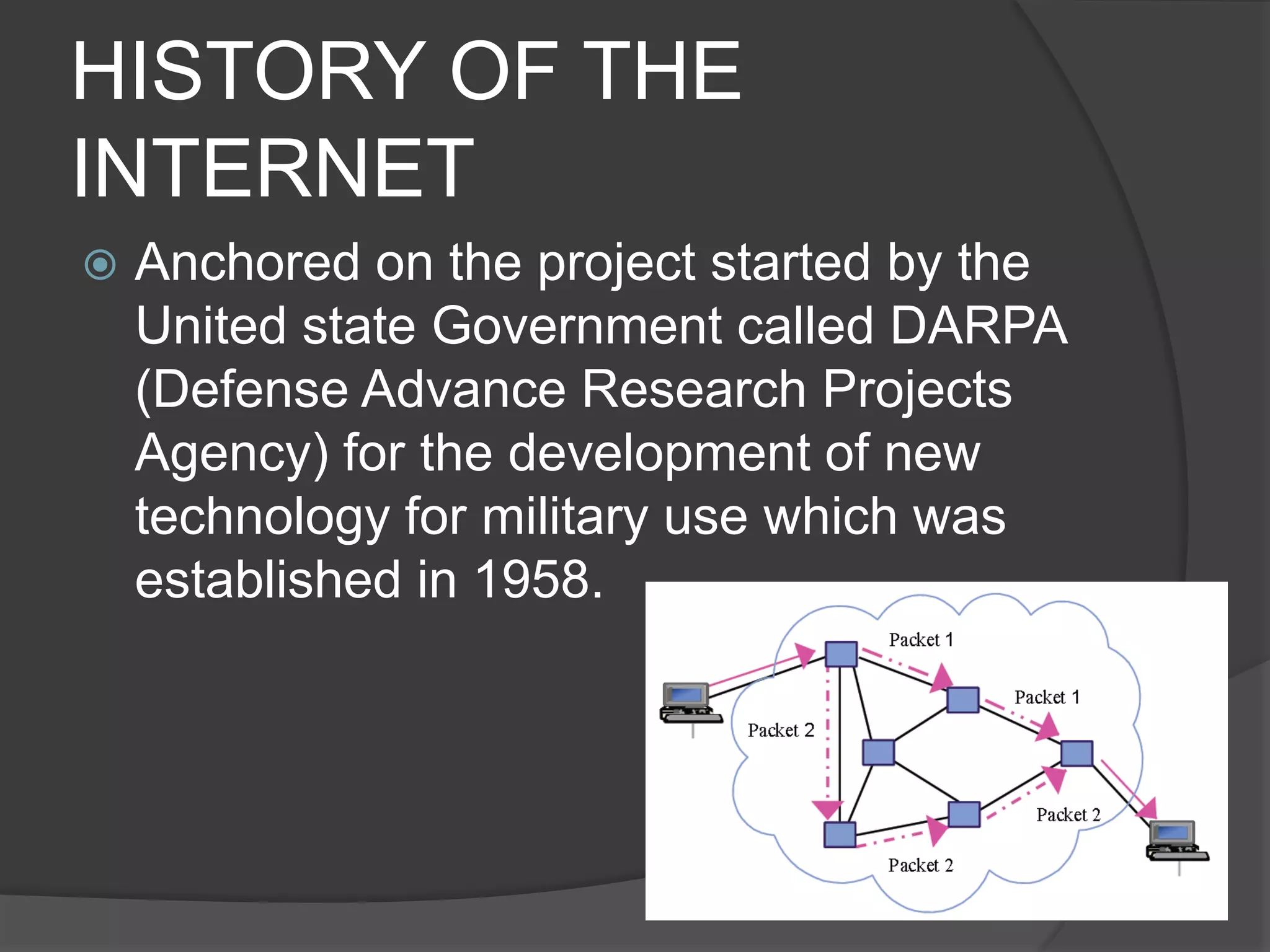
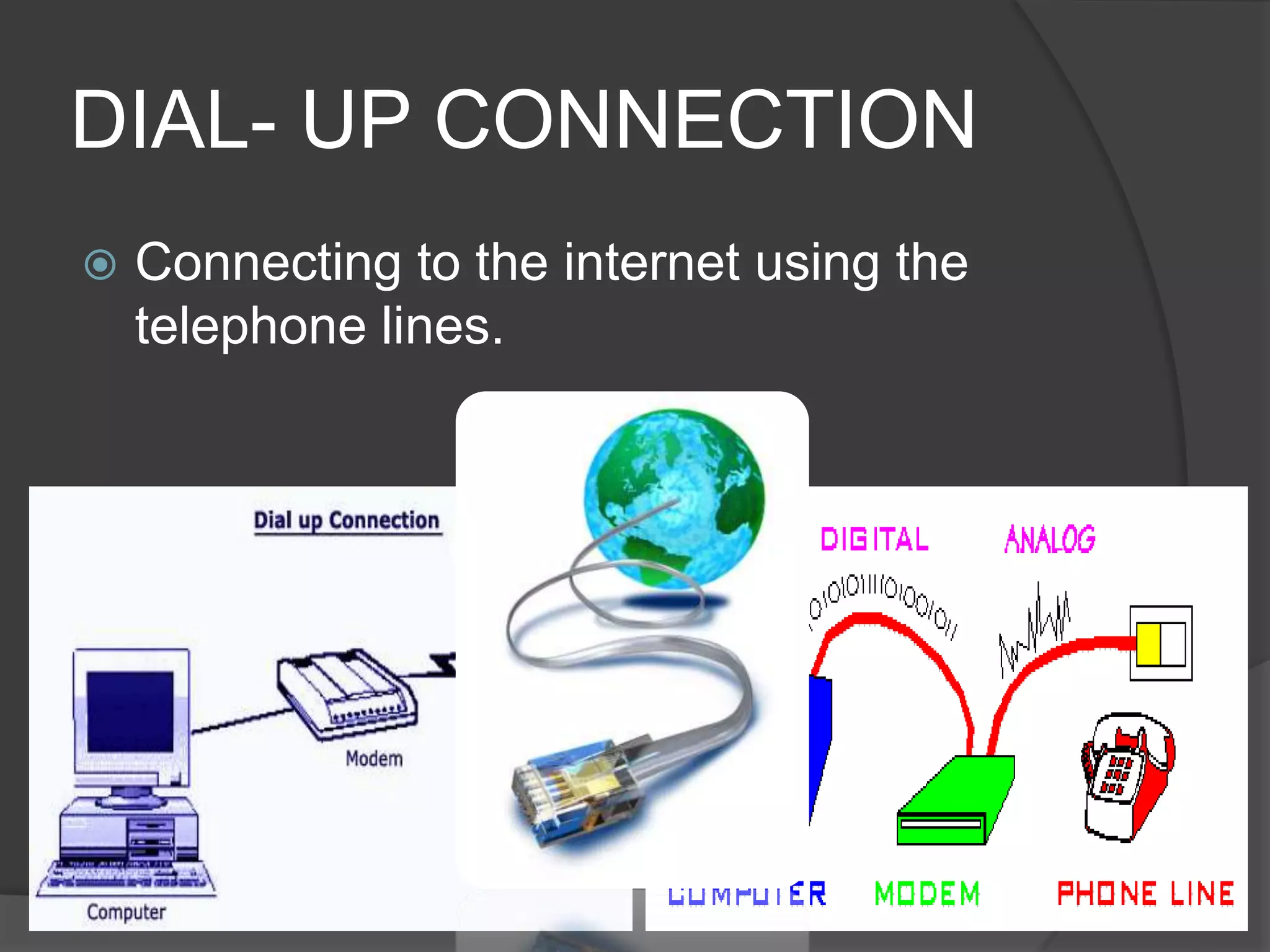
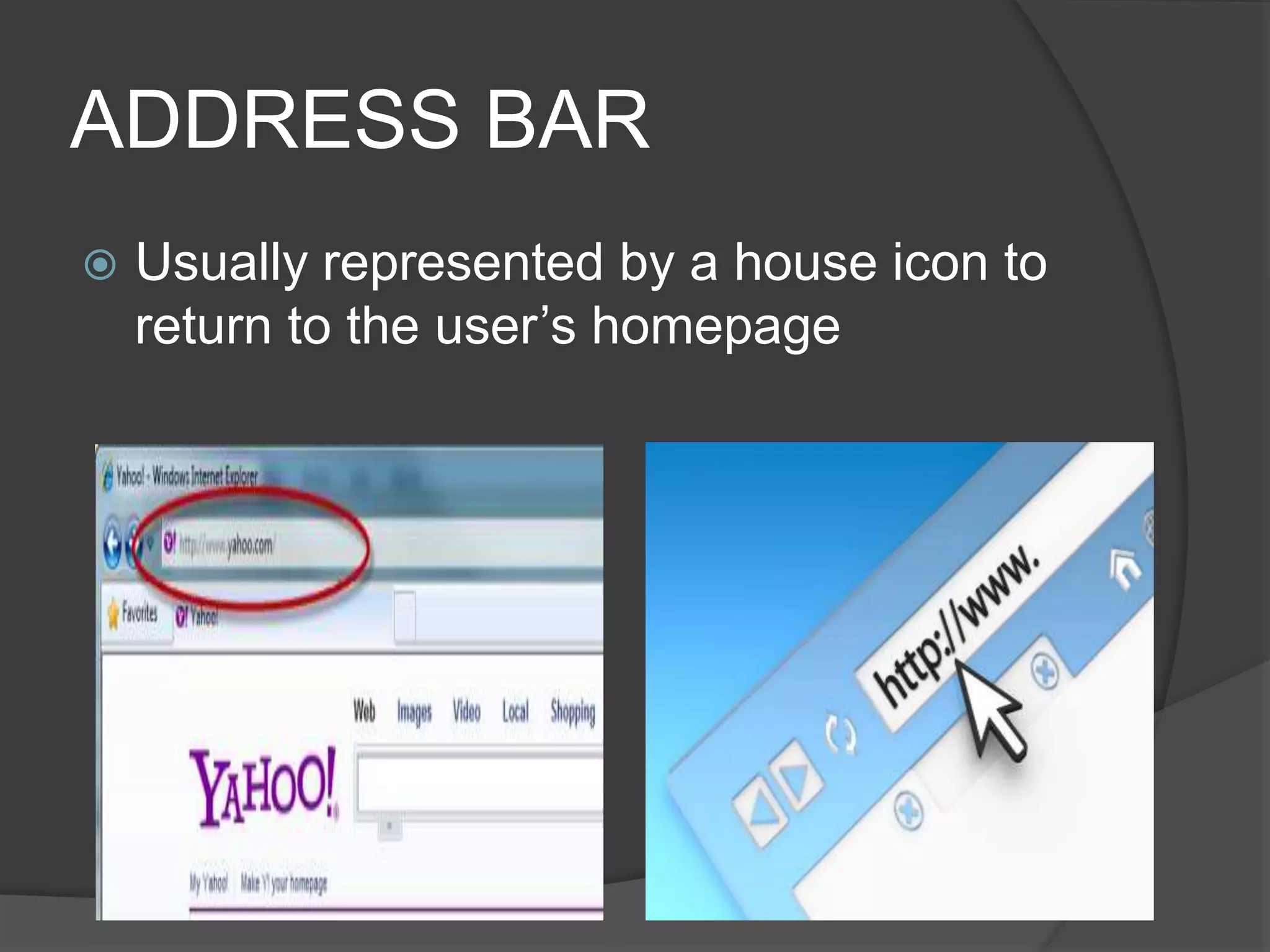
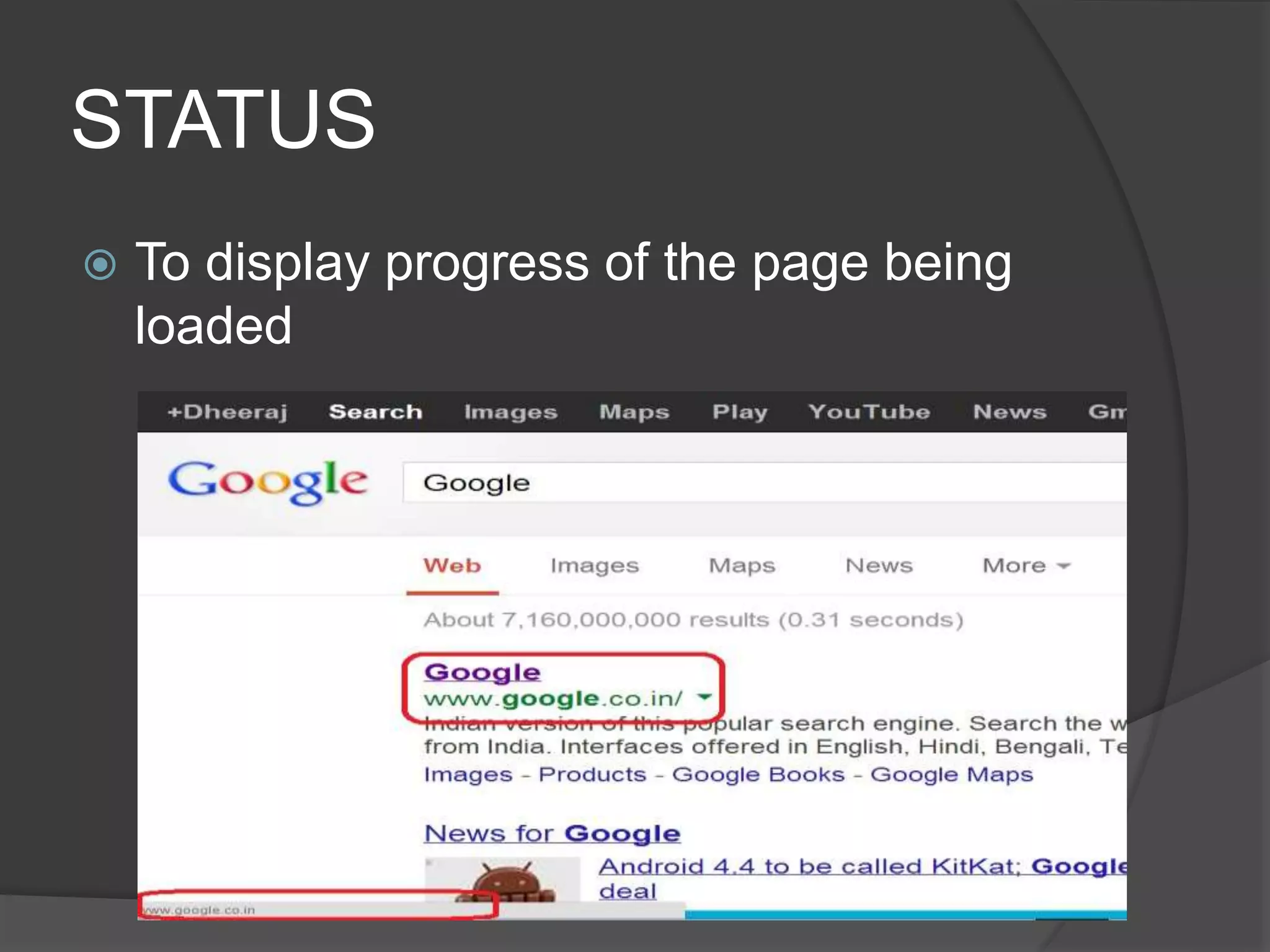
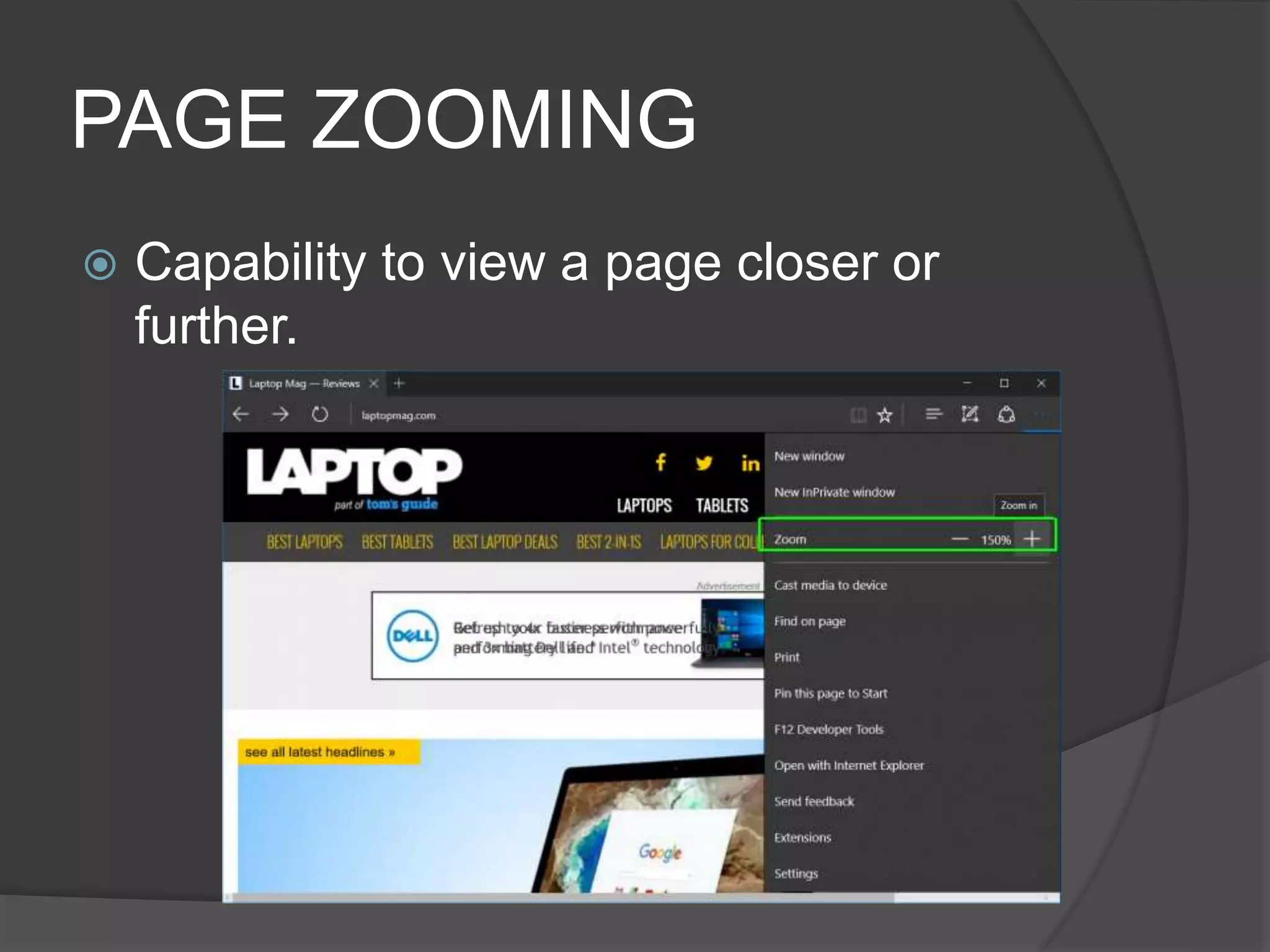
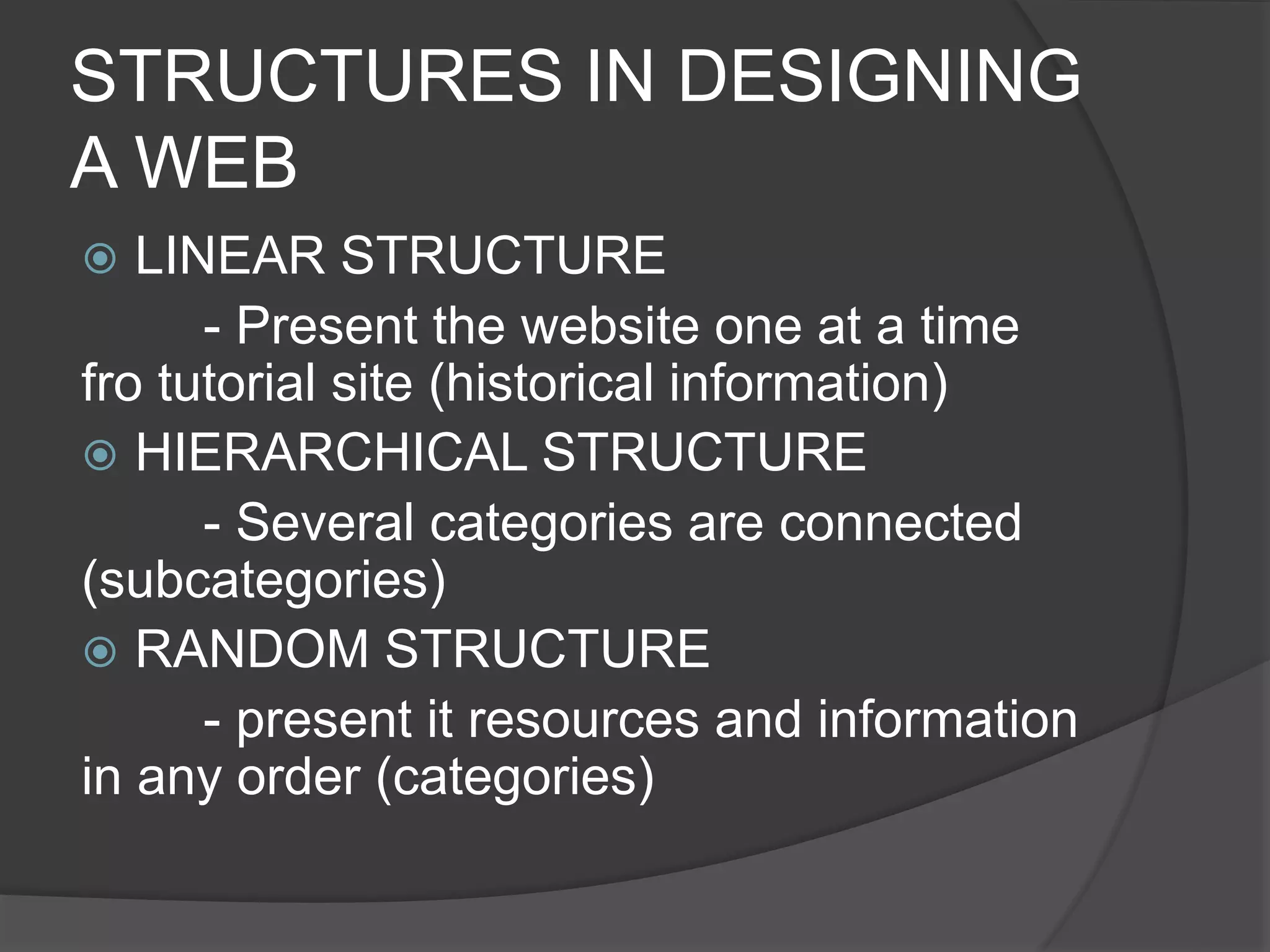
The document defines key terms related to web design and networking. It explains that a network connects computers to share resources, the internet interconnects computers globally, and the world wide web allows resources to be interconnected via the internet. It also defines other common web design elements like web pages, home pages, and navigation buttons.