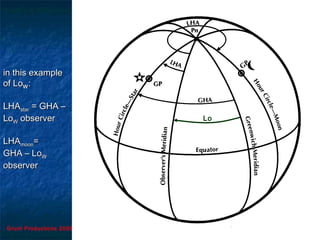
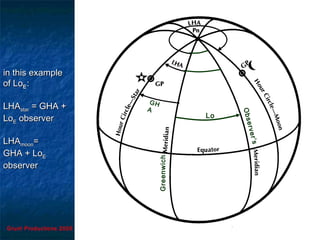
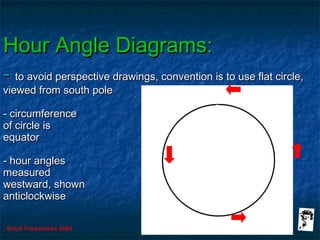
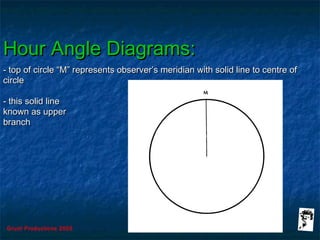
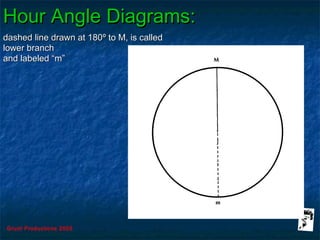
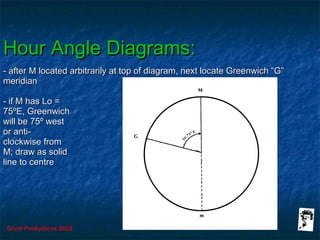
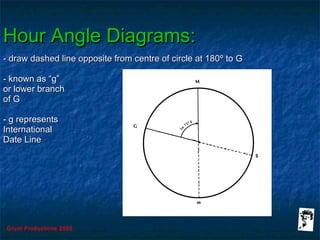
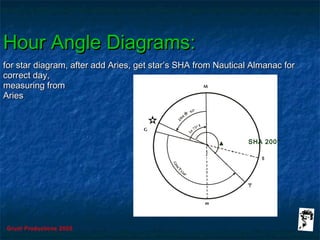
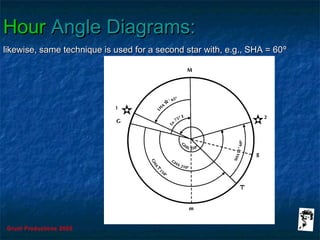
This document discusses hour angles and Aries as they relate to celestial navigation. It defines key terms like declination, Greenwich hour angle (GHA), local hour angle (LHA), and sidereal hour angle (SHA). It explains that the Nautical Almanac contains tables with the geographical position of celestial bodies by the second. It also notes that SHA is measured from the point of Aries instead of Greenwich for stars to make the almanac thinner. Diagrams are used to illustrate the relationships between an observer's meridian, Greenwich, Aries, and the hour angles of bodies.