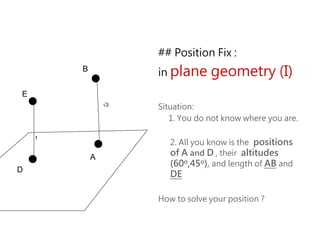
1) The document discusses celestial navigation techniques, including methods for determining speed, direction, and position using various historical instruments.
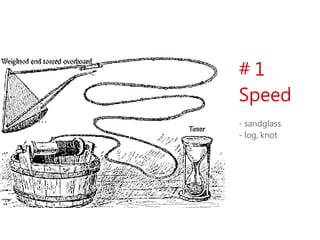
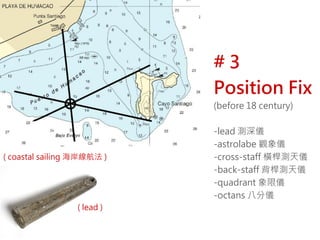
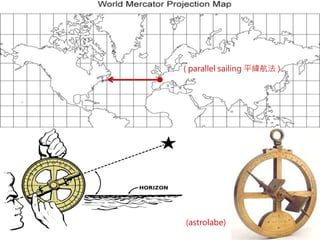
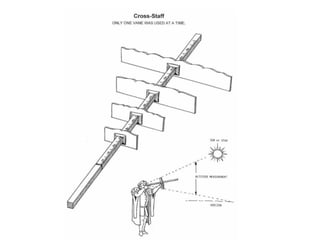
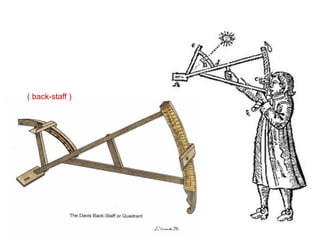
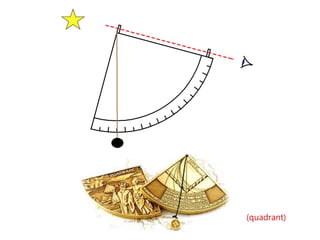
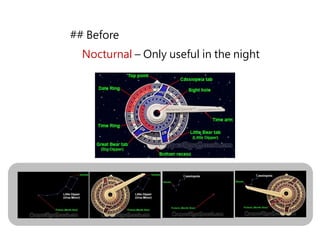
2) Key instruments mentioned include the sandglass, log, compass, lead, astrolabe, cross-staff, back-staff, quadrant, octant, chronometer and sextant.
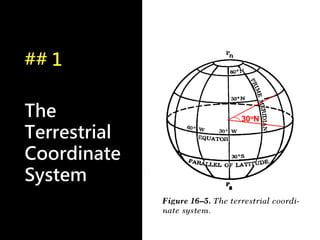
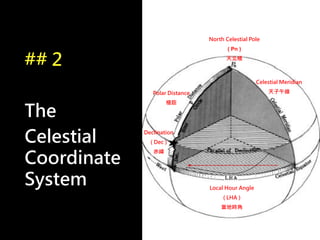
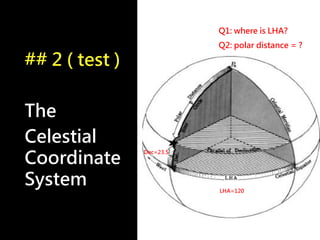
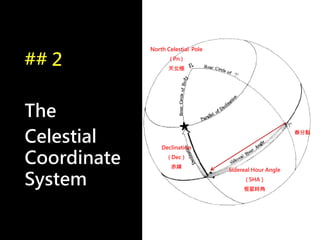
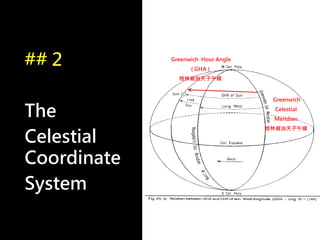
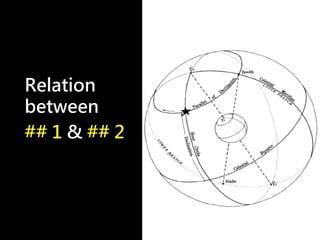
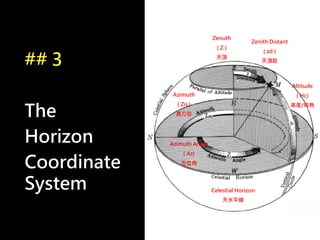
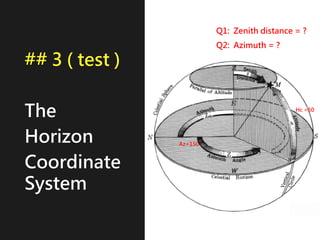
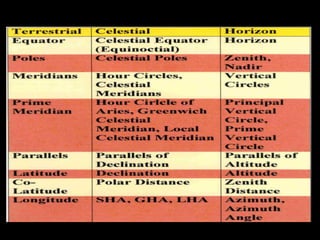
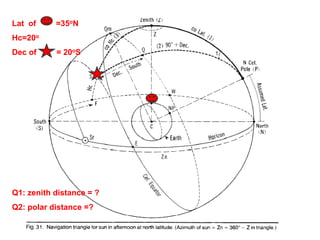
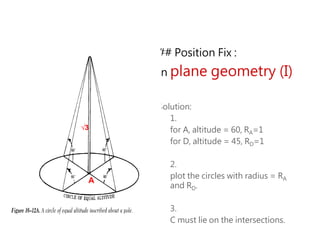
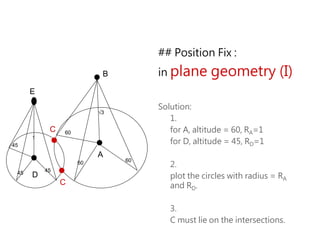
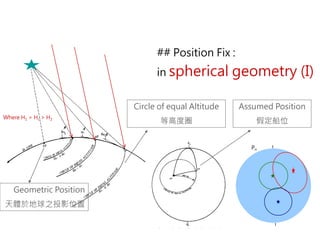
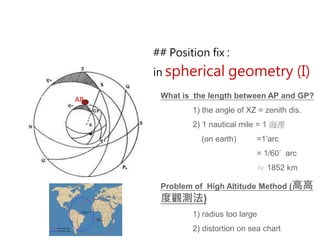
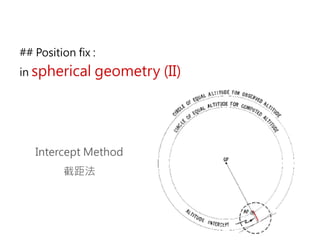
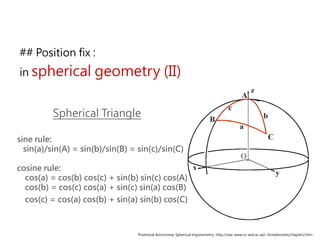
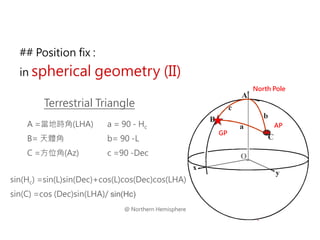
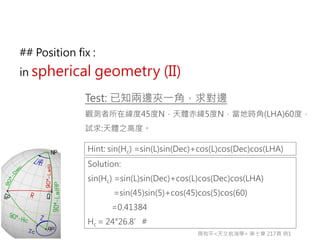
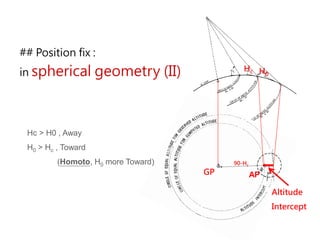
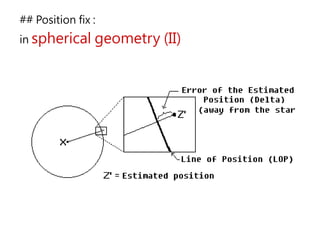
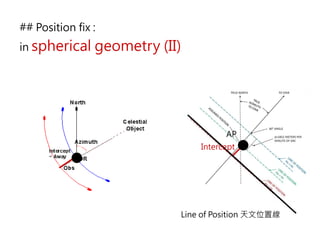
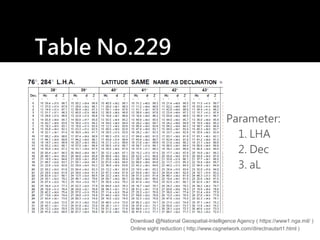
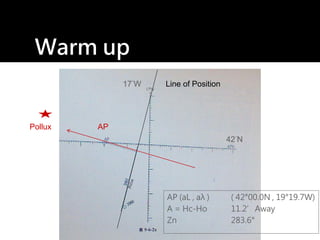
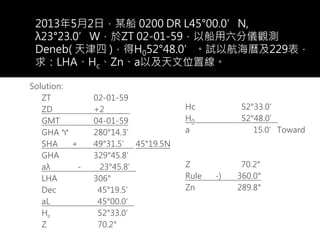
3) The document also covers the three coordinate systems used in celestial navigation: terrestrial, celestial, and horizon. It provides examples of how sights are reduced using the Nautical Almanac and tables to determine position.