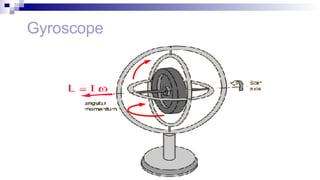
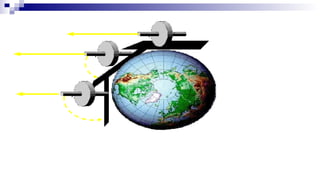
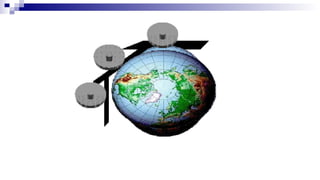
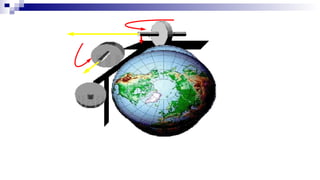
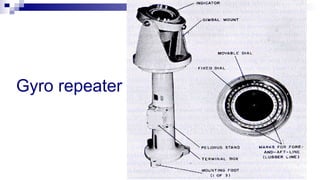
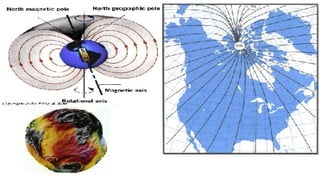
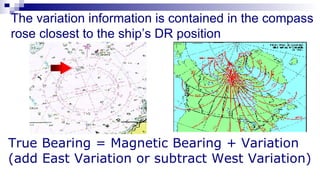
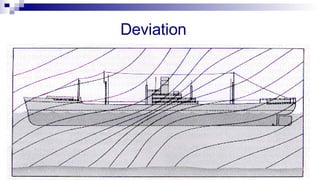
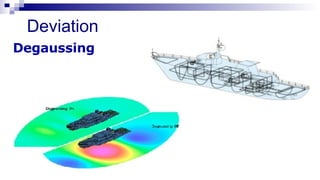
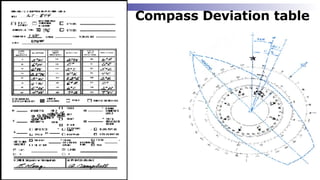
The document discusses gyrocompasses and magnetic compasses. It describes gyrocompass theory including how gyroscopes maintain orientation to true north. It also discusses gyro error determination and correction. Magnetic compass theory is explained including variation, deviation, and magnetic compass error. Methods to determine gyro error and apply corrections are provided along with examples of solving for true course from other compass readings.