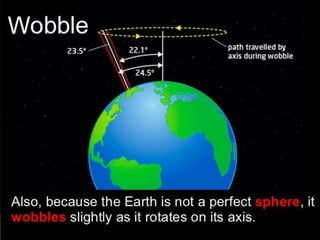
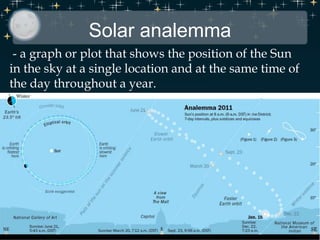
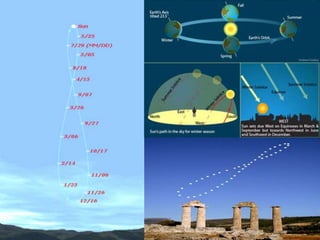
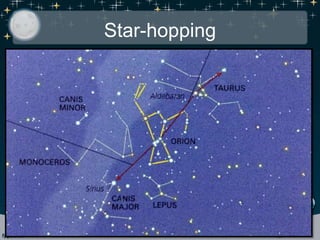
This document discusses various celestial objects and concepts related to observing the night sky, including:
- The celestial sphere, an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth on which stars and other celestial objects appear to be located. Important circles on the celestial sphere include the celestial equator and the ecliptic.
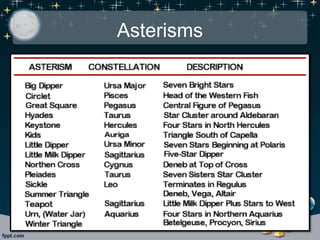
- Constellations, patterns of stars grouped together, of which there are 88 officially recognized. Asterisms are smaller distinctive star groups within constellations.
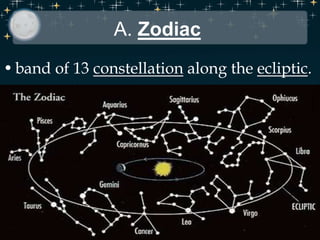
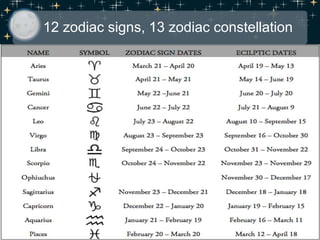
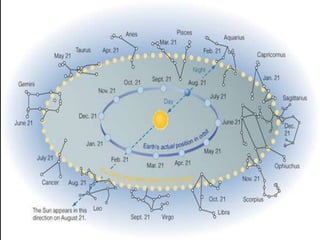
- The zodiac, a band of 13 constellations along the ecliptic through which the sun passes each year.
- How the night sky appearance changes based on one's latitude on Earth. Tools for observing and measuring positions of celestial objects