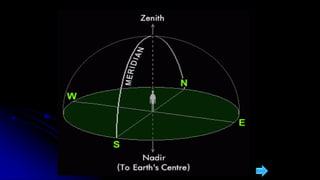
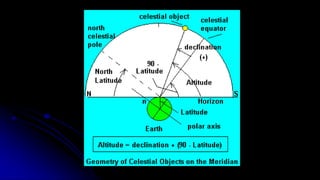
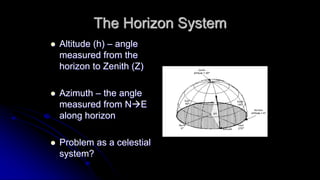
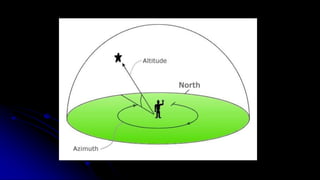
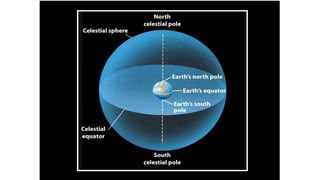
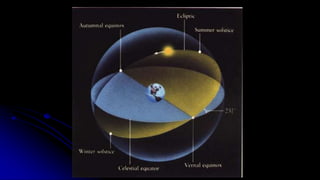
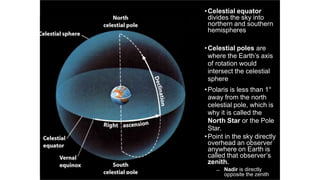
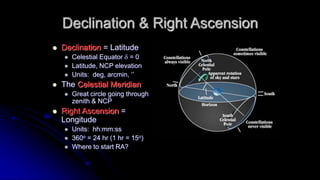
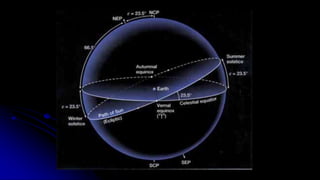
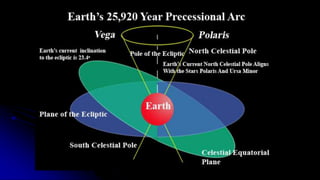
This document discusses coordinate systems used to describe the positions of objects in the sky. It describes two main coordinate systems: the horizon system which uses altitude and azimuth, and the equatorial system which uses right ascension and declination based on the celestial sphere. The celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere where stars appear to reside, with the same poles and equator as the Earth. Right ascension is similar to longitude, measured in hours, minutes, and seconds along the celestial equator. Declination is similar to latitude, measured in degrees north or south from the celestial equator. These equatorial coordinates slowly change over long periods of time due to changes in the equinoxes and Earth's rotation.