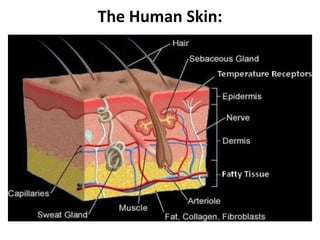
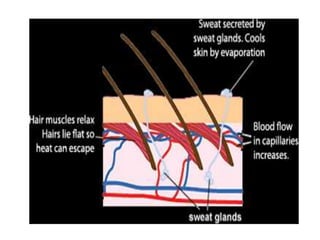
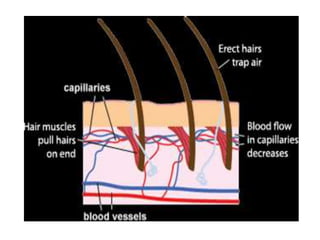
This document discusses homeostasis and temperature regulation in the human body. It explains that the body maintains a constant internal environment through homeostasis. The hypothalamus acts as the body's thermostat to monitor core temperature and initiate responses like sweating and shivering to cool down or heat up the body when temperature fluctuates outside the normal range. A variety of mechanisms in the skin like vasodilation, erecting hairs, and sweating help regulate heat exchange and maintain a stable core temperature.