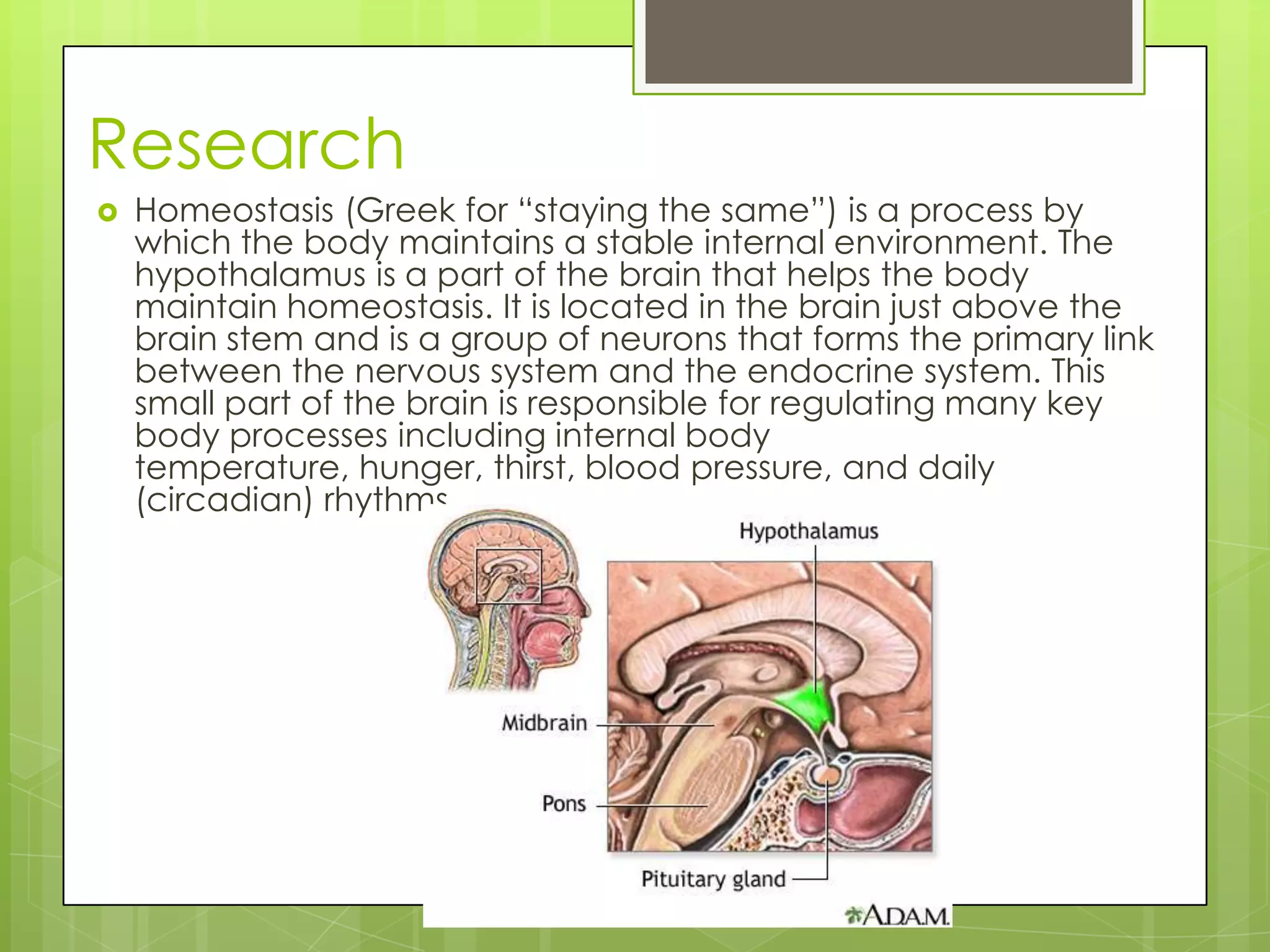
The document discusses homeostasis and how the body maintains internal stability. It defines homeostasis as the process by which the body maintains a stable internal environment. It states that the hypothalamus, located in the brain, helps regulate key body processes like temperature, hunger, blood pressure, and circadian rhythms to keep homeostasis. When the body experiences internal changes, the hypothalamus works with other systems like the nervous and endocrine systems to restore the body's systems back to their normal states.