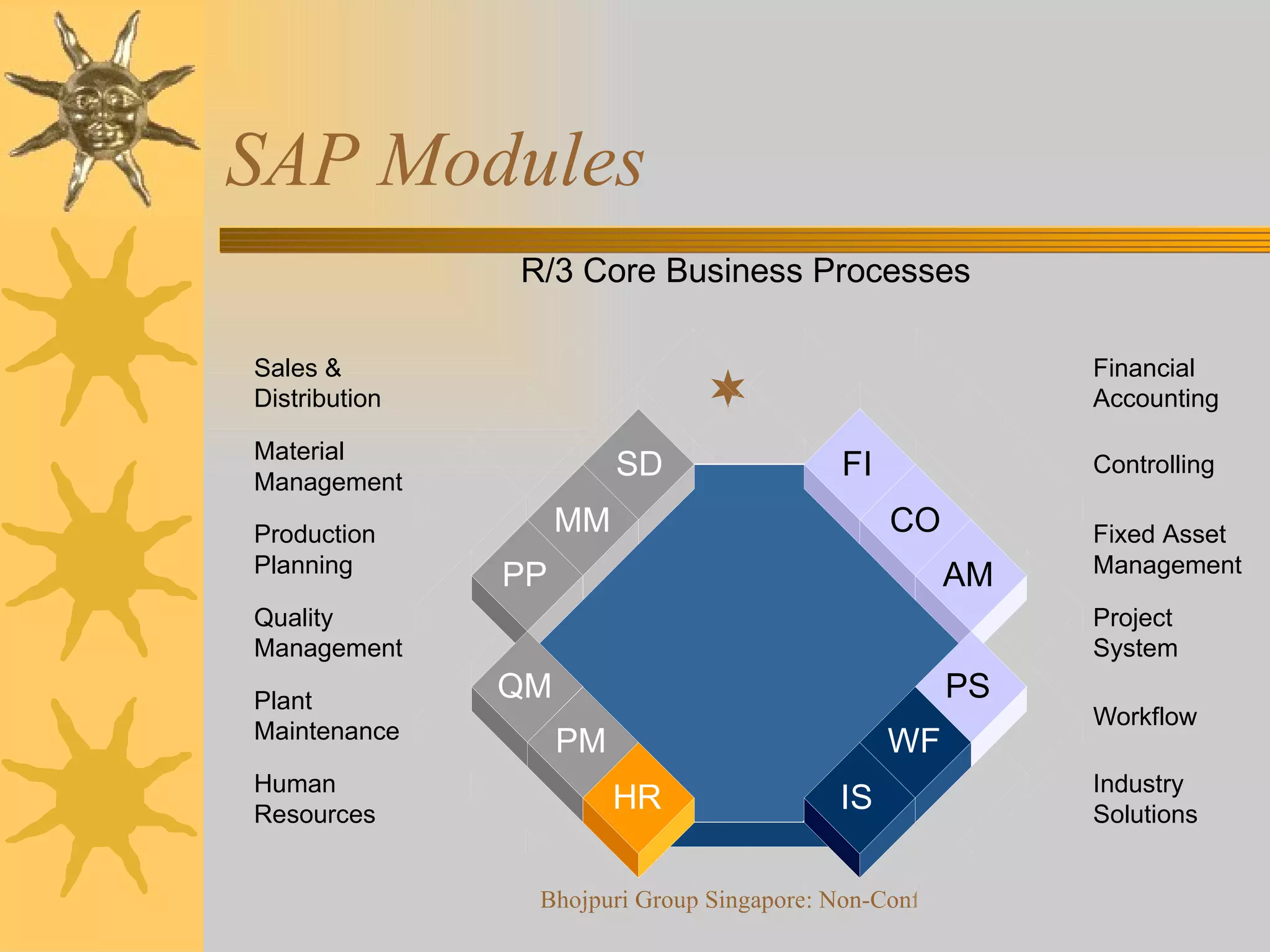
The document provides an overview of the history and evolution of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and SAP software. It discusses:
1) ERP systems evolved from inventory management and materials requirements planning systems used in manufacturing to integrate enterprise-wide processes across functions and locations.
2) SAP was founded in 1972 and released its first ERP software R/2 in 1979, with subsequent releases integrating more functions and capabilities.
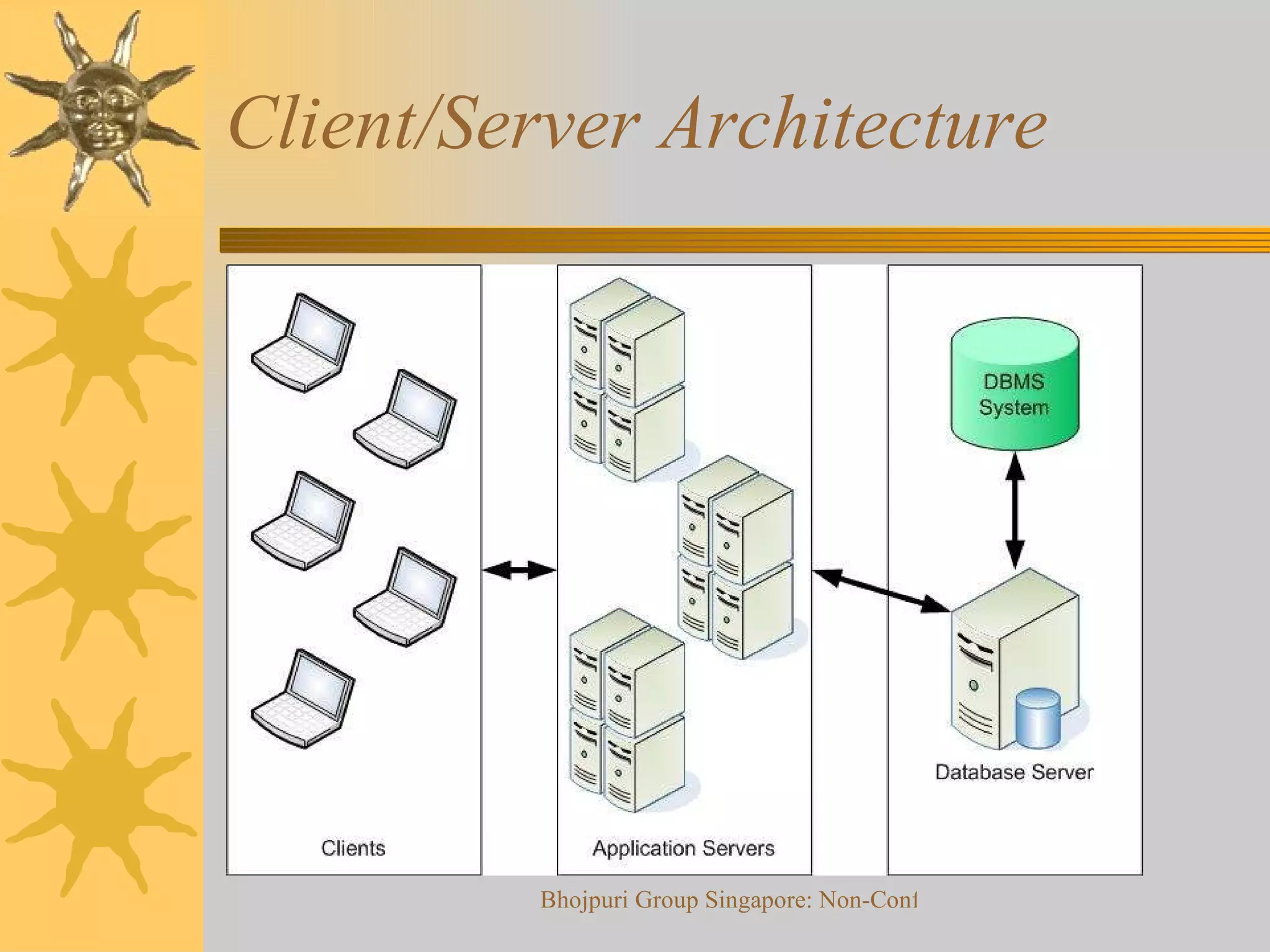
3) Modern ERP systems provide real-time data processing, integration across various business modules, and flexibility to support different business types and industries.