This document provides an introduction to SAP, including:
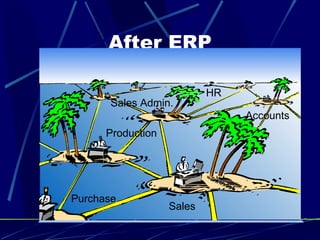
1. ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning and allows integration of business functions like inventory, orders, customer service, finance and HR into a single system.
2. ERP systems were developed to address issues with separate computer systems that didn't communicate and required duplicate data entry.
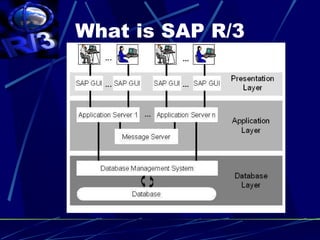
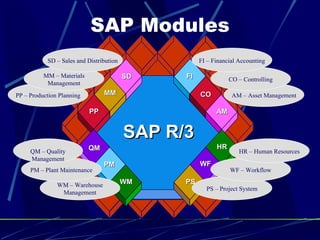
3. SAP is one of the leading ERP software providers, with over 56,000 installations serving 12 million users in 120 countries. It was founded in 1972 and comprises fully integrated modules covering all aspects of business.