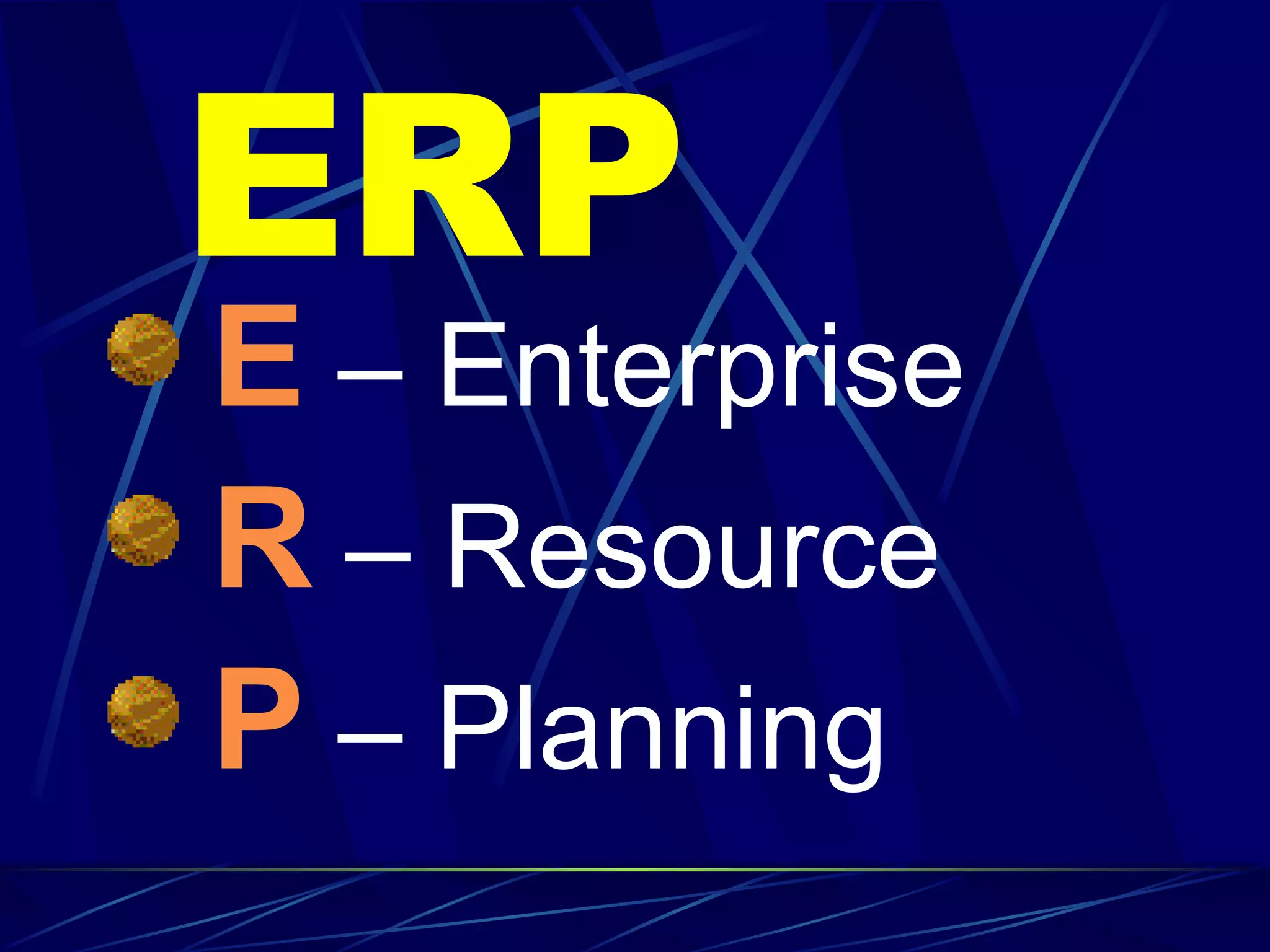
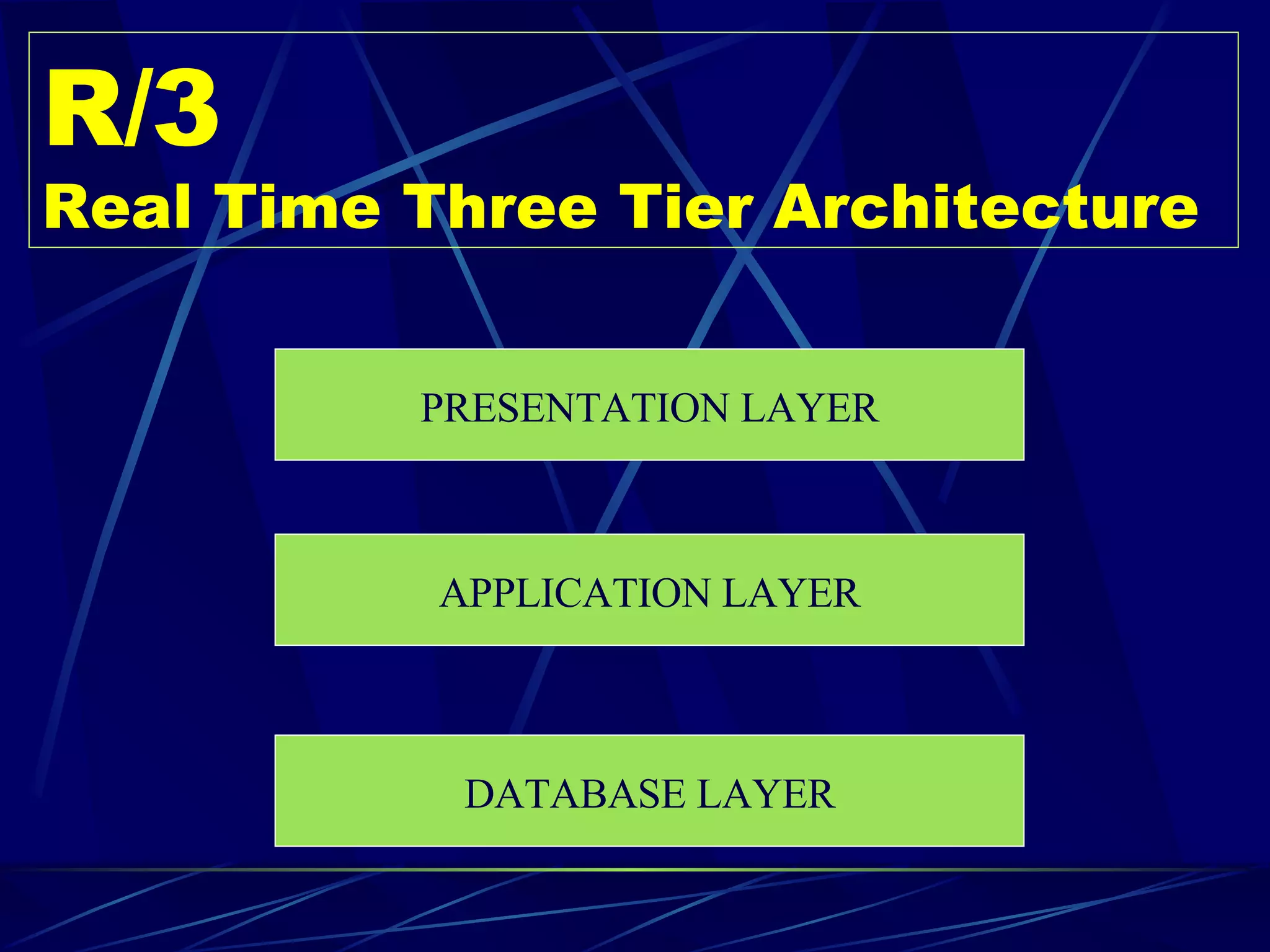
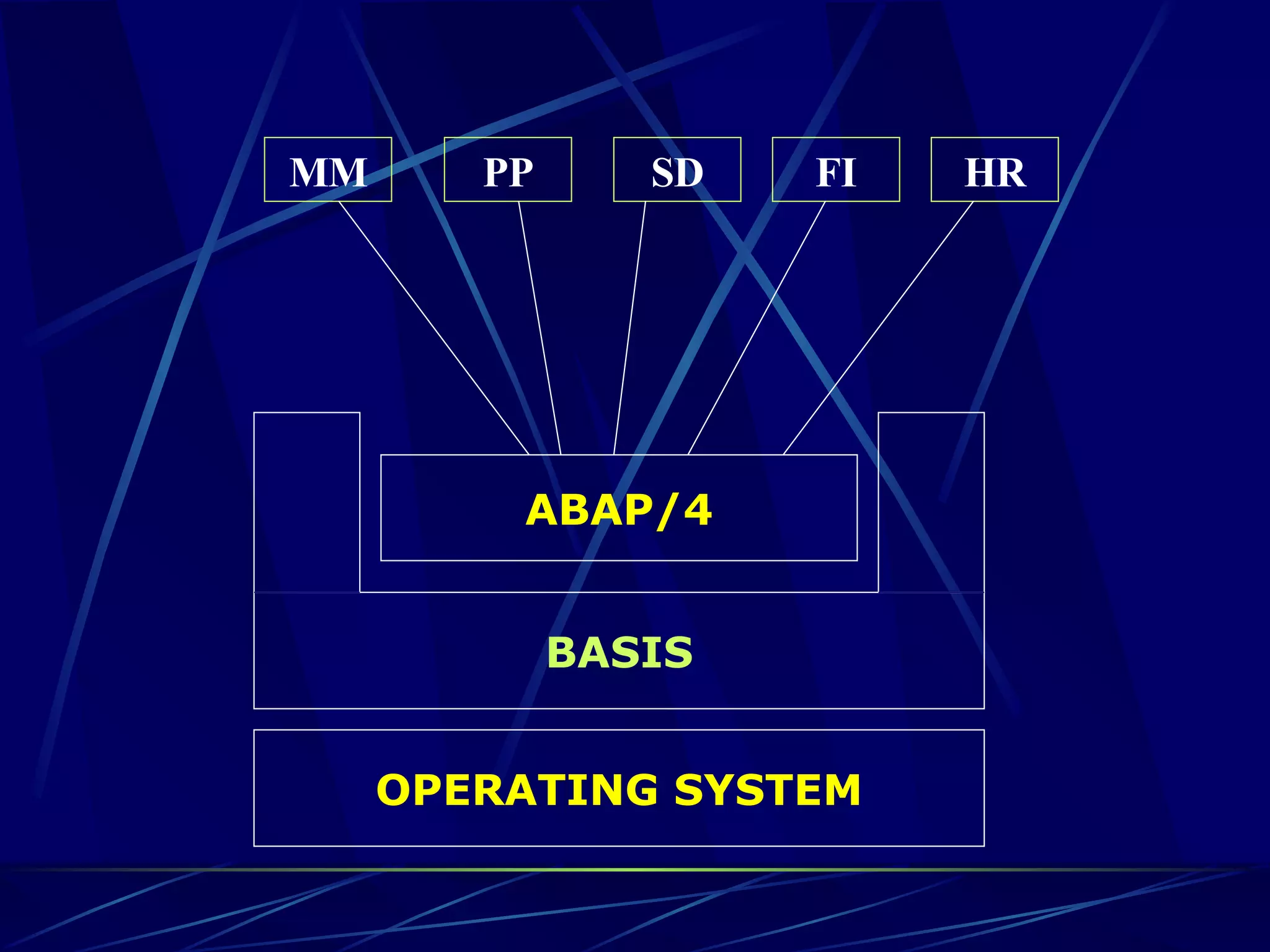
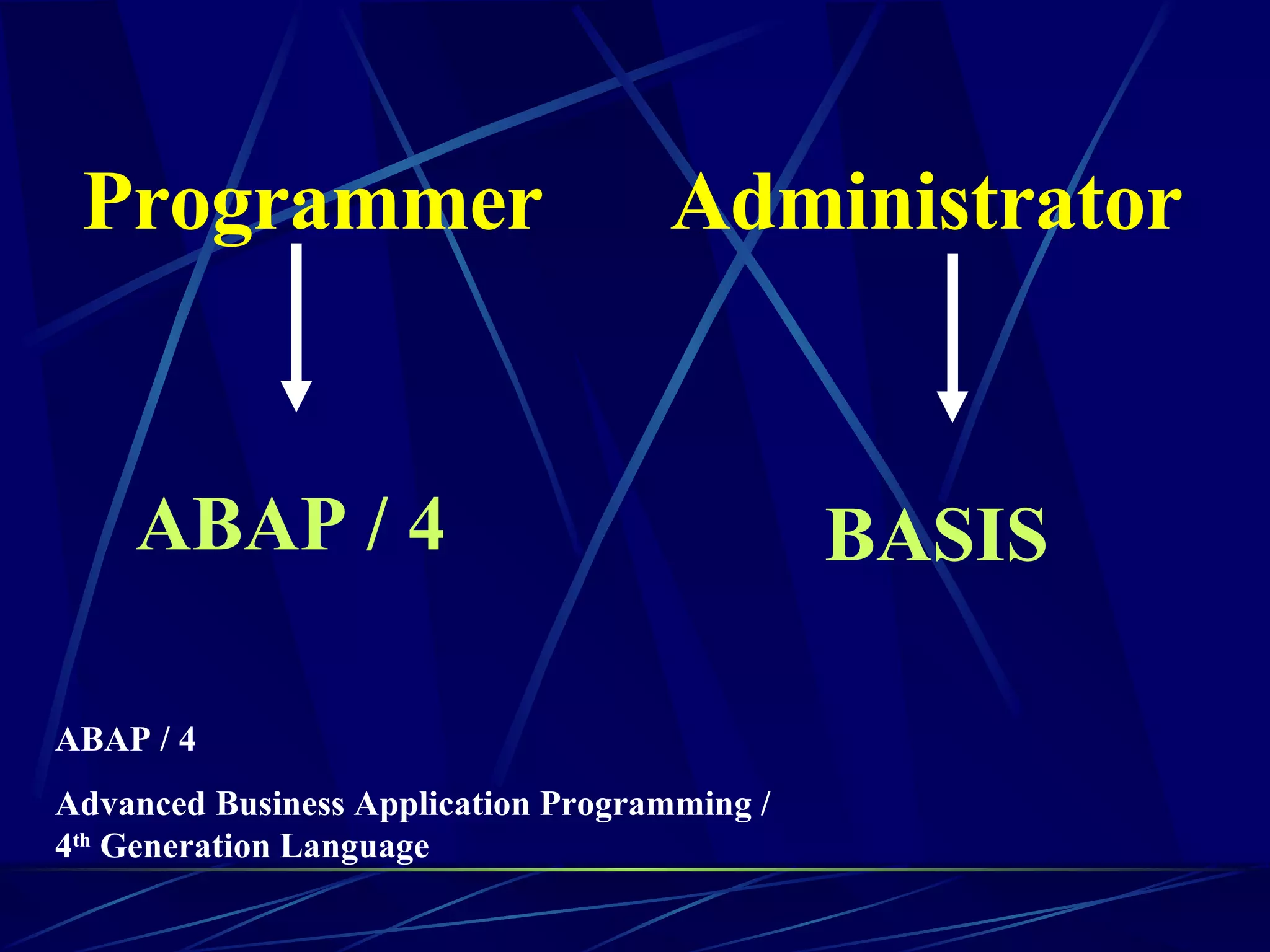
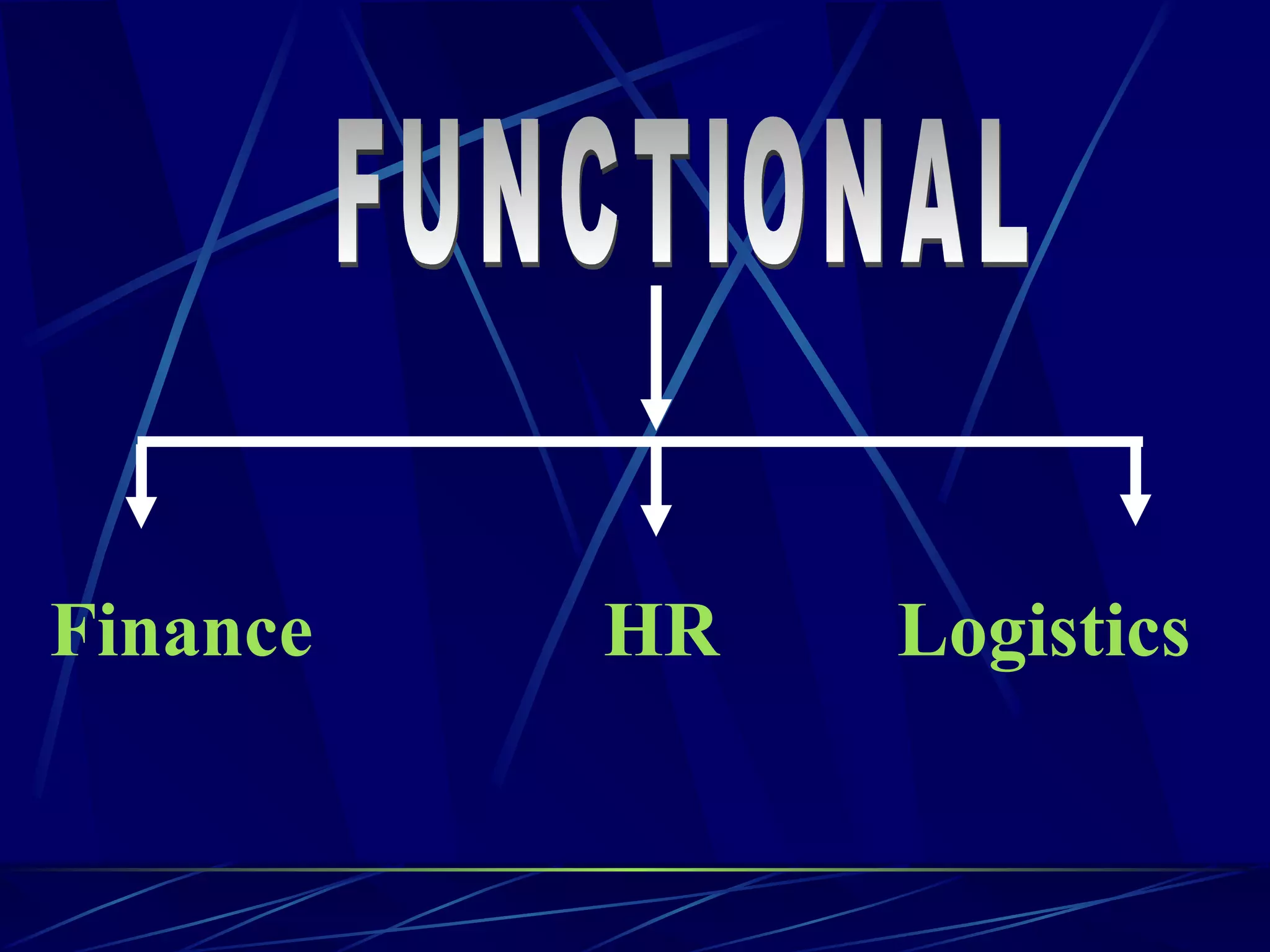
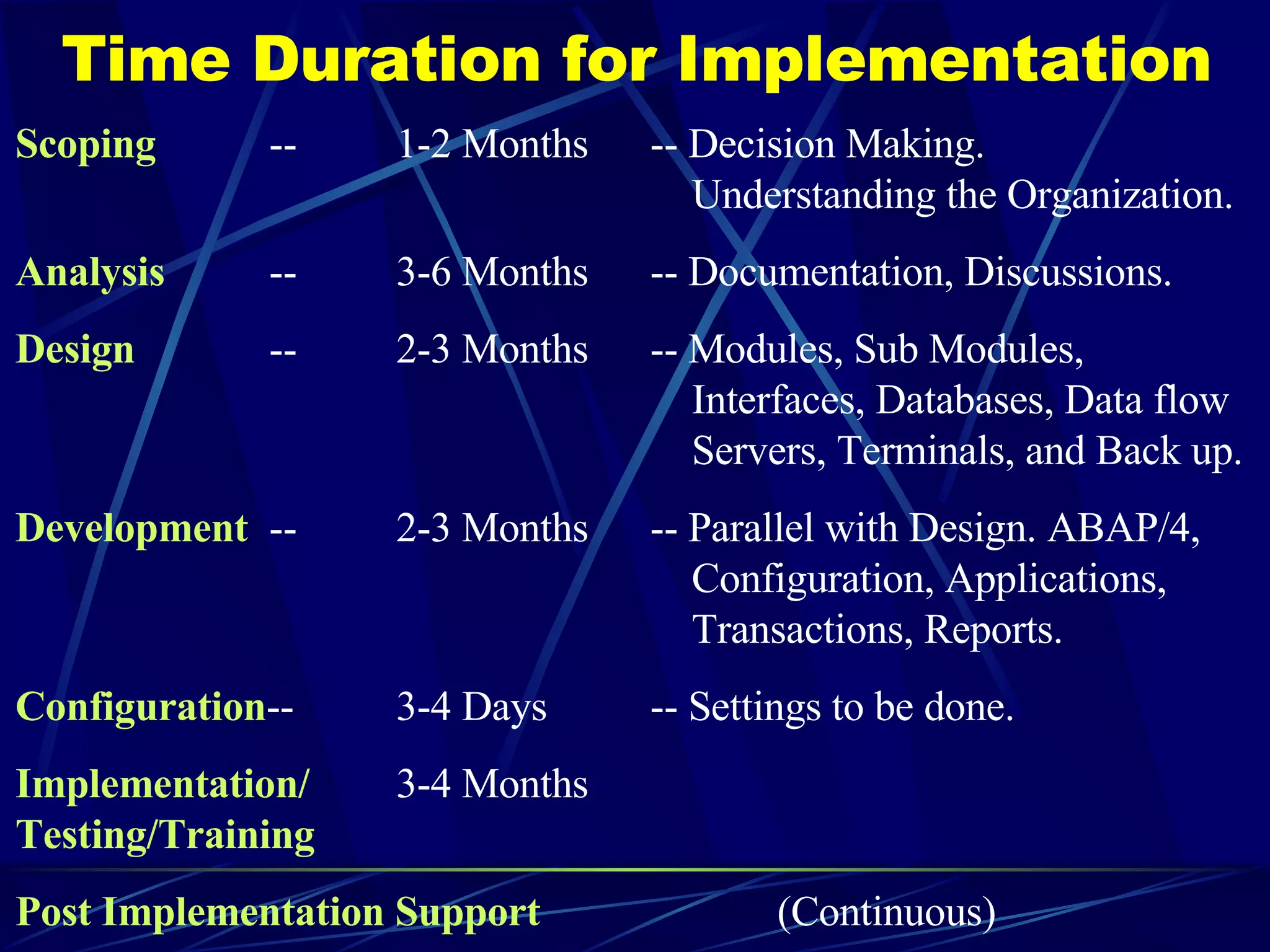
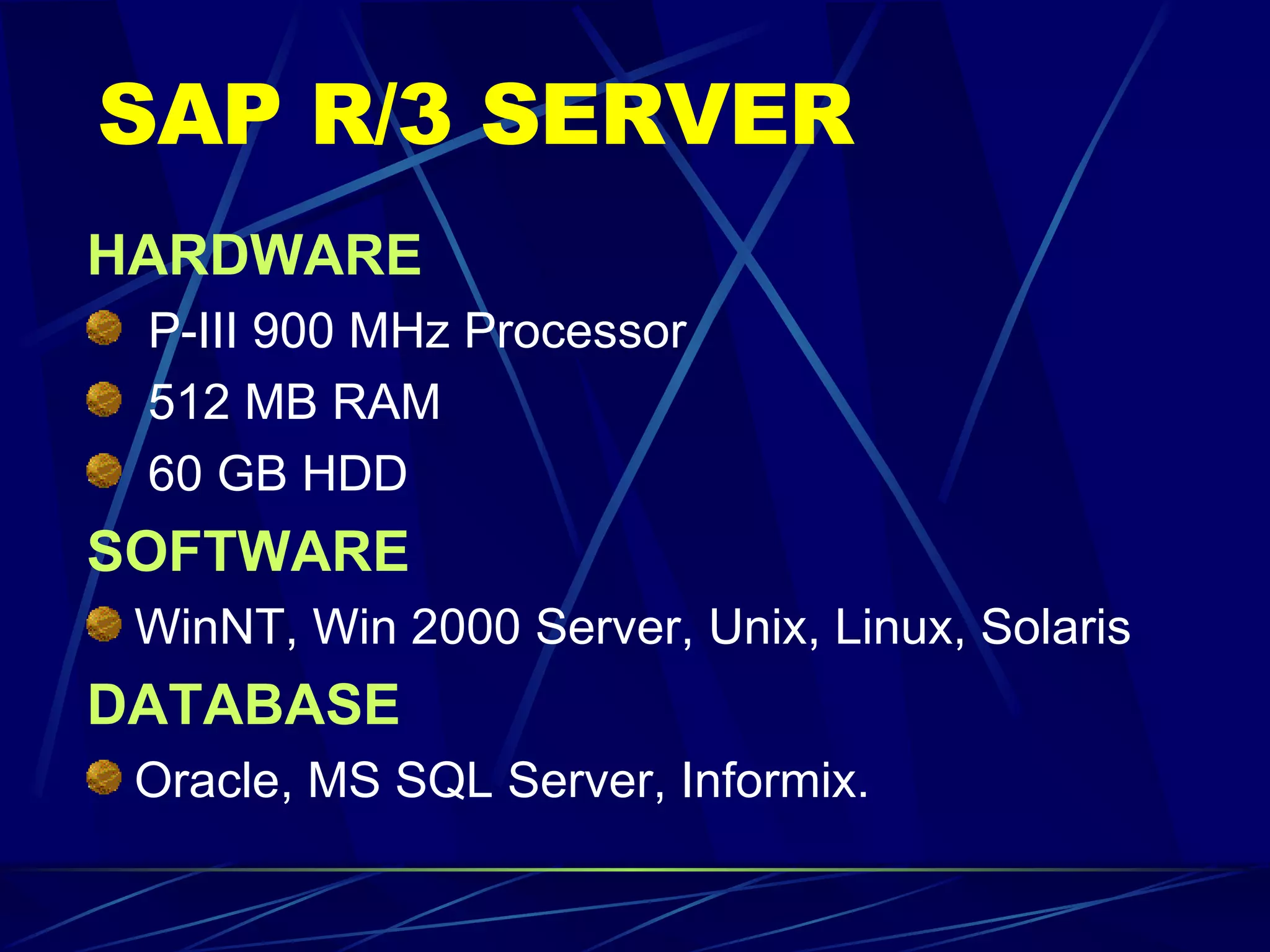
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It is a software system that integrates all departments of a business like planning, manufacturing, sales, marketing etc. ERP careers exist in two areas - implementation and software development. SAP is a leading global ERP software provider with over 7500 customers in over 90 countries. SAP R/3 is its flagship product which uses a three-tier architecture with presentation, application and database layers.