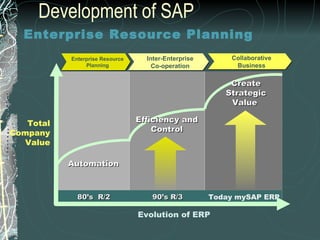
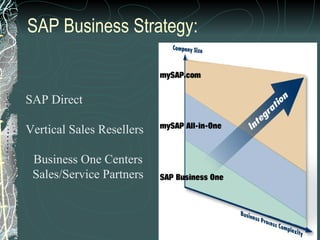
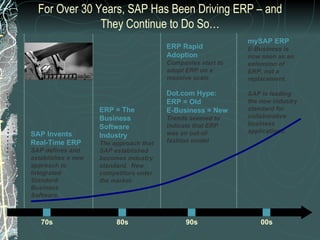
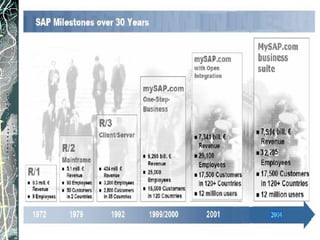
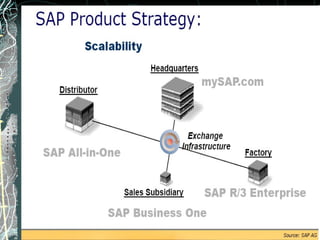
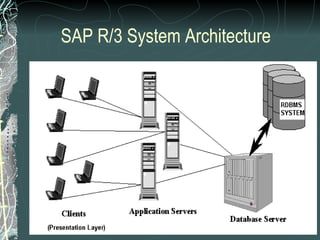
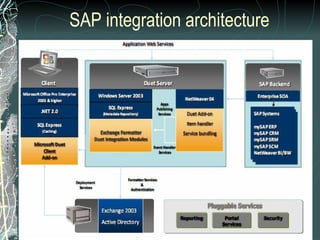
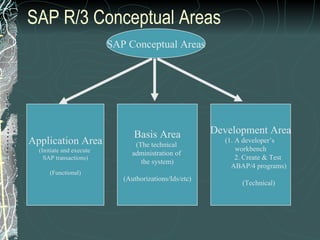
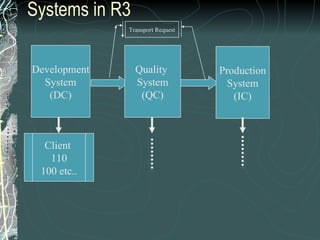
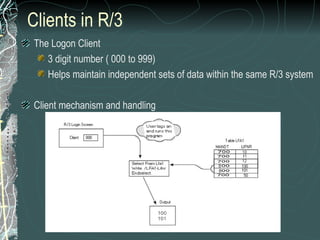
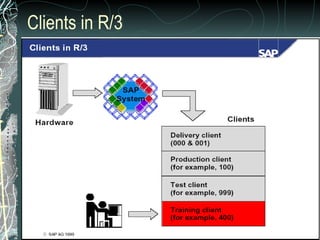
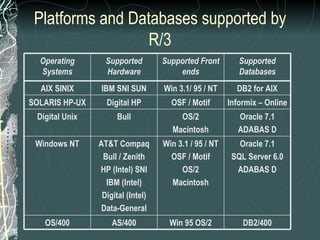
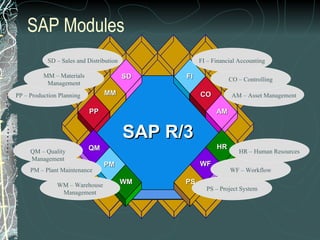
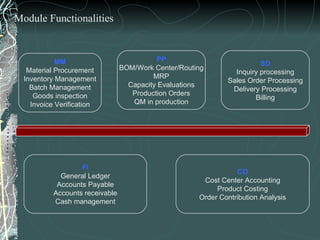
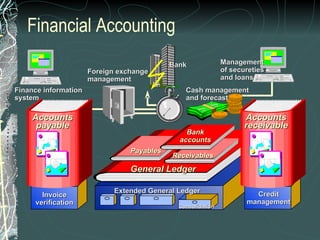
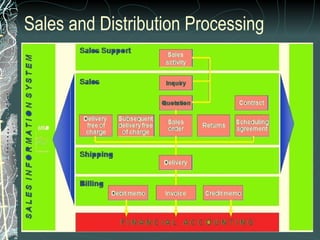
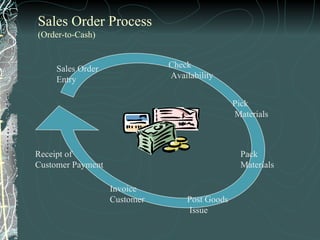
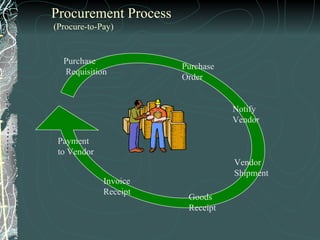
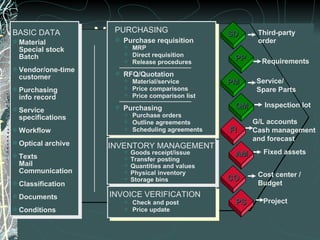
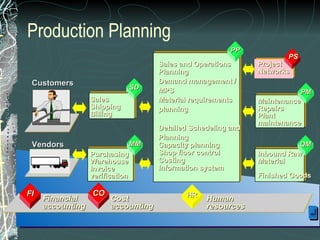
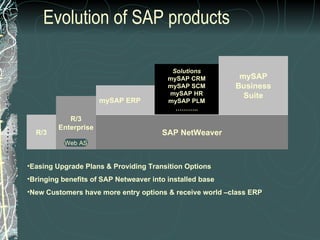
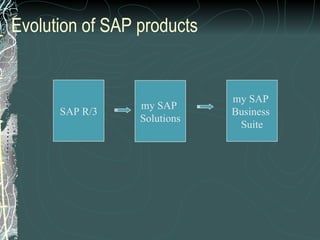
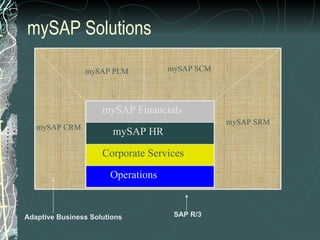
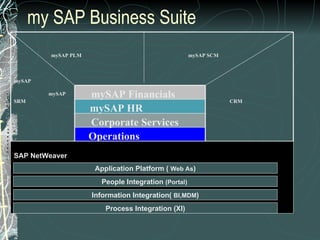
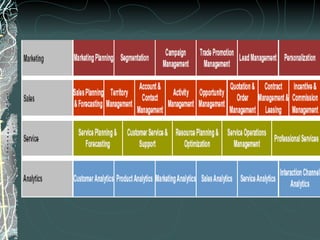
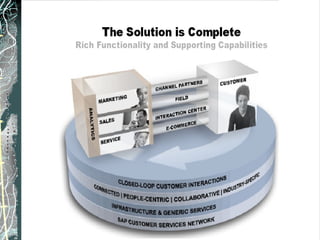
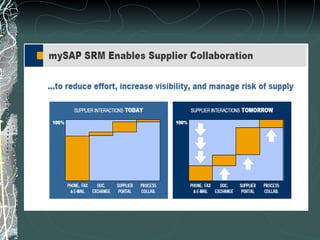
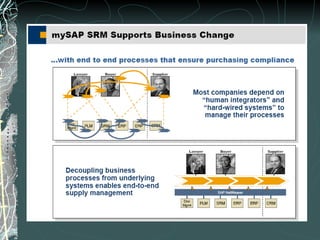
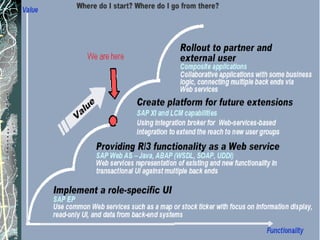
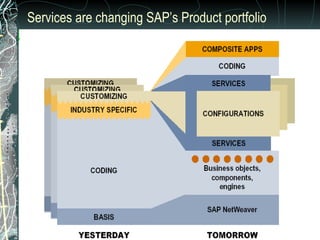
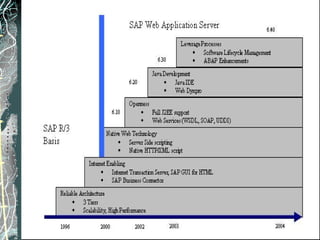
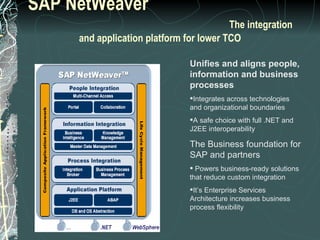
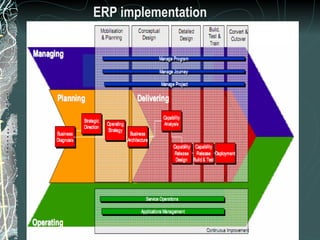
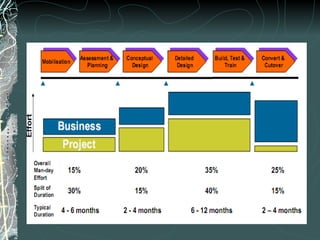
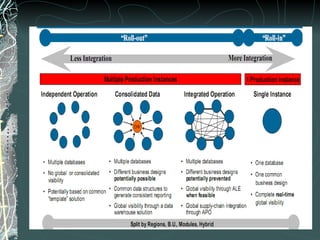
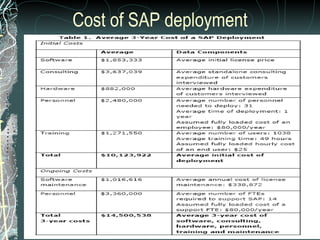
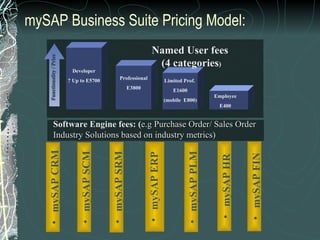
The document provides a history and overview of SAP systems and mySAP ERP. It discusses the evolution of SAP from its founding in 1972 as a company focused on data processing to its current flagship product, mySAP ERP. Key topics covered include the development of different SAP systems over time (R/1, R/2, R/3), the 3-tier architecture of SAP R/3, and descriptions of various SAP modules.