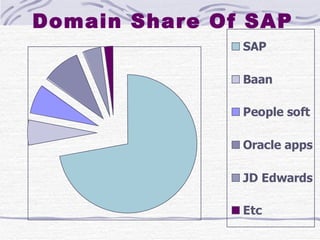
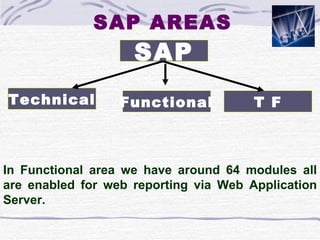
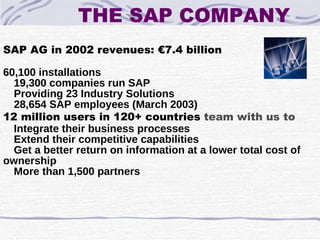
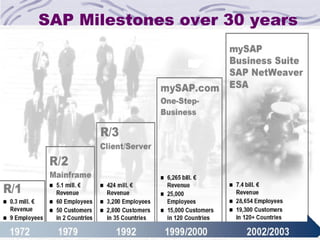
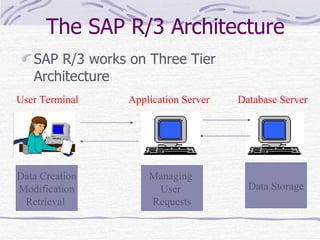
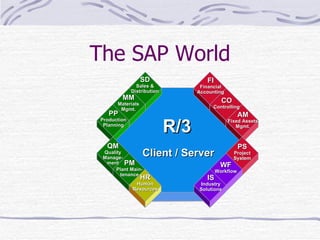
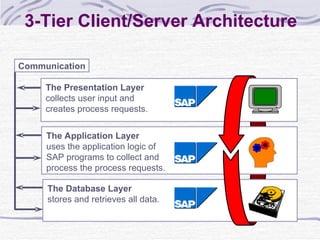
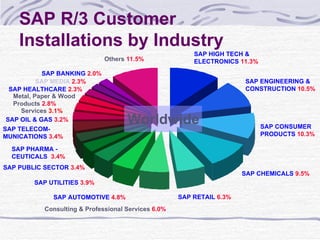
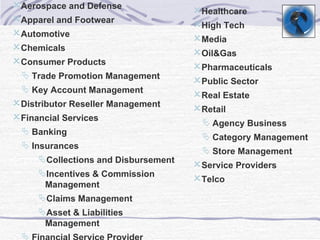
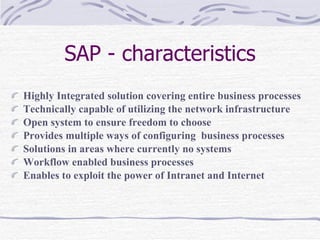
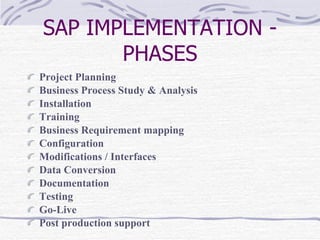
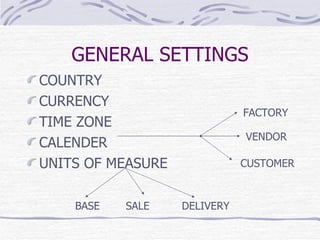
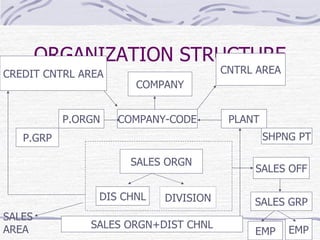
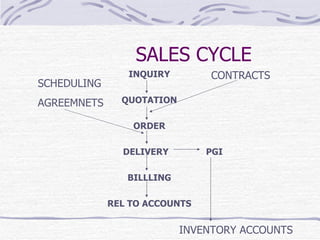
The document provides an overview of SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) module. It discusses the evolution of ERP systems and highlights key features of SAP like its integrated nature, industry specific solutions, and ability to utilize network infrastructure. It also summarizes the sales cycle in SAP SD, including functions like pricing, shipping, billing and special functionalities like rebate processing and variant configuration.