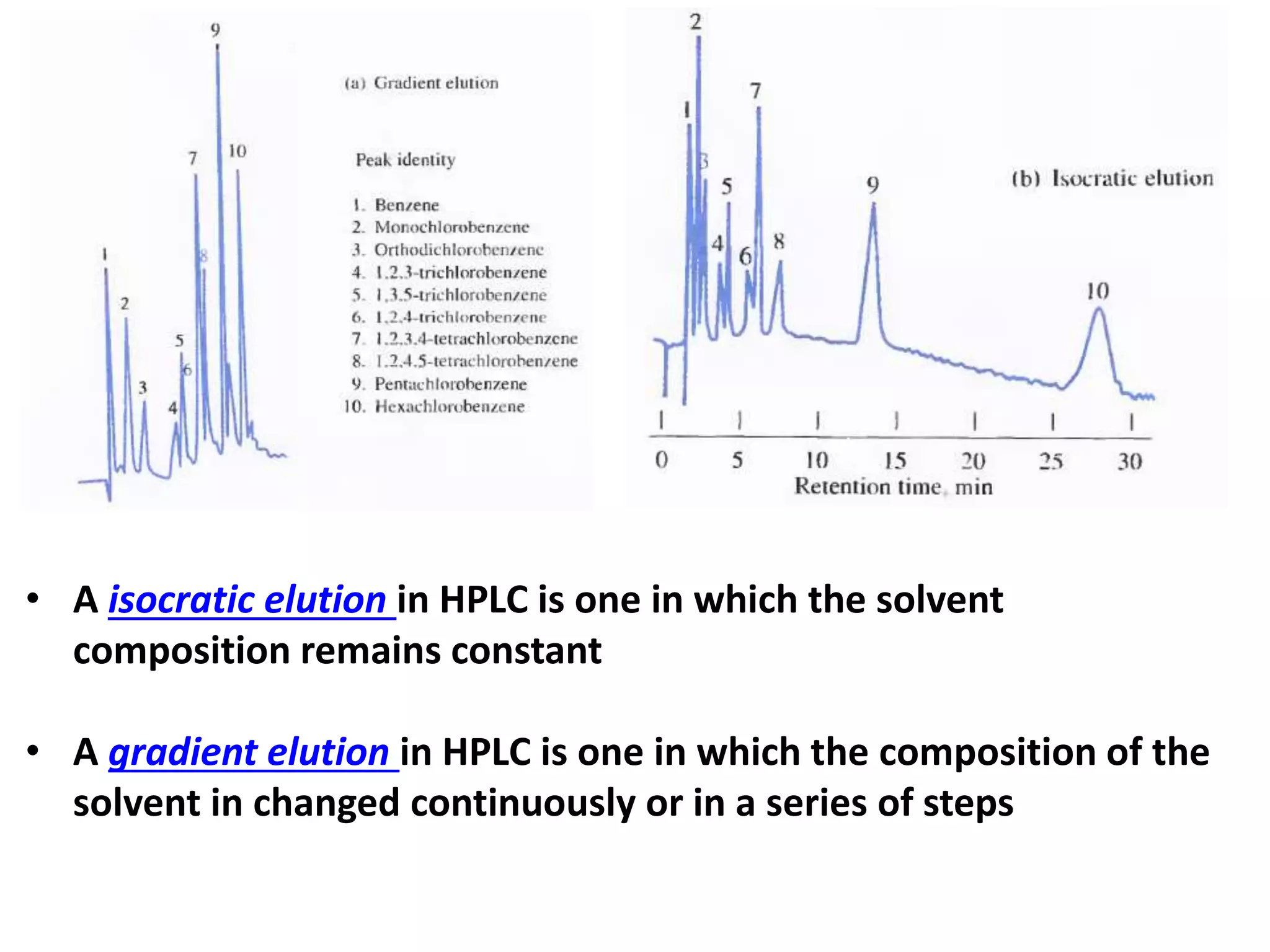
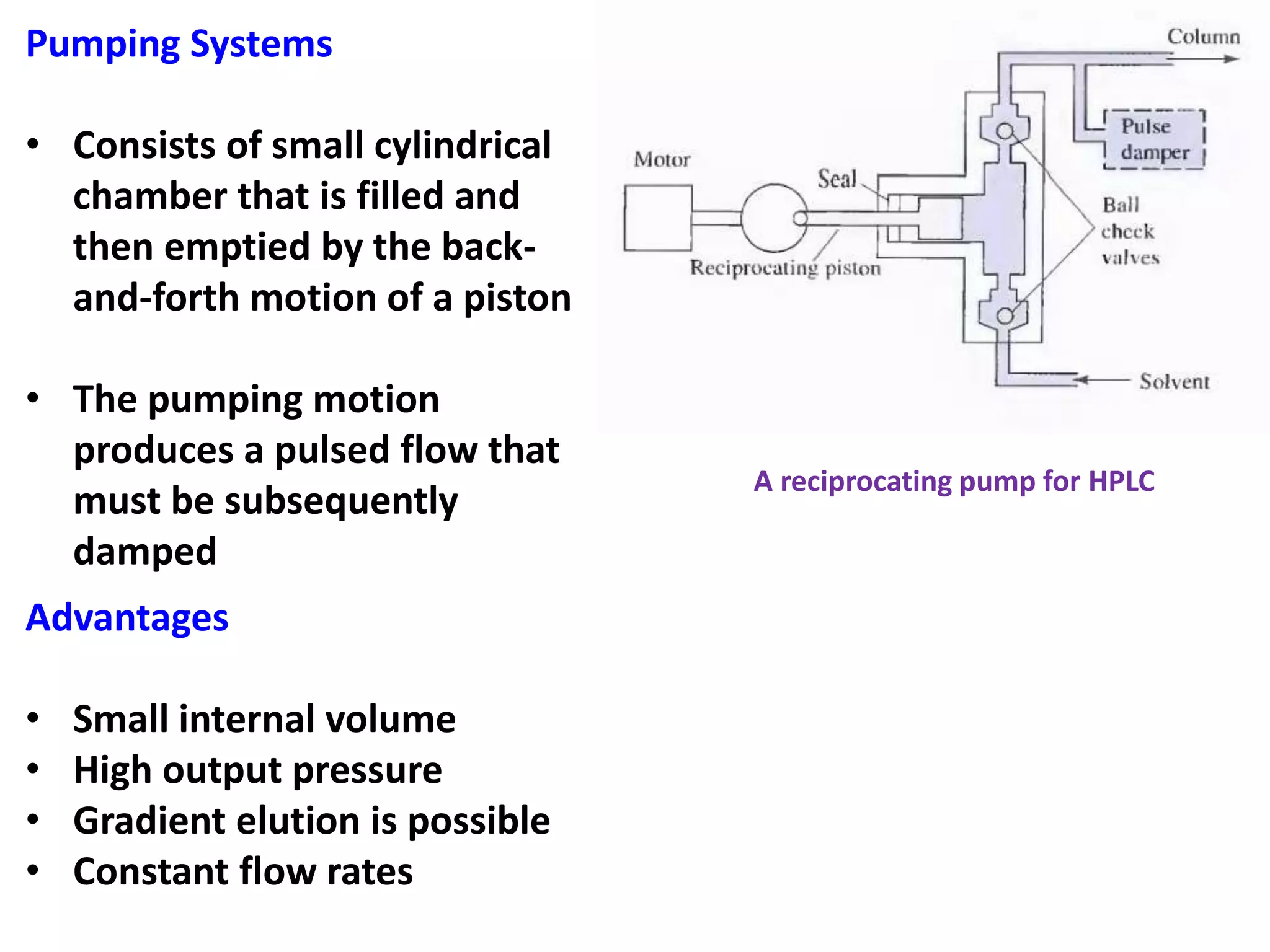
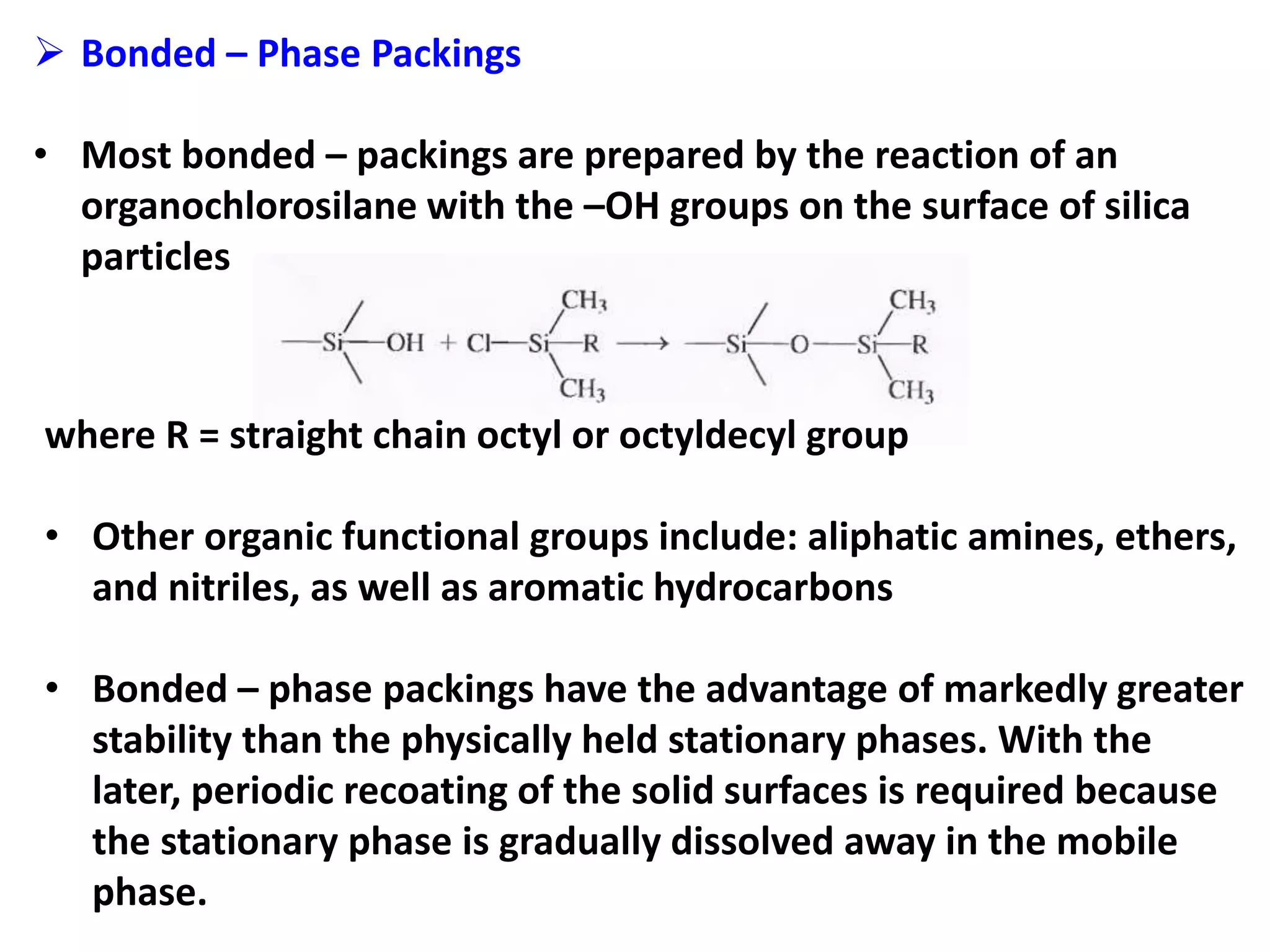
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is the most widely used type of liquid chromatography. It employs high pressure to pass a liquid mobile phase and sample mixture through a column packed with a solid stationary phase. There are several types of HPLC based on the separation mechanism and stationary phase used, including partition, adsorption, ion exchange, size exclusion, and affinity chromatography. HPLC instrumentation includes pumps to pressurize the mobile phase, injection systems, columns of varying lengths and diameters, and detectors. Common applications involve the separation of pharmaceuticals, proteins, and other biological molecules.