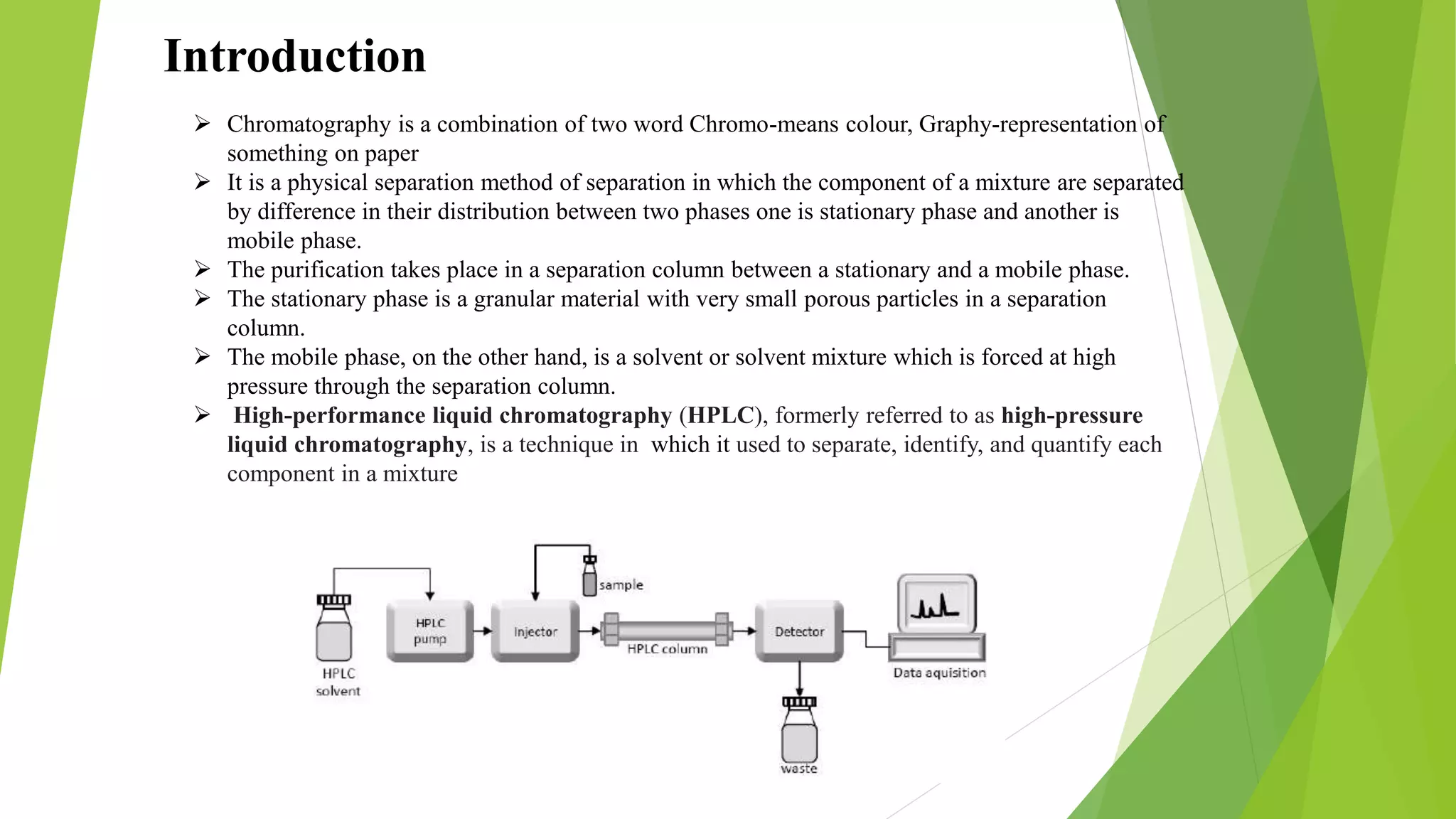
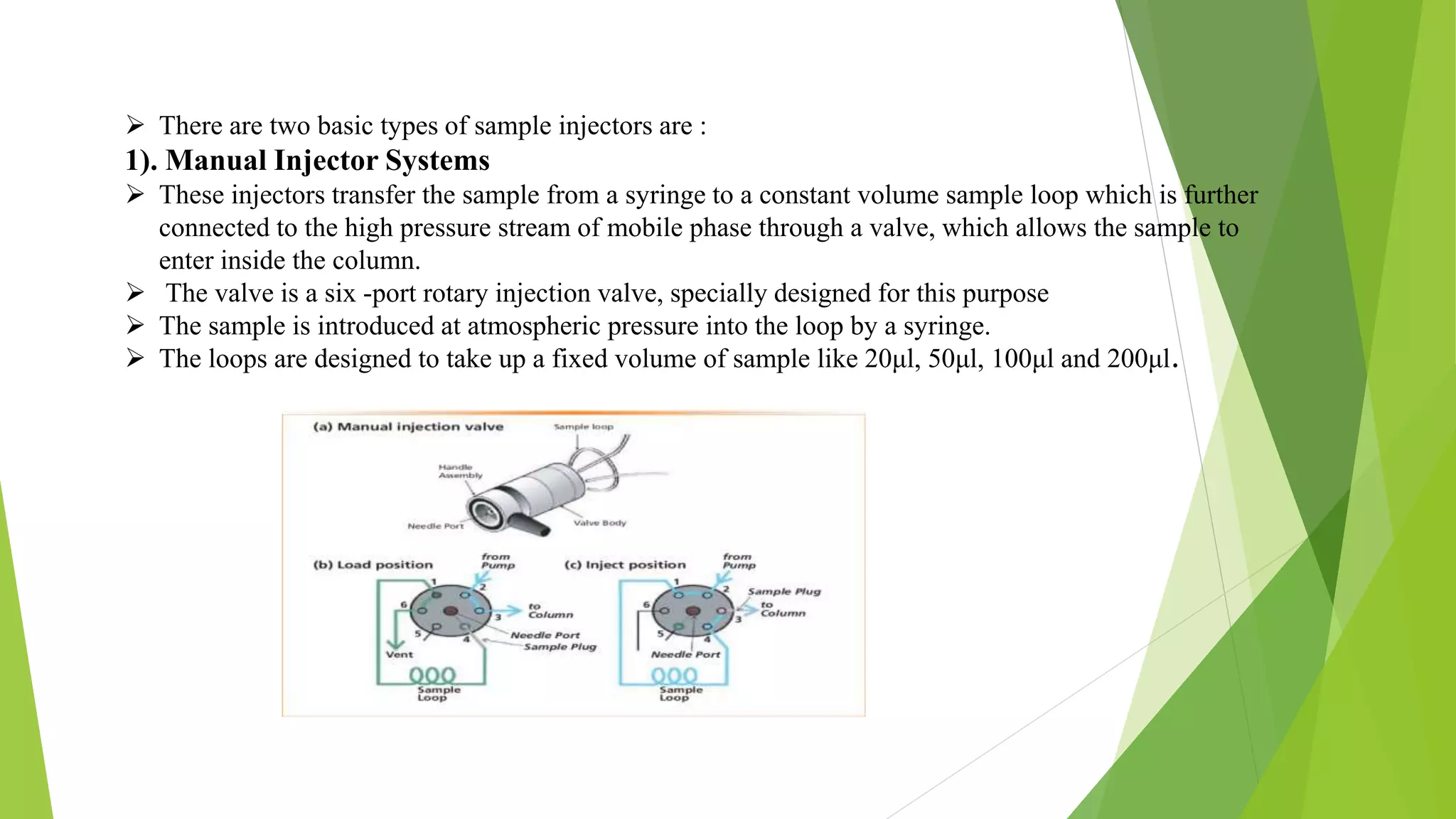
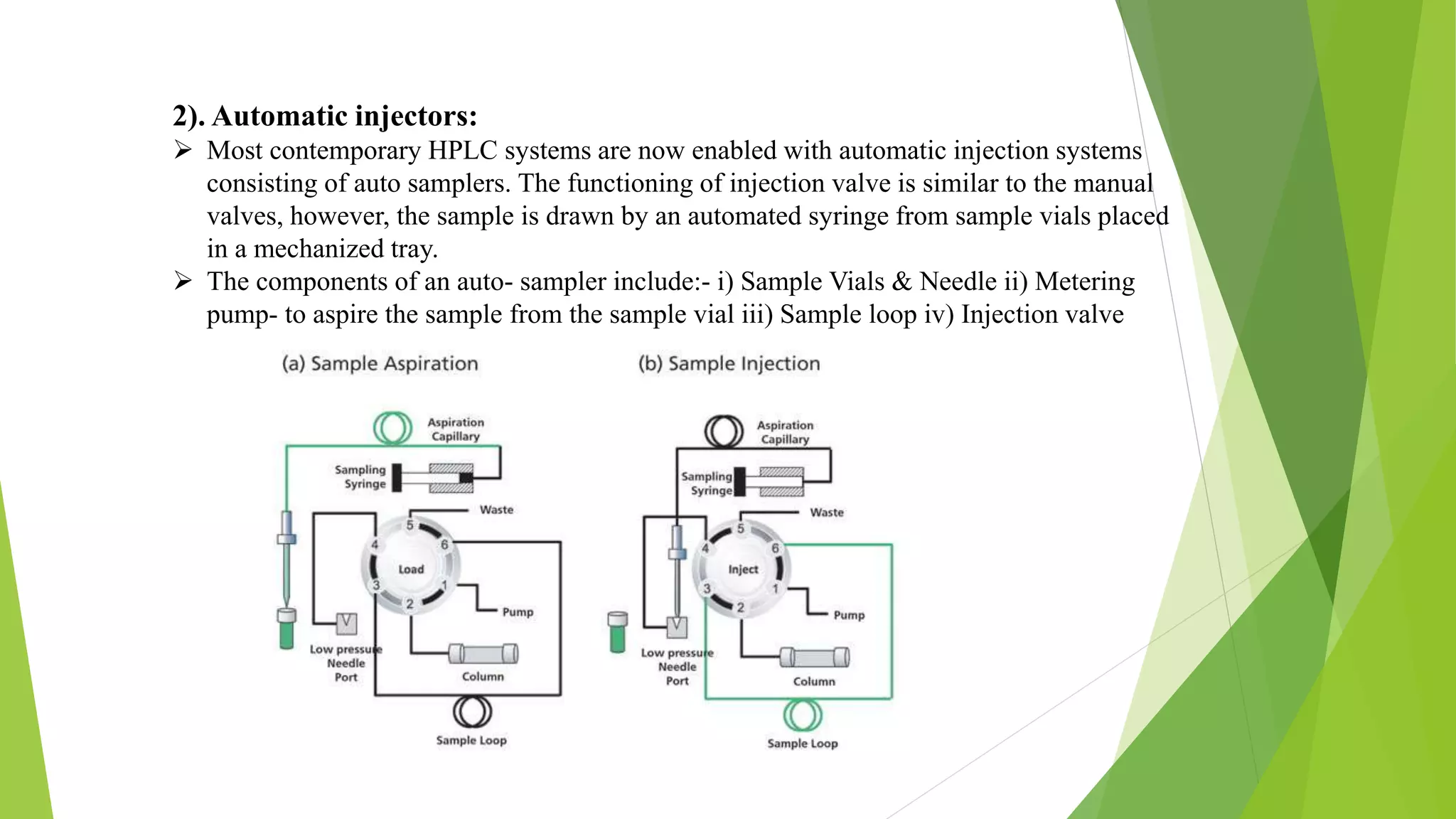
Chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures by distributing components between a stationary and mobile phase. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) uses high pressure to pass a solvent or solvent mixture through a column containing a stationary phase to separate components in a mixture. HPLC consists of several major components including a pump, injector, column, column compartment, detector, and degasser. The injector introduces the sample into the mobile phase which passes through the column, allowing separation based on interactions between components and the stationary phase. A detector then measures and records separated components as they elute from the column.