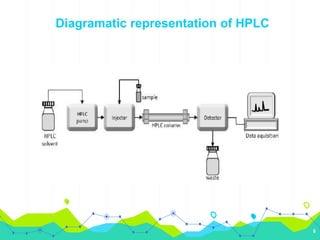
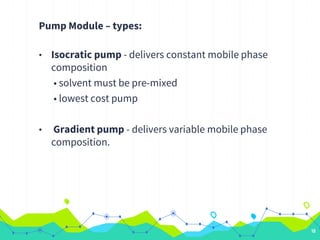
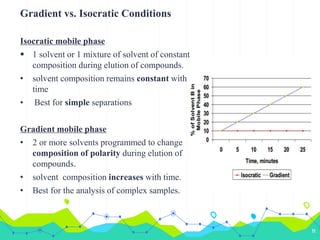
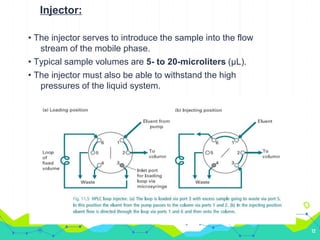
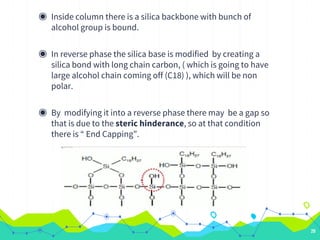
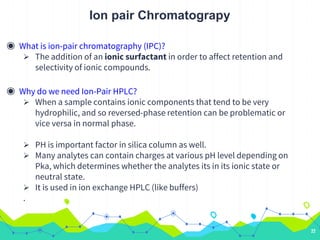
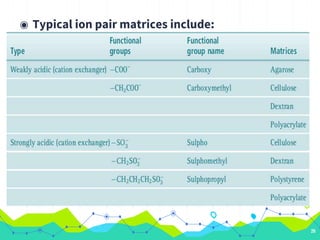
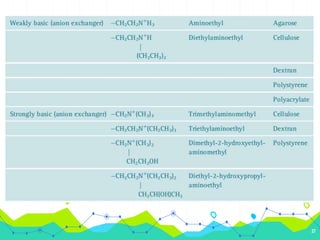
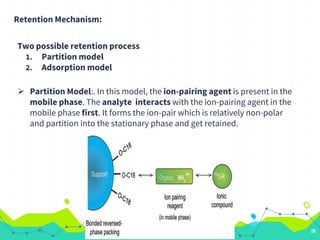
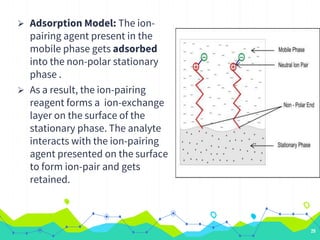
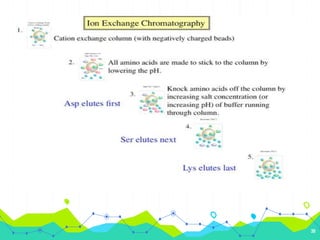
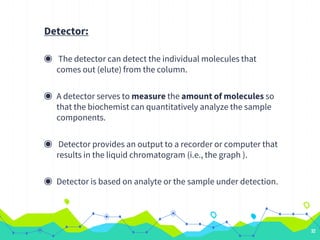
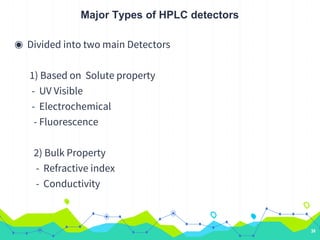
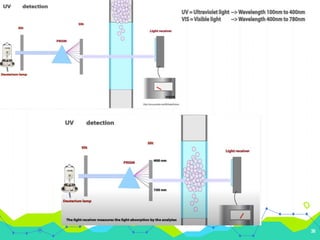
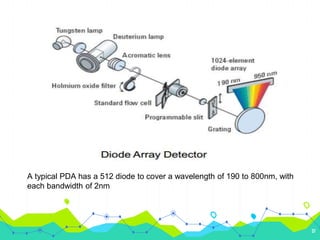
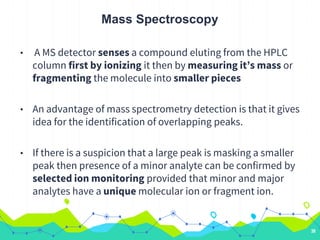
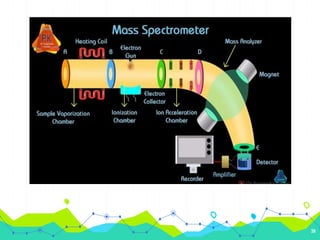
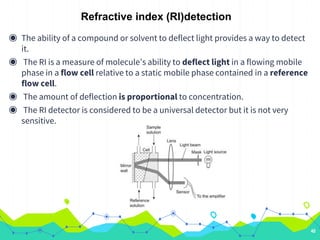
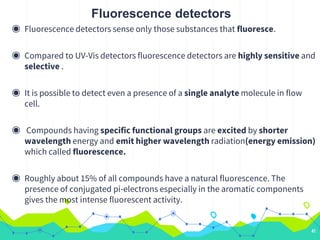
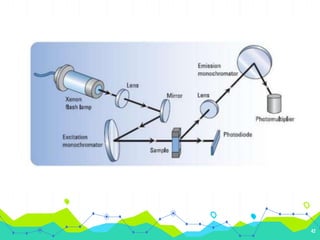
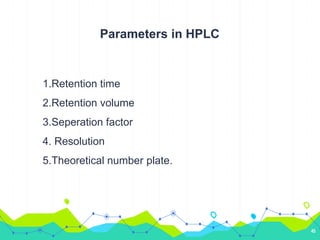
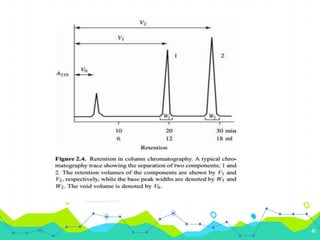
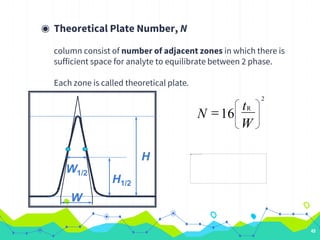
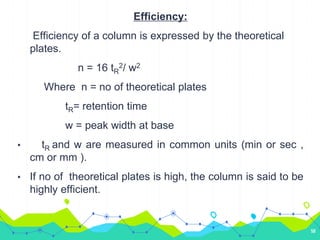
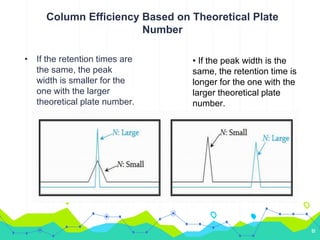
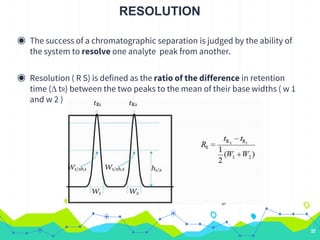
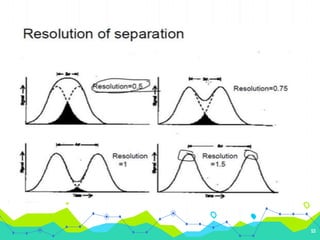
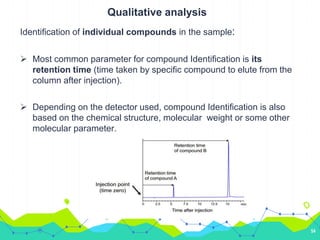
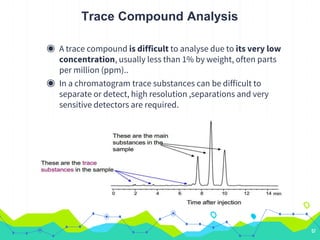
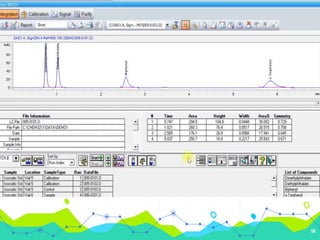
HPLC involves injecting a liquid sample into a column packed with tiny adsorbent particles. Components are separated as they interact differently with the stationary phase and are eluted by the mobile phase. The separated components are then detected and analyzed. Key components of HPLC include the solvent reservoir, pump, injector, column, and various detectors. There are different modes of separation including reversed phase, normal phase, ion exchange, and size exclusion chromatography. Parameters like retention time, theoretical plate number, and resolution are used to characterize chromatographic separations.