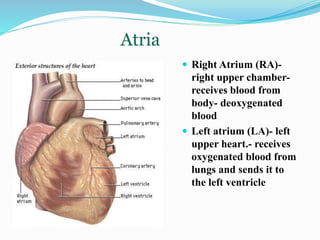
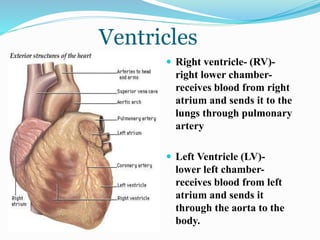
This document describes the structure and function of the cardiovascular system. It details the major organs including the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries. The heart is described as having four chambers - two atria that receive blood and two ventricles that pump blood out. Blood moves through the heart chambers via valves between the atria and ventricles. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart while veins return deoxygenated blood back to it. Capillaries allow for the exchange of oxygen and nutrients with body tissues. In conclusion, the right side of the heart contains deoxygenated blood and the left side contains oxygenated blood, and the heart chambers work together to pump this blood throughout the body