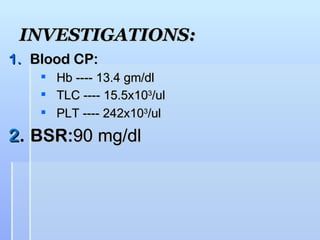
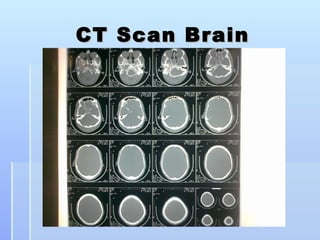
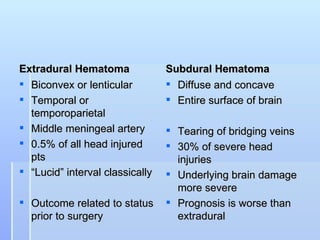
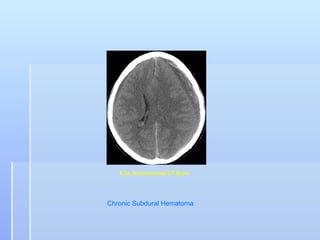
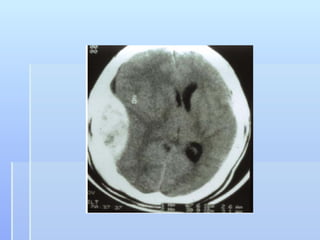
This document describes the case of a 56-year-old male who presented with drowsiness and vomiting after a fall and head injury. On examination, he had a Glasgow Coma Scale of 13/15. Imaging showed a subdural hematoma. He underwent surgical evacuation of the subdural hematoma. The document then provides background information on subdural hematomas including causes, risk factors, classification, signs and symptoms, diagnosis using CT scans, and treatment options including conservative management or craniotomy. Guidelines for management of mild, moderate and severe traumatic brain injuries are also summarized.