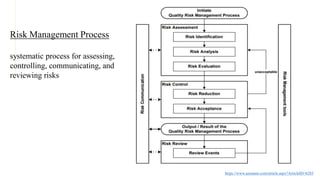
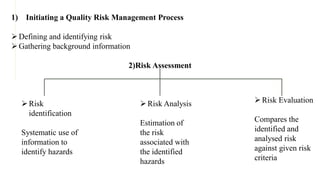
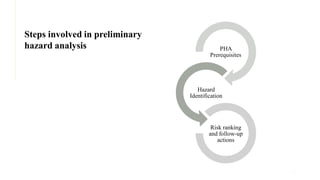
The document discusses hazard and risk management, outlining the processes of identifying, assessing, and controlling risks to protect life, health, property, and the environment. It emphasizes the importance of risk assessment for decision-making, compliance, and resource allocation while detailing methods such as failure mode effects analysis and hazard analysis. Additionally, it introduces a systematic risk management process that includes risk identification, analysis, evaluation, control, communication, and review.