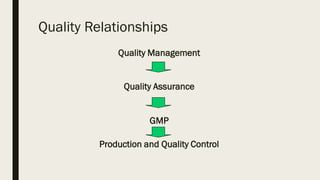
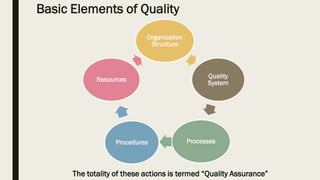
This document discusses Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for pharmaceutical products as outlined by the World Health Organization (WHO). It provides definitions and explanations of key GMP concepts including quality assurance, quality management, and ensuring consistent production of pharmaceuticals according to appropriate quality standards. It also discusses WHO involvement in establishing GMP guidelines and differences between GMP and current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP). The document outlines basic GMP principles for quality management, sanitation, qualification and validation, complaints and recalls, and more. It emphasizes that quality failures can result in regulatory warnings, market withdrawals, supply disruptions, and loss of credibility with patients and regulators.