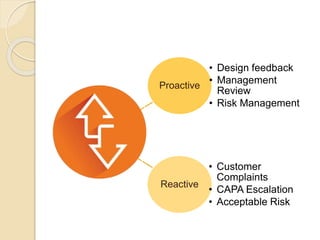
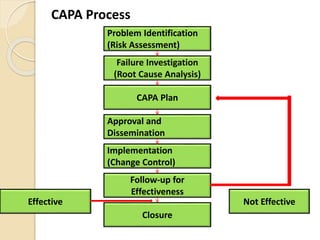
The document discusses various tools and methods for hazard and risk management. It describes 12 different tools/methods: self-protective measures, training and reinforcement, communication/incentives, risk definition, risk assessment, risk control hierarchy, proactive vs reactive approaches, CAPA process, product review requirements, hazard identification/assessment/control process, and statistical tools like control charts. For each, it provides an overview and potential applications in risk management.