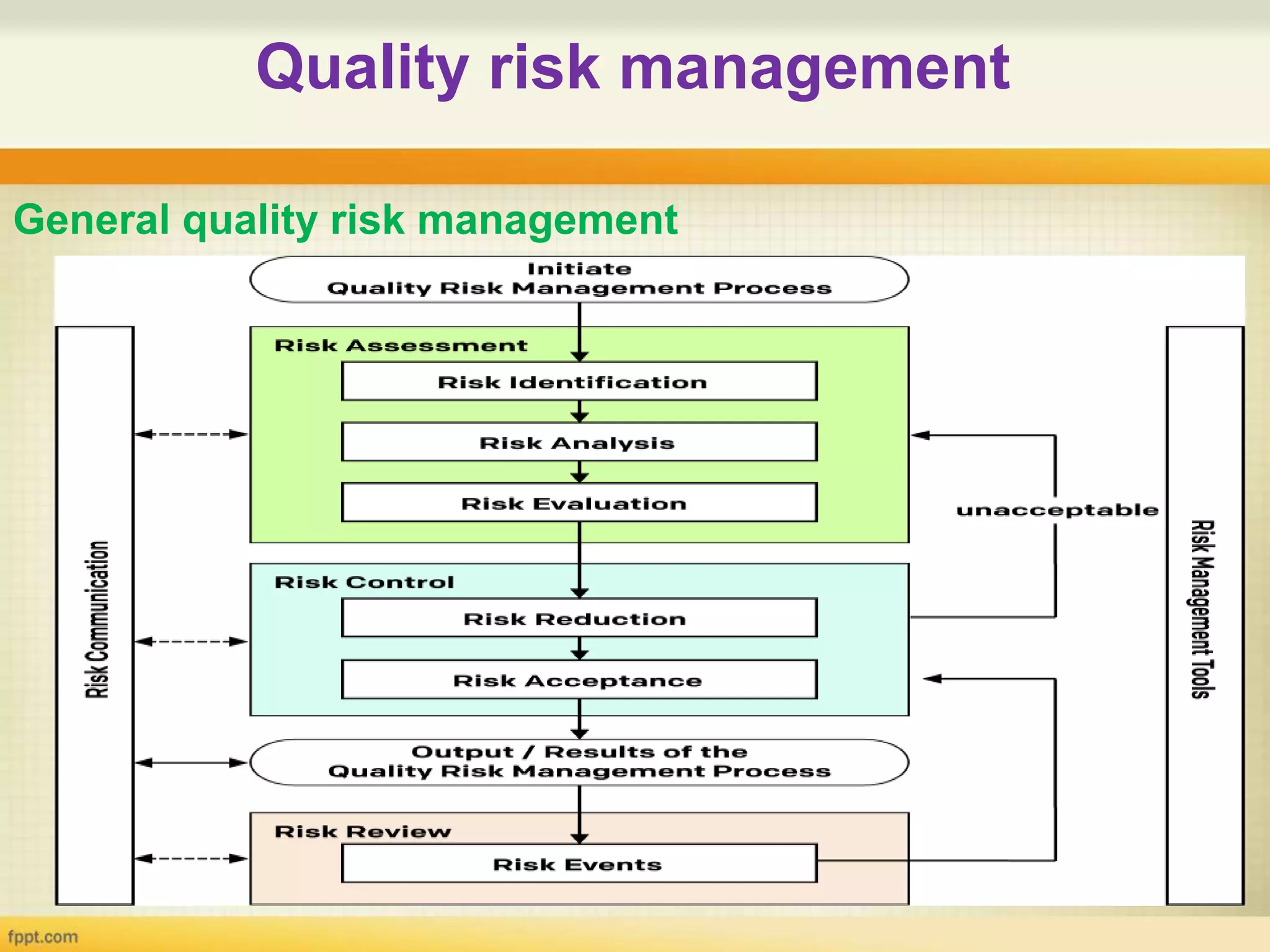
1. Quality risk management involves identifying potential risks, analyzing their likelihood and consequences, and taking actions to address unacceptable risks.
2. Various tools can be used for quality risk management including Failure Mode and Effects Analysis, Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, and Fault Tree Analysis.
3. These tools help identify hazards, evaluate risks, and prioritize risks so that appropriate actions can be taken to control risks and improve quality.