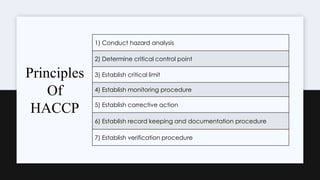
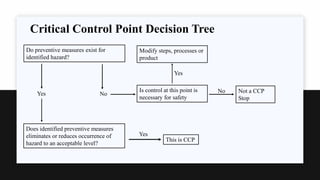
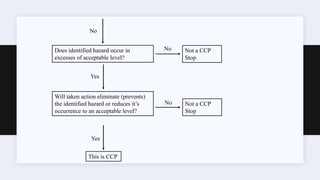
The document presents an overview of the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system, emphasizing its role in identifying and controlling food safety hazards through a systematic and scientific approach. It details various steps including hazard analysis, determining critical control points, establishing critical limits, and implementing monitoring and corrective procedures. The importance of record-keeping and verification to ensure food safety is also highlighted.