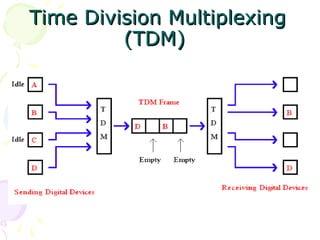
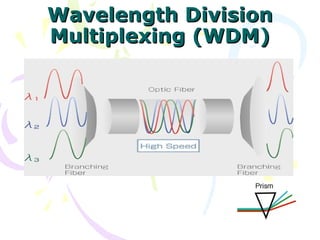
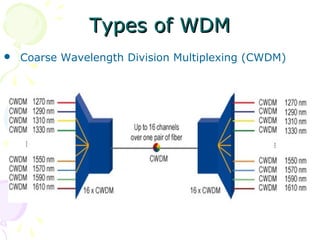
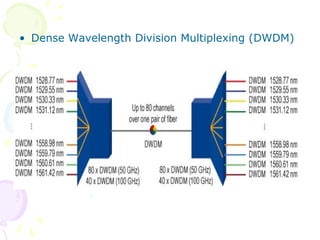
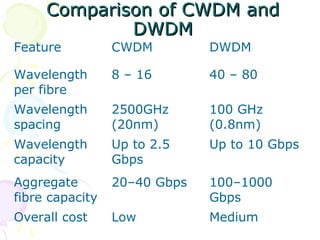
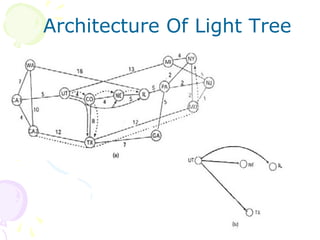
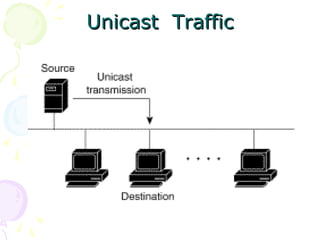
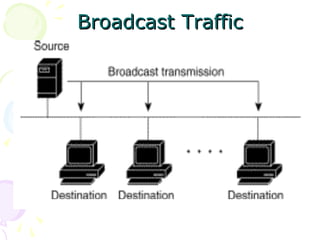
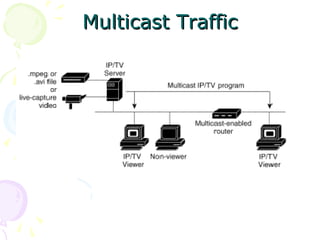
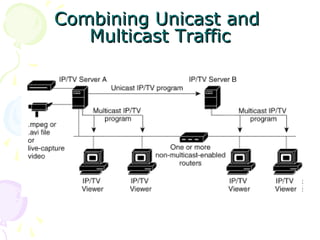
The document discusses light trees, which are used in wavelength routed optical networks employing wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM). A light tree enables single-hop communication from a source to multiple destinations using a minimum number of opto-electronic devices. It supports unicast, broadcast, and multicast traffic. Light trees can increase network throughput and provide high bandwidth communication over long distances for applications such as videoconferencing and internet television.