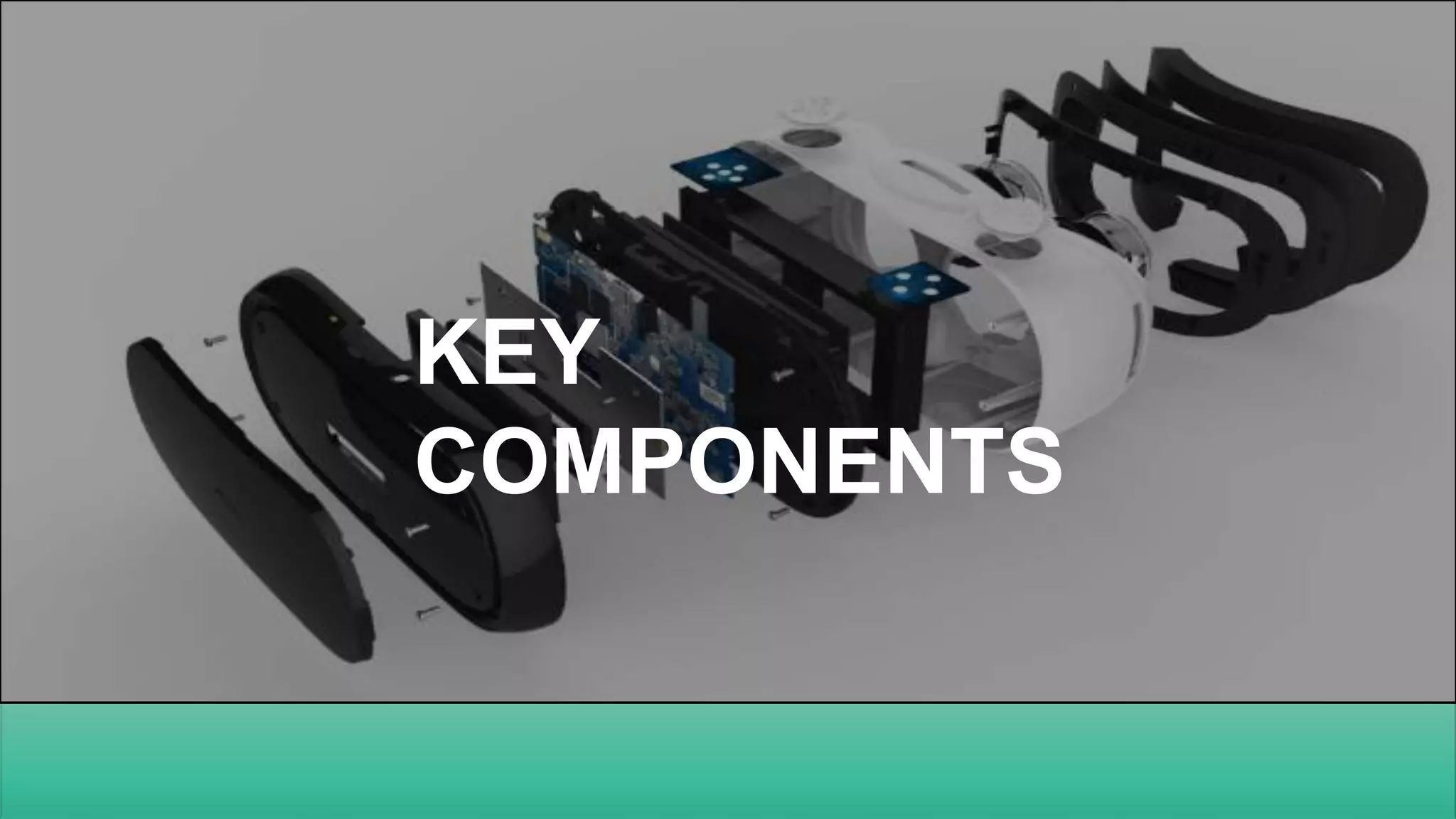
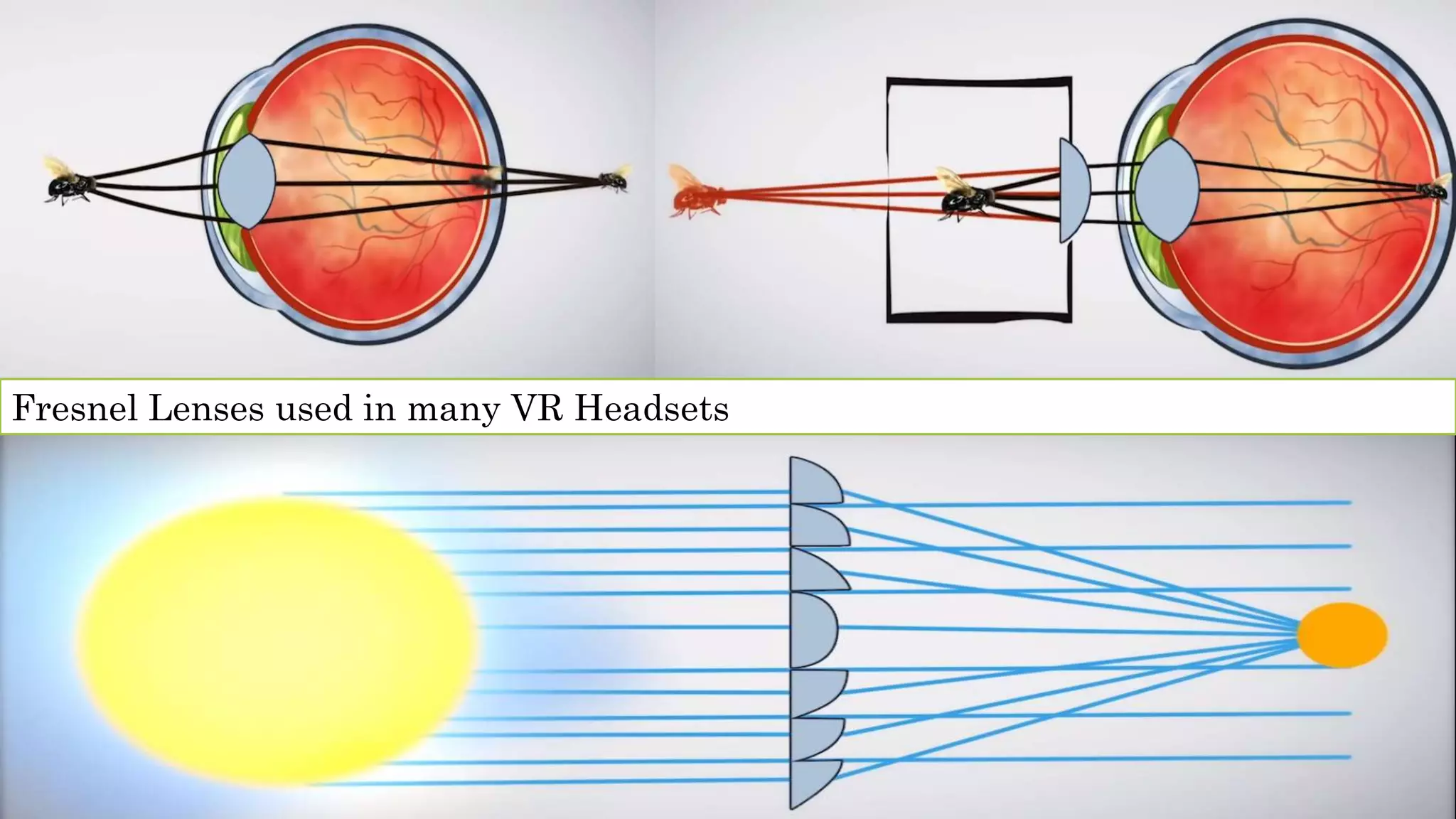
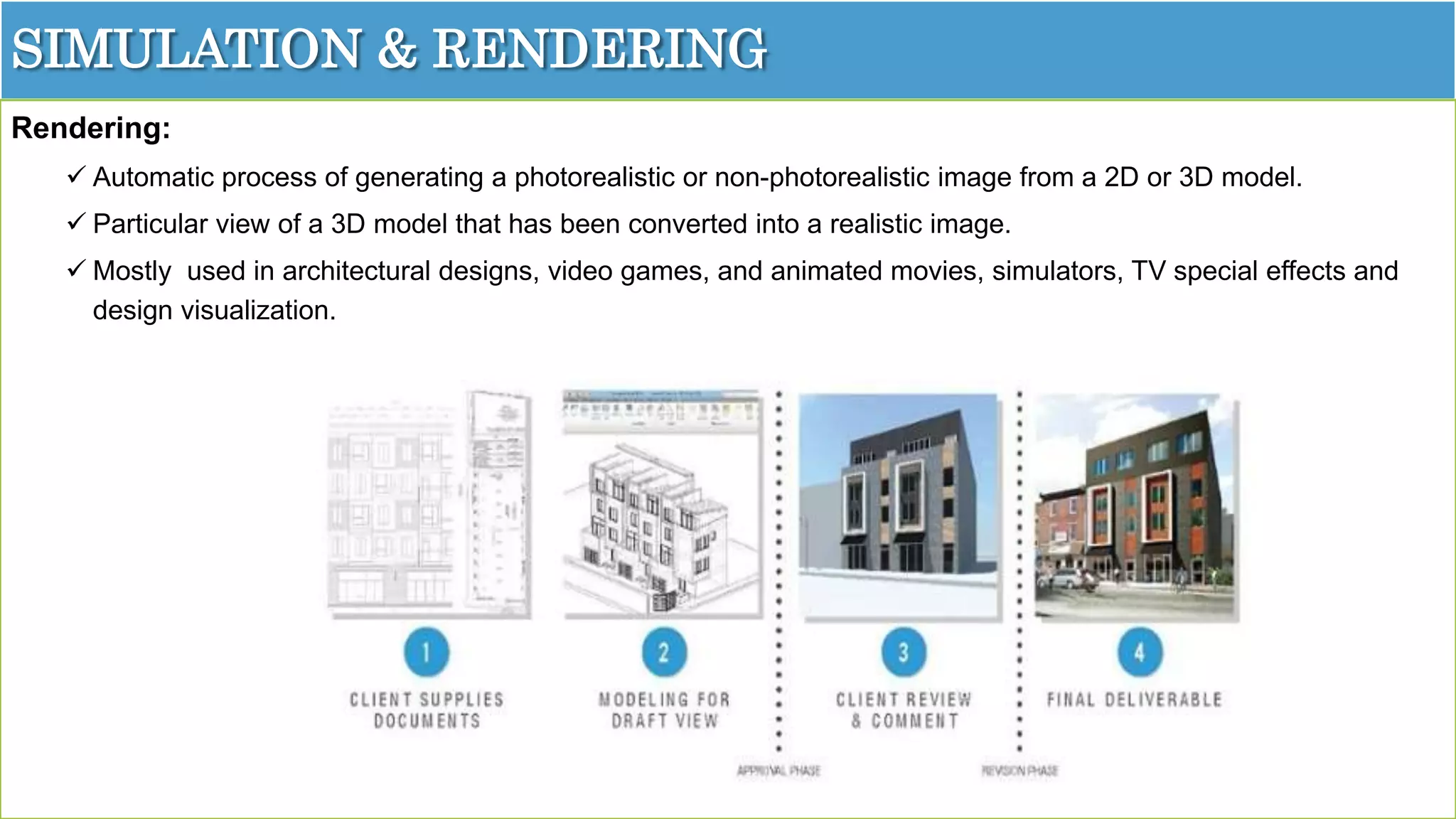
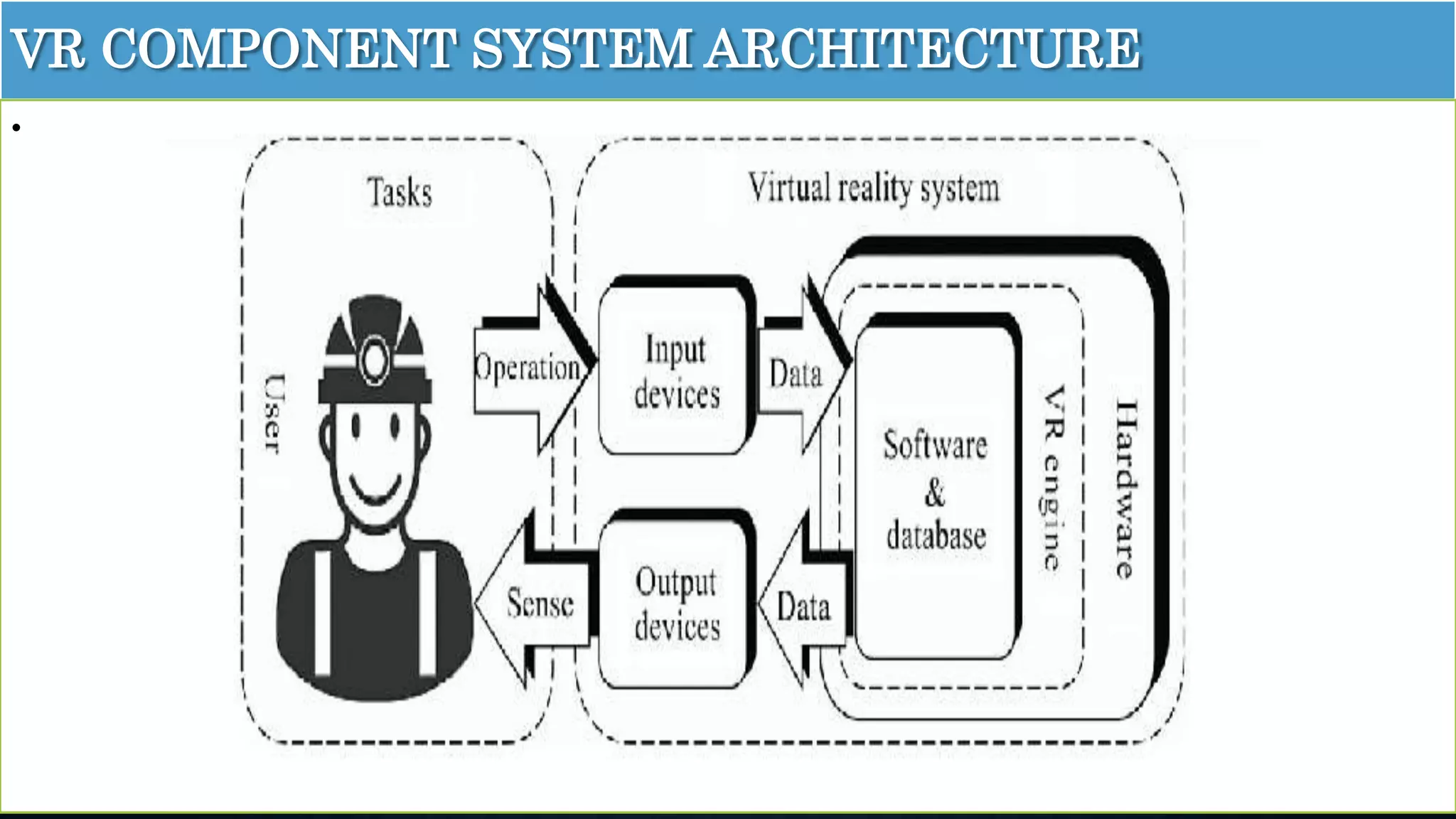
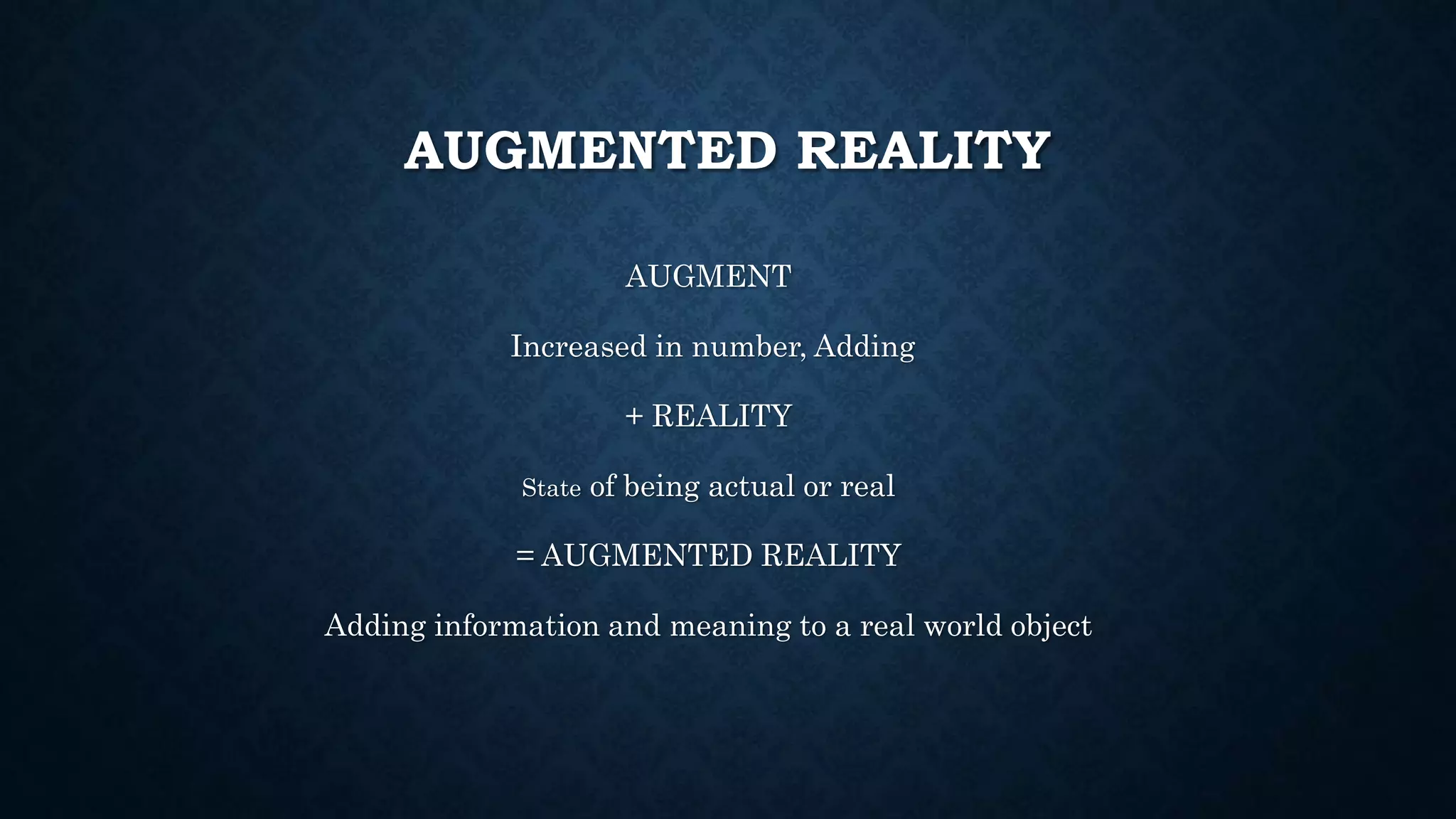
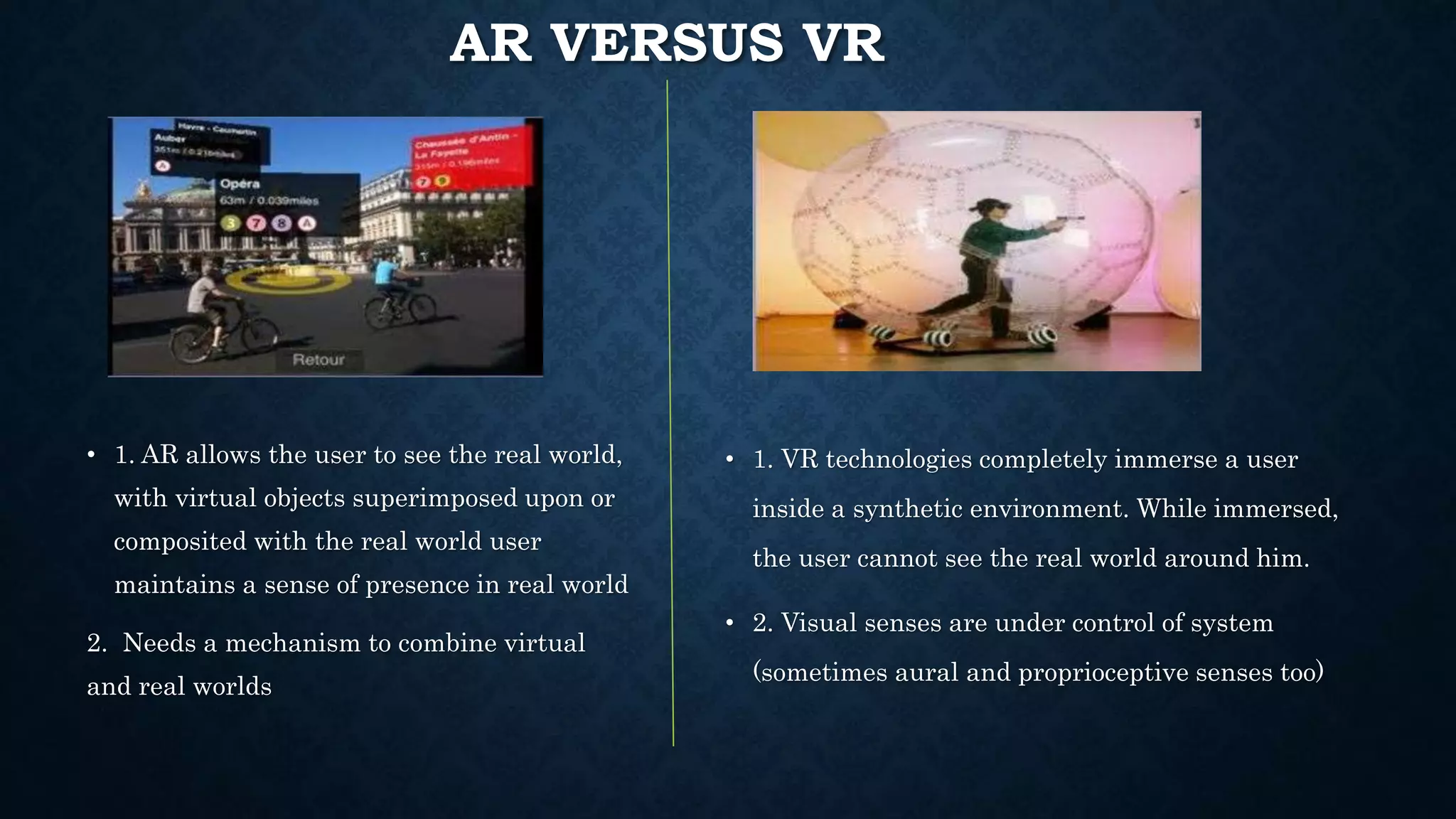
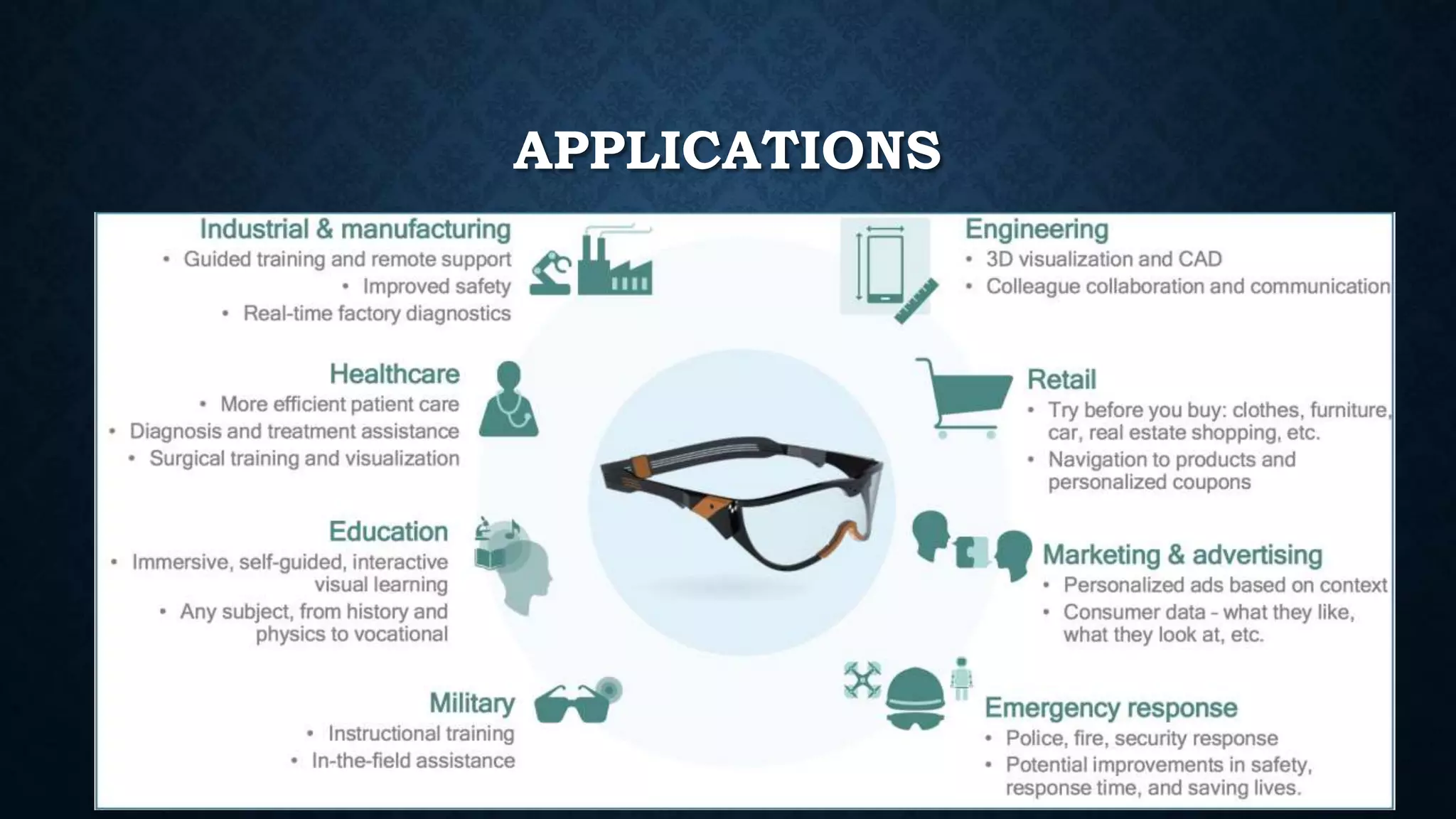
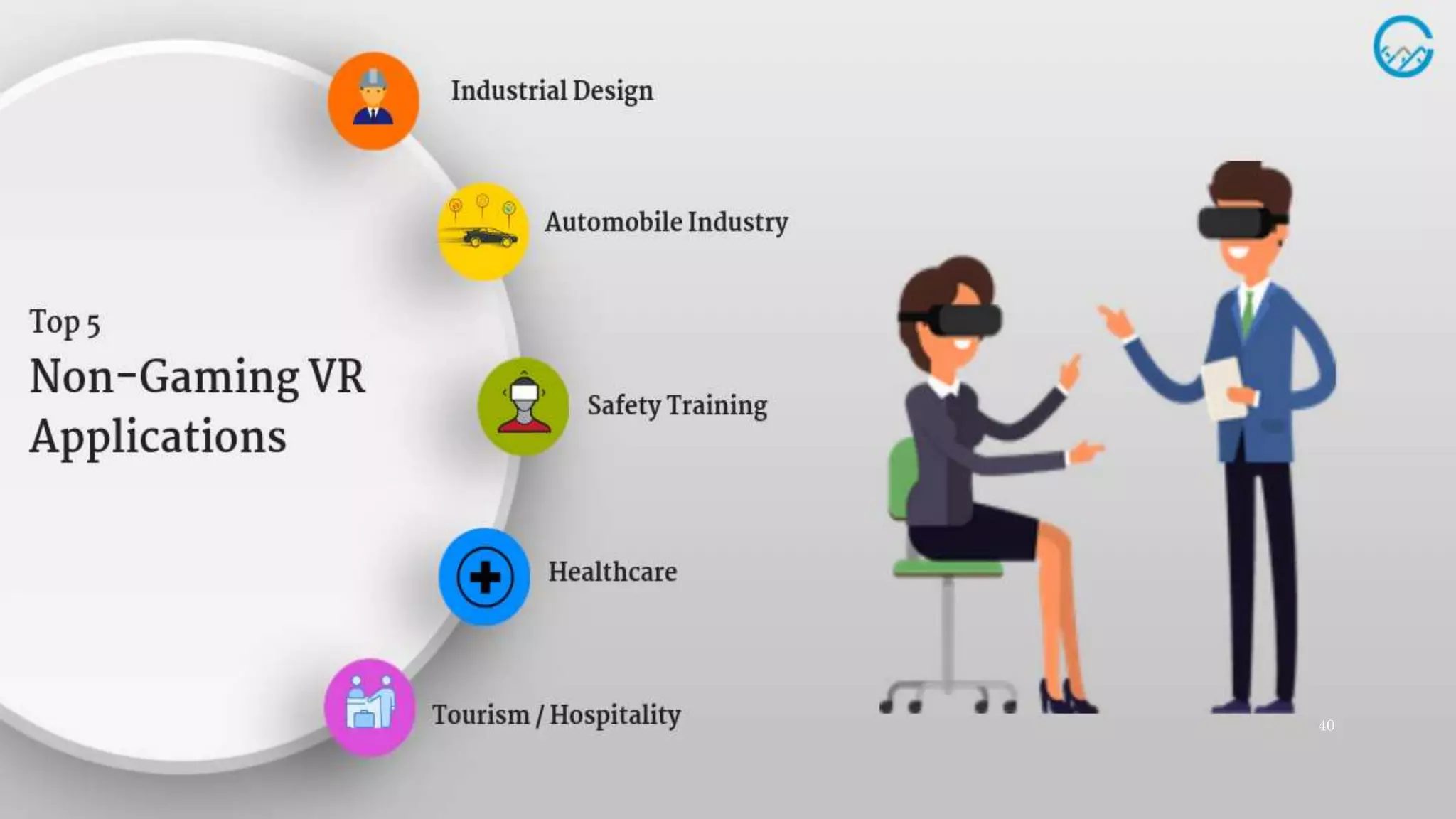
The document details an overview of virtual reality (VR) systems, categorizing them into non-immersive, immersive, semi-immersive, and distributed systems based on immersion and technology used. It also elaborates on key components like sensors, head-mounted displays, and navigation techniques, while discussing factors critical to VR performance, such as field of view, frame rate, and latency. Additionally, the document touches on augmented reality (AR), contrasting its functionalities and applications with VR, and highlights the potential and challenges of these technologies.