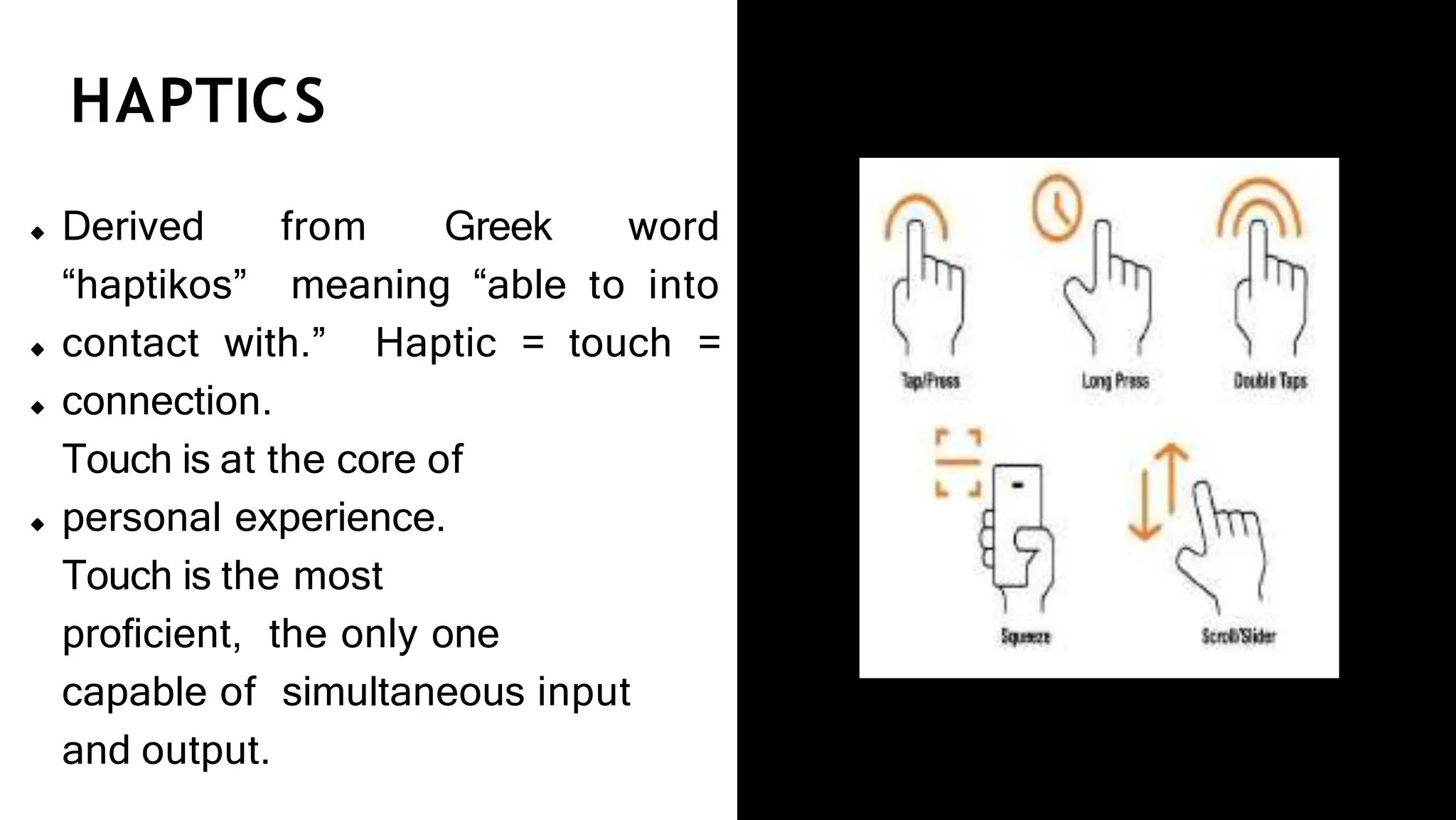
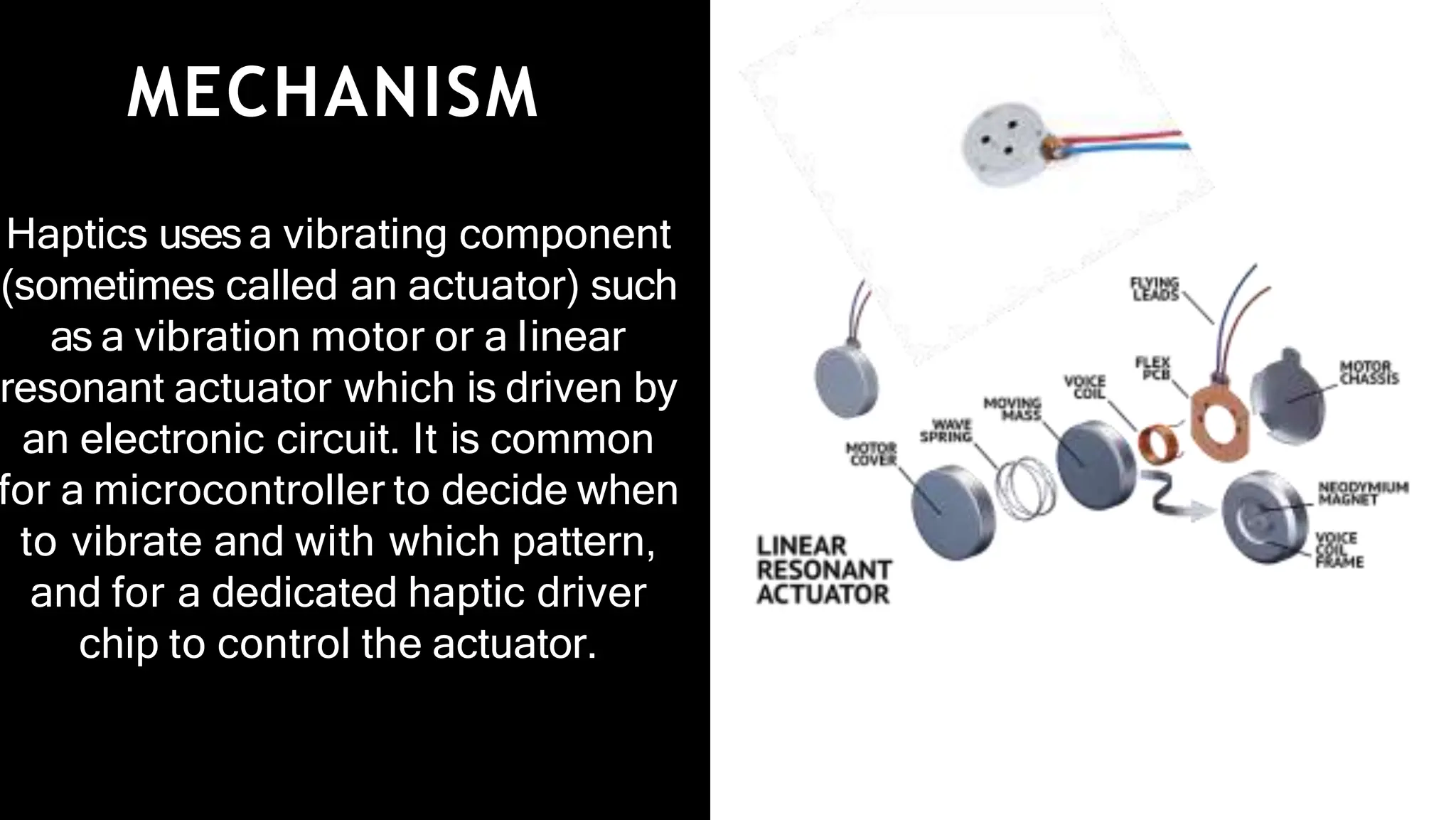
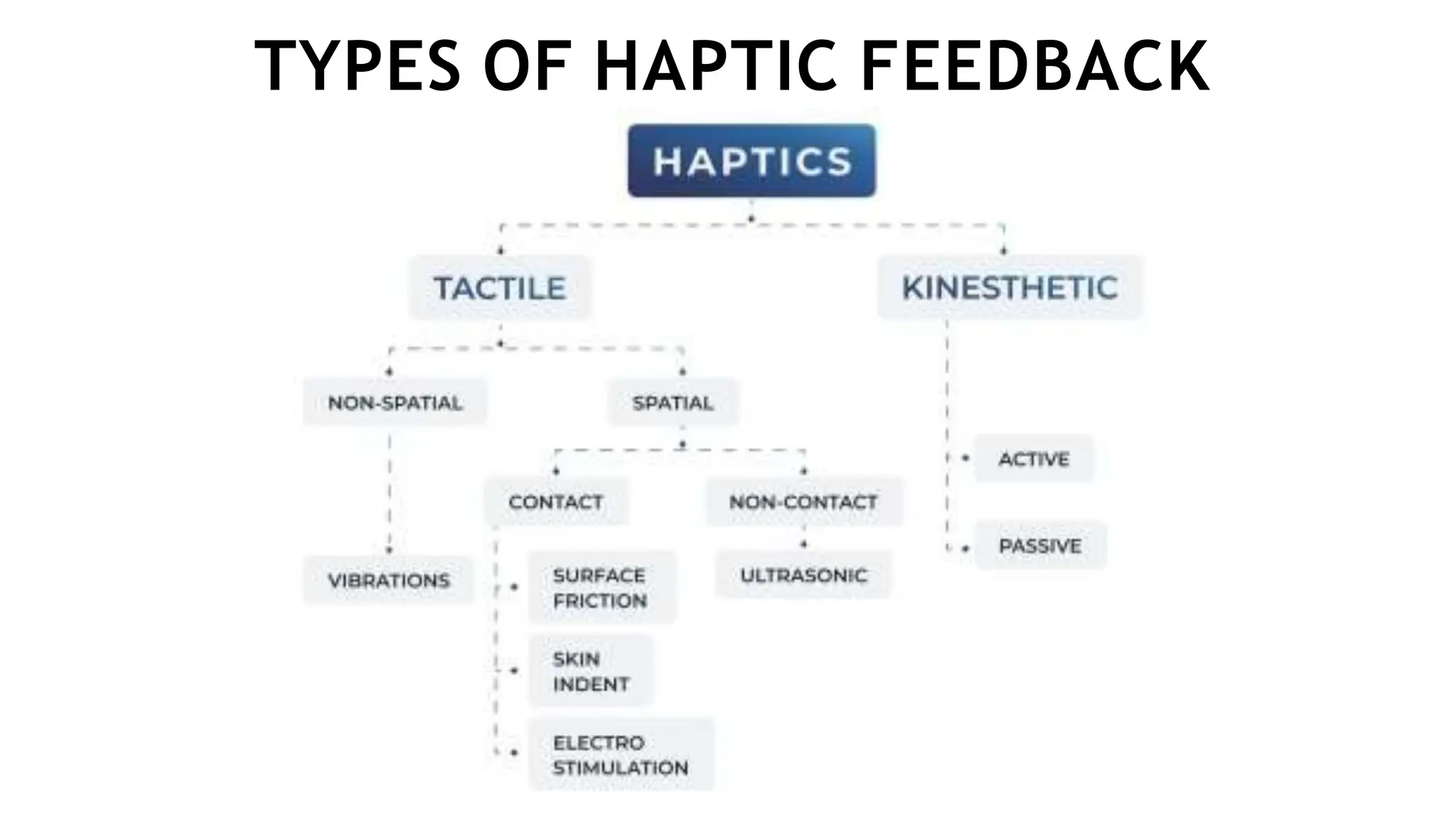
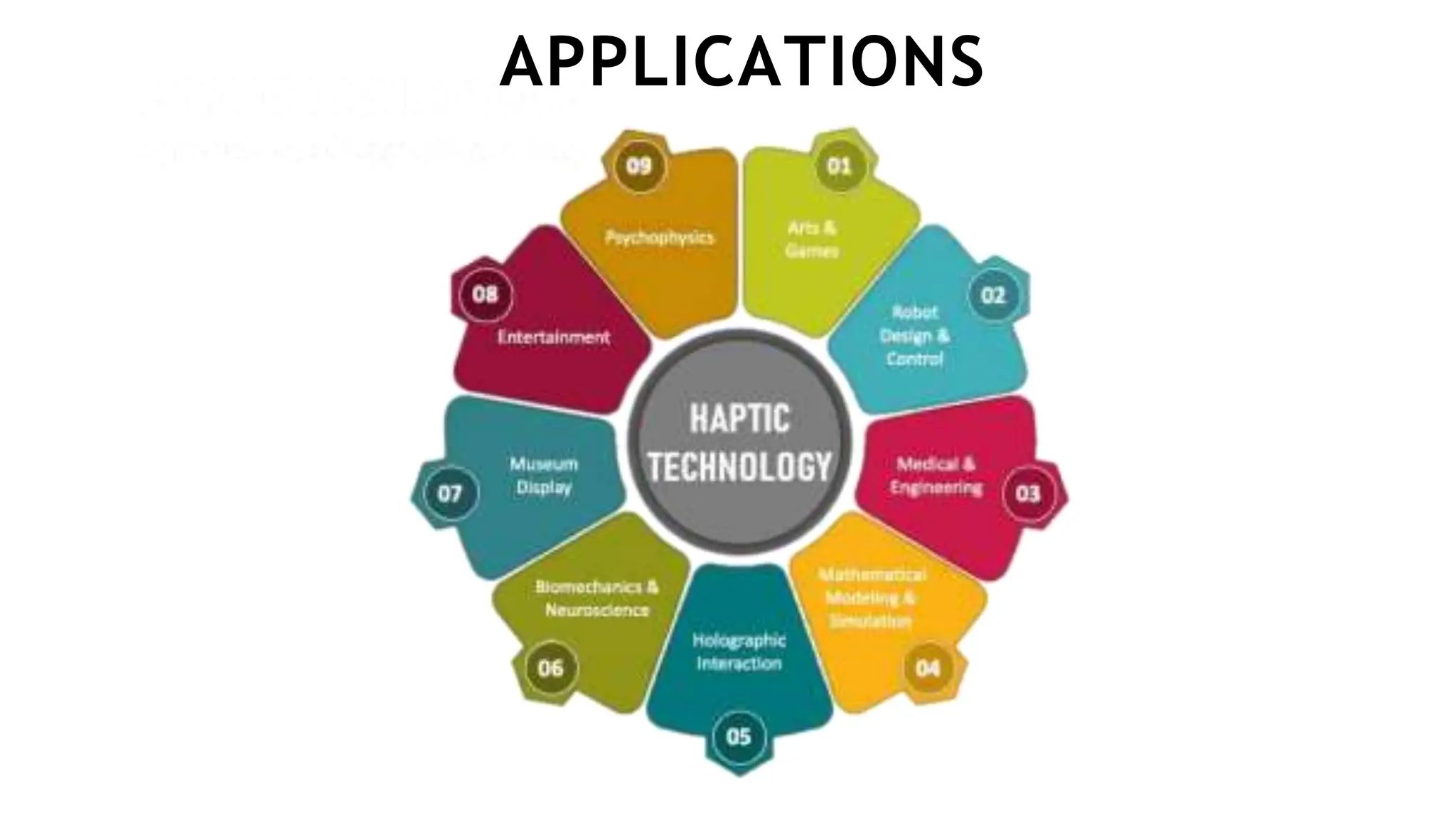
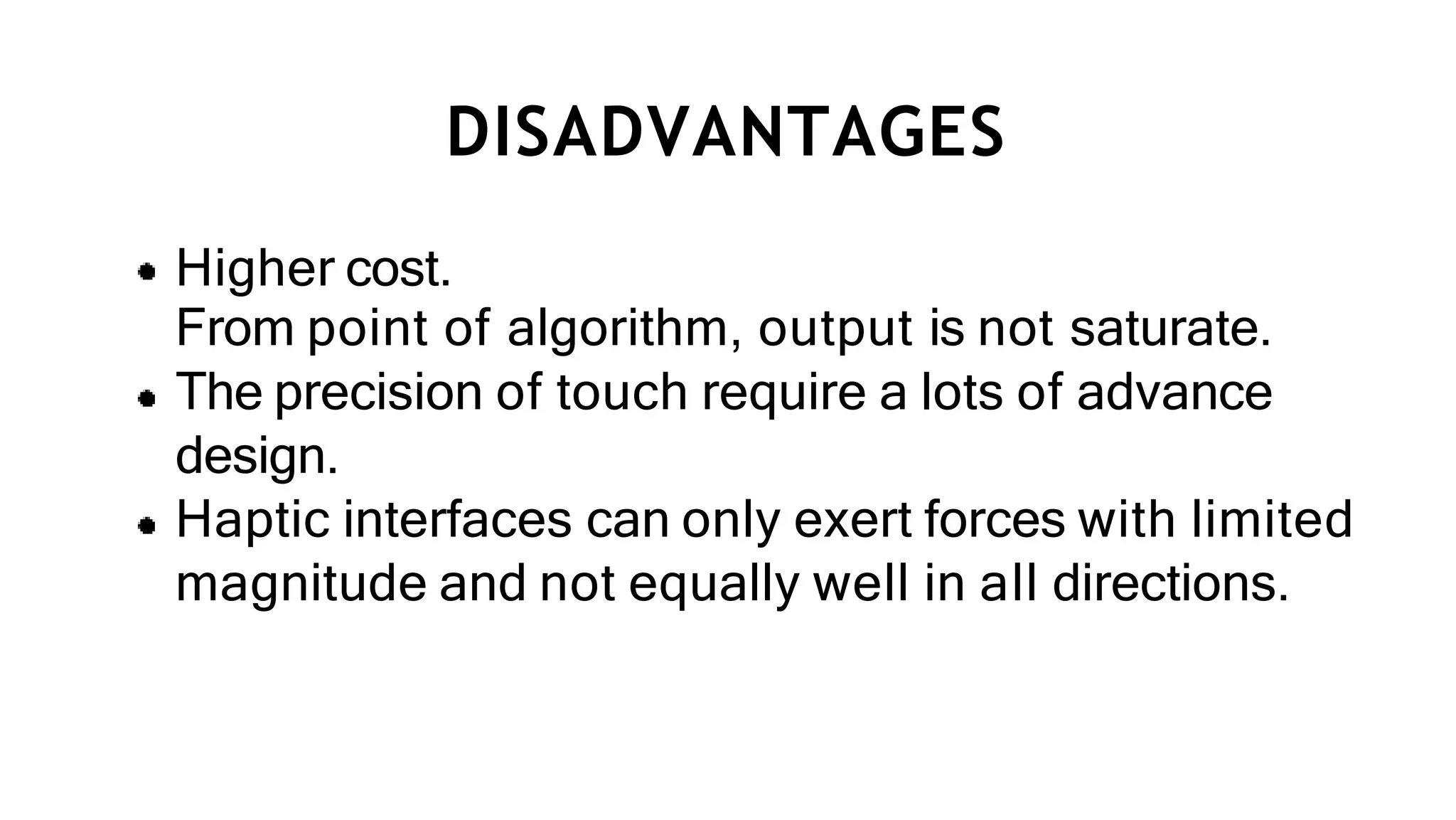
This document provides an overview of haptic technology presented by G. Uttam Netha. It begins with an introduction to haptics, then discusses the history and mechanisms. It describes different types of haptic feedback like tactile and kinesthetic and covers applications in gaming, virtual reality, medicine, automotive, mobile phones, and the military. The document outlines advantages like reduced work time but also disadvantages such as higher costs. It concludes by discussing future developments and challenges in creating more realistic haptic experiences.