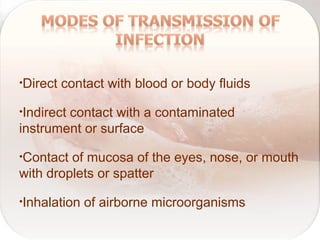
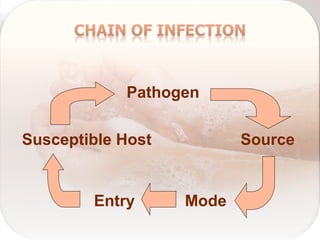
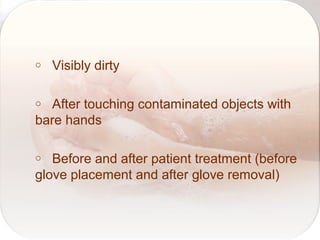
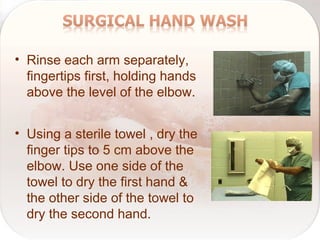
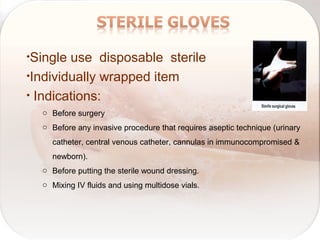
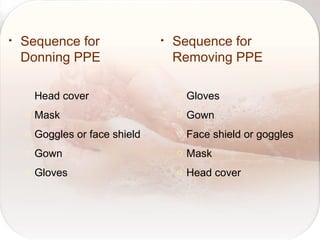
Hospital-acquired infections are infections acquired in a hospital setting after at least 48 hours of admission. They pose a significant financial burden and risk to patients that increases with longer hospital stays. Standard precautions like proper hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment, cleaning of equipment and surfaces can prevent the transmission of infections between patients and healthcare workers through contact with bodily fluids or contaminated items. Proper hand hygiene, which includes hand washing with soap and water or use of alcohol-based hand rub, is especially important before and after contact with patients to limit the spread of pathogens.