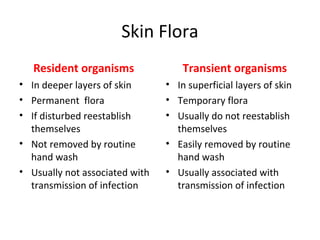
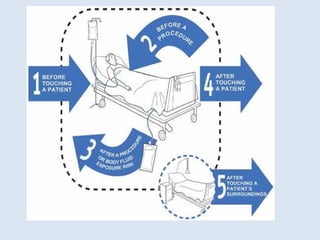
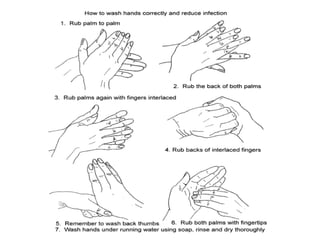
This document discusses hand hygiene and its importance in preventing infection. It notes that the 10 most common ways of spreading diseases are through the 10 fingers. Proper hand hygiene, which includes both hand washing with soap and water and use of alcohol-based hand sanitizers, is the simplest and most effective measure to prevent infection. Transient bacteria acquired from patients and the environment are more easily transmitted and removed with hand hygiene, while resident bacteria that normally inhabit the skin are more difficult to remove. The document provides guidelines on when hand hygiene should be performed and the proper techniques for routine hand washing and use of alcohol-based hand rubs.