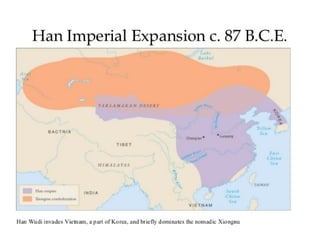
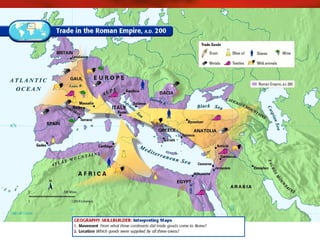
The Qin Dynasty (221-206 BCE) established China's first empire under Shi Huangdi. It promoted legalism, bureaucratic administration and centralized control. Shi Huangdi ordered the burning of Confucian texts and buried scholars alive. The dynasty collapsed after his death due to oppression and succession struggles. The Han Dynasty (206 BCE-220 CE) established a synthesis of legalism and Confucianism. Emperor Wu strengthened the government and expanded the empire through war and colonization, but struggled against the nomadic Xiongnu. The Han developed a stable bureaucracy and society structured around Confucian family and social values. The Silk Road flourished during this period, facilitating trade and cultural exchange between China and the

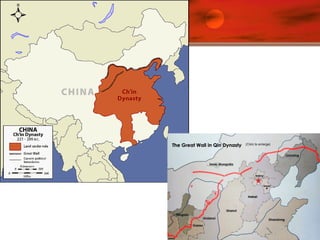
![Qin [Ch’in] Dynasty, 221-206 B.C.E.
Established China’s first empire
Shi Huangdi (221-206 B.C.E)
Legalist rule
Bureaucratic administration
Centralized control
Military expansion – focus on military power
Book burnings targeted
Confucianists
Buried protestors alive!
Built large section of the Great Wall](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handynasty14-151121180406-lva1-app6892/85/Han-Dynasty-Classical-China-3-320.jpg)






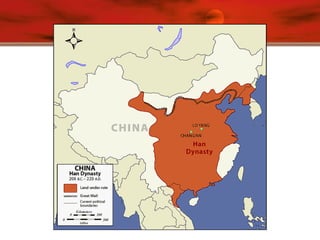
![Han Dynasty Overview
206 B.C.E.-220 C.E.
“People of the Han” original Chinese
Expanded China’s borders and developed a
system of government that lasted for centuries
Paper invented [105 B.C.E.]
Silk Road trade develops; improves life for many
Confucianism became foundation of society
Buddhism introduced into China](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handynasty14-151121180406-lva1-app6892/85/Han-Dynasty-Classical-China-11-320.jpg)




































![Han Decline - Wang Mang
Usurping of Han power
Xin dynasty [9-23 CE]
Death of a child emperor led to attempt
of by military official Wang Mang to
create new dynasty – Confucian reformer
Flooding and course changes of the Yellow
River disrupted daily and economic life
Invasions of Xiongnu and rebellion in 23 CE
opened door for return of Han](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handynasty14-151121180406-lva1-app6892/85/Han-Dynasty-Classical-China-53-320.jpg)
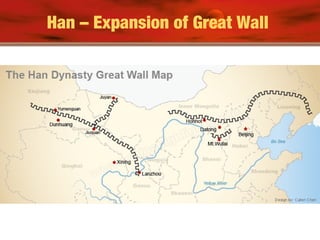
![Later or Eastern Han
Return of the Han– Later Han Dynasty
A Weakened Han Dynasty [23-220 CE]
Han weakness enabled barbarians to live
inside the Great Wall, serve in army, and
intermarry with Chinese
Led to sinicization (adoption of Chinese
culture) of barbarians
Han failed to force local government
officials to send tax revenues to central
government](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handynasty14-151121180406-lva1-app6892/85/Han-Dynasty-Classical-China-54-320.jpg)


