The document provides a summary of Chinese dynasties from 1500 BCE to 1911 CE. It focuses on details about the Shang Dynasty, which ruled from around 1500 BCE to 1027 BCE. Key points:
- The Shang Dynasty was the first dynasty to create a stable government in China, laying the foundations for future dynasties. They developed writing, calendar, arts, and bronze casting.
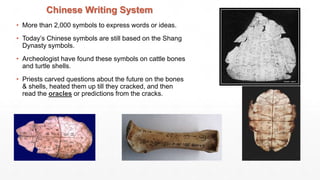
- Kings ruled as absolute monarchs. Society was divided into classes like nobles, artisans, farmers and slaves. Religion involved ancestor worship and divination rituals using oracle bones.
- The Qin Dynasty unified China's warring states in 221 BCE. The First Emperor standardized laws, currency and measurements. Not