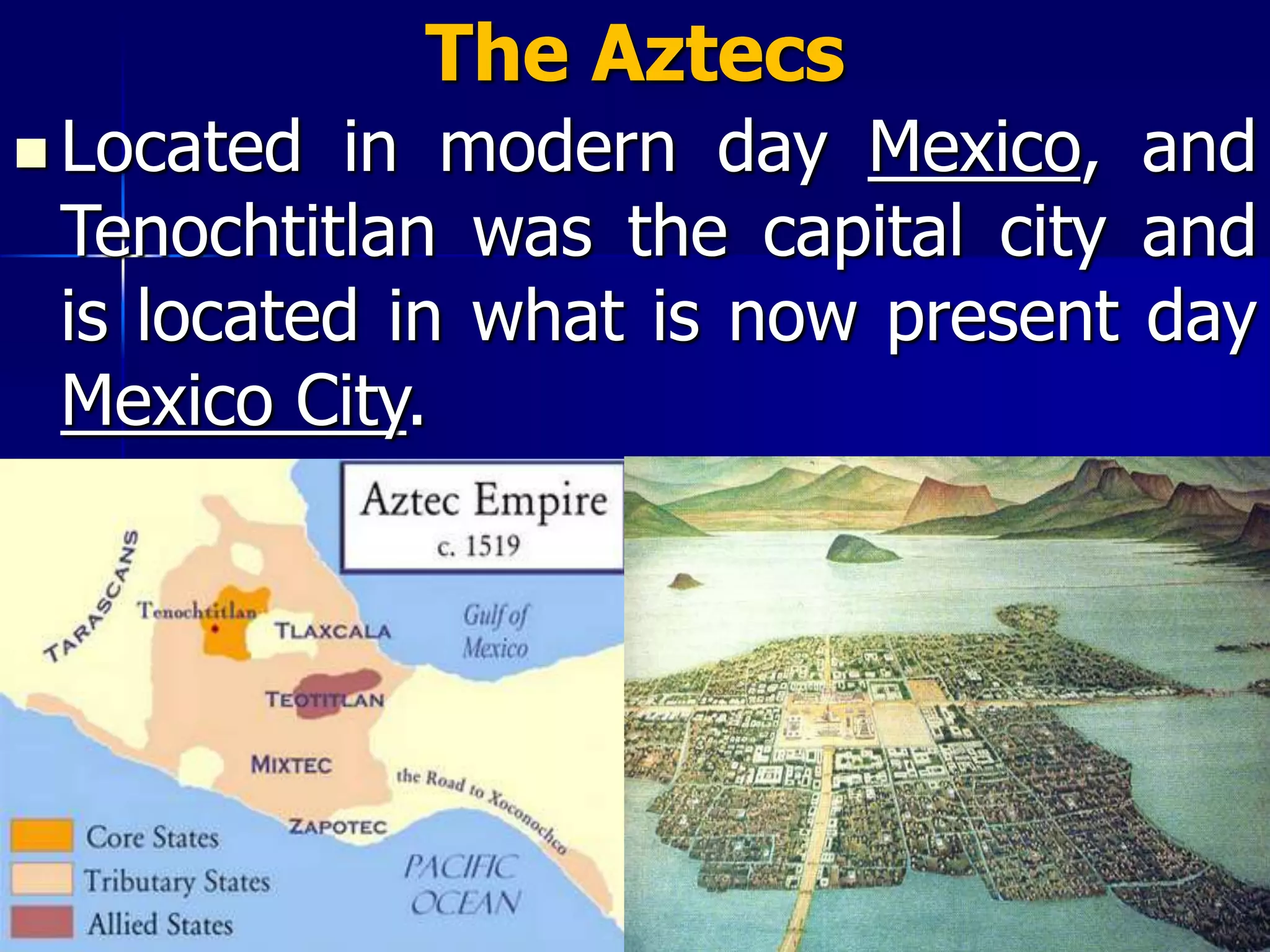
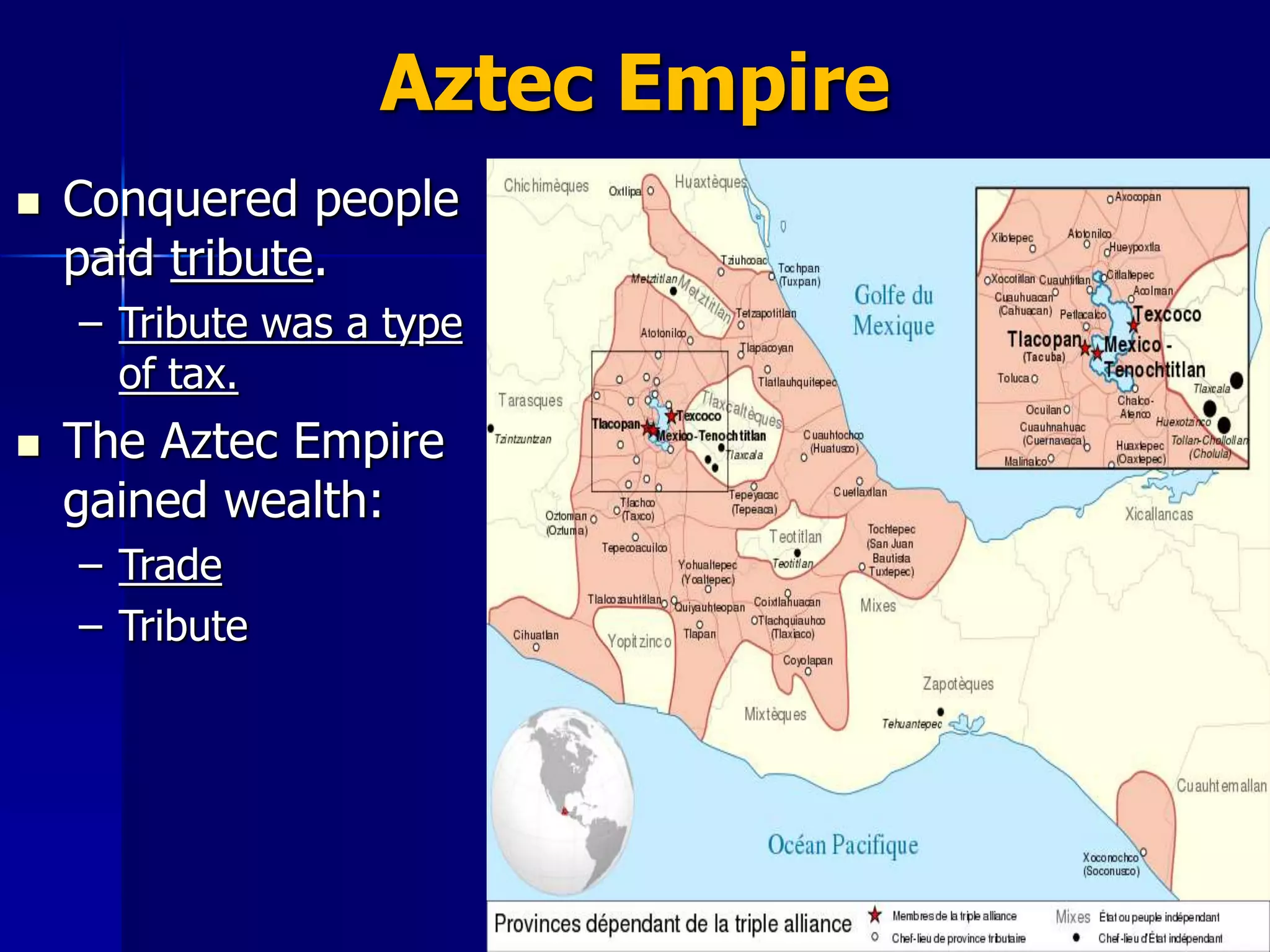
The Aztec civilization, which thrived in southern Mexico from around 900 CE until its fall in 1521, was established by the Mexica who settled in Tenochtitlán, their capital. The empire grew through military conquests, establishing trade networks, and utilizing unique agricultural practices such as chinampas for farming in swampy regions. The Aztec society included social classes and public education, but ultimately fell to Spanish conquistadors led by Hernán Cortés due to superior weaponry, strategic alliances, and disease.