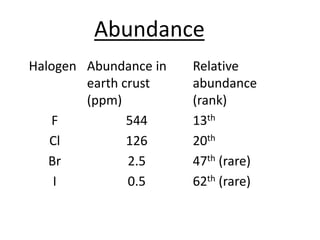
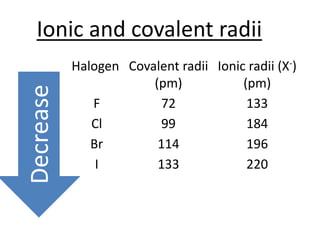
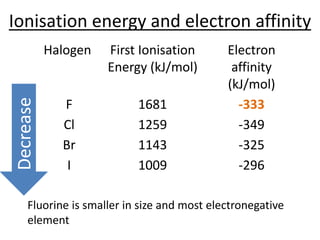
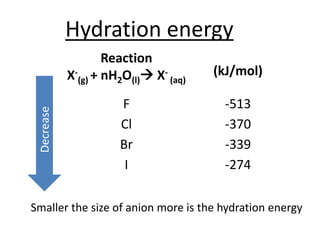
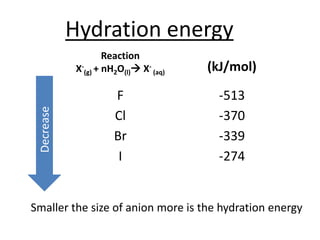
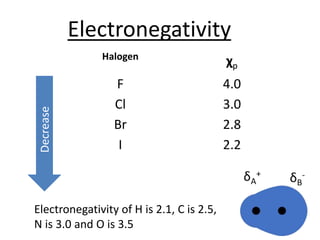
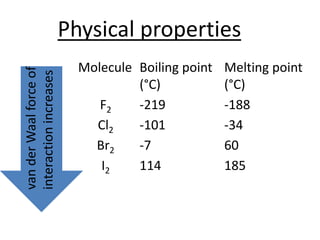
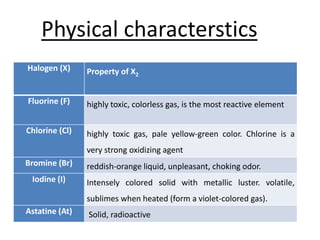
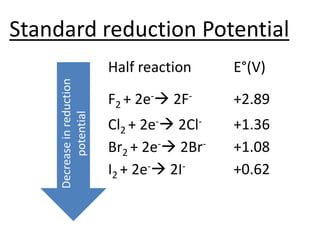
Halogens are located in group 17 of the periodic table. Their electronic configurations show increasing atomic numbers and electron shells. The most common oxidation state is -1, with fluorine having the highest electronegativity and tendency to gain electrons. Abundance in the earth's crust and physical properties like size, ionization energy, and melting/boiling points decrease down the group. Hydration energy also decreases as halogen size increases.

![Atomic
number
Halogen Symbol Electronic
configuration
9 Fluorine F [He]2s22p5
17 Chlorine Cl [Ne]3s23p5
35 Bromine Br [Ar] 3d104s24p5
53 Iodine I [Kr] 4d105s25p5
85 Astatine At [Xe] 4f145d106s26p5
Halogens](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/halogens-211005042055/85/Halogens-3-320.jpg)
![Halogen Electronic
configuration
Oxidation state
F [He]2s22p5 -1, 0
Cl [Ne]3s23p5 -1, 0, +1, +3, +4, +5, +6, +7
Br [Ar] 3d104s24p5 -1, 0, +1, +3, +4, +5, +6
I [Kr] 4d105s25p5 -1, 0, +1, +3, +5, +7
Oxidation state
Most common and stable oxidation state among halogen is -1
as after acquiring one electron they get their octet complete.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/halogens-211005042055/85/Halogens-4-320.jpg)