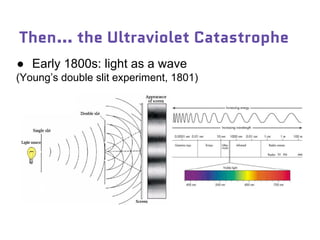
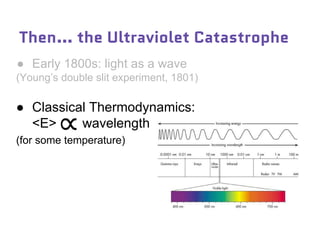
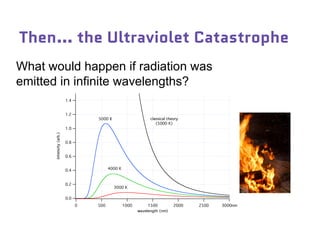
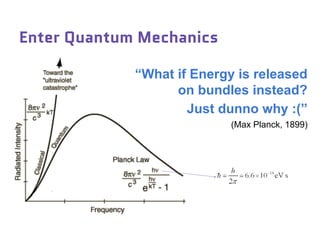
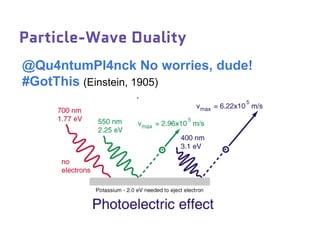
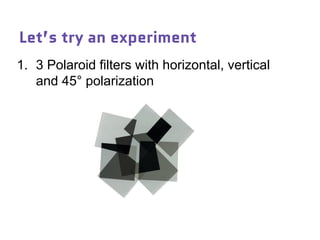
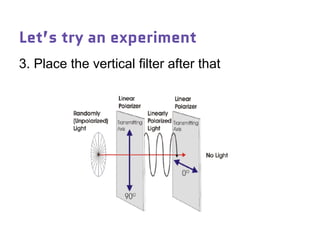
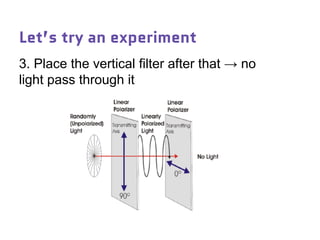
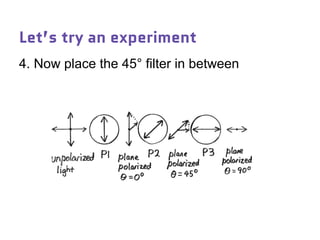
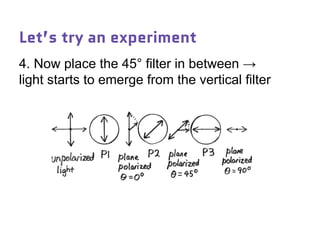
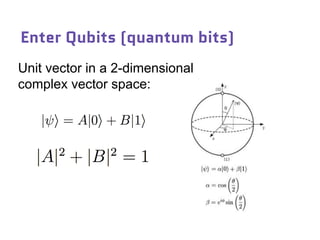
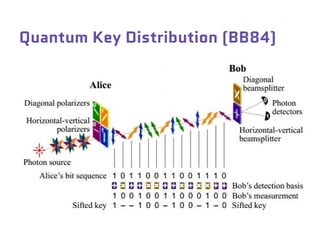
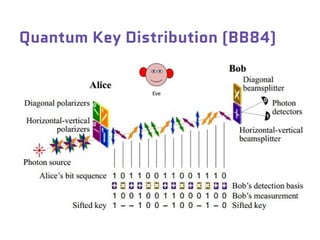
Dr. Marina von Steinkirch discusses the implications of quantum mechanics and quantum computing on security, particularly in the context of cryptography. She explains quantum key distribution methods and the challenges in building quantum computers, emphasizing how advancements could disrupt current internet security. The talk highlights the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics and addresses concerns regarding the future of secure communications.