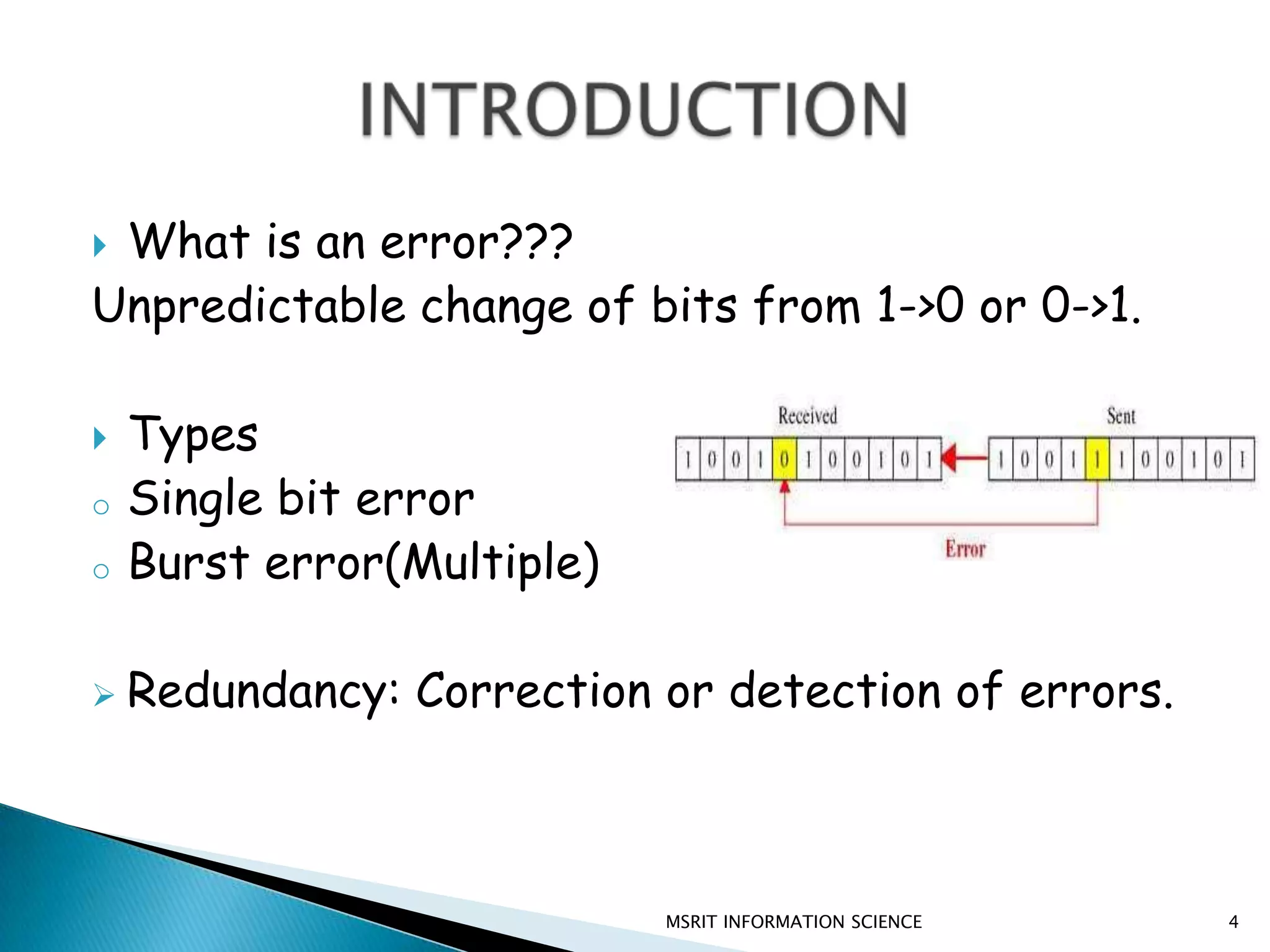
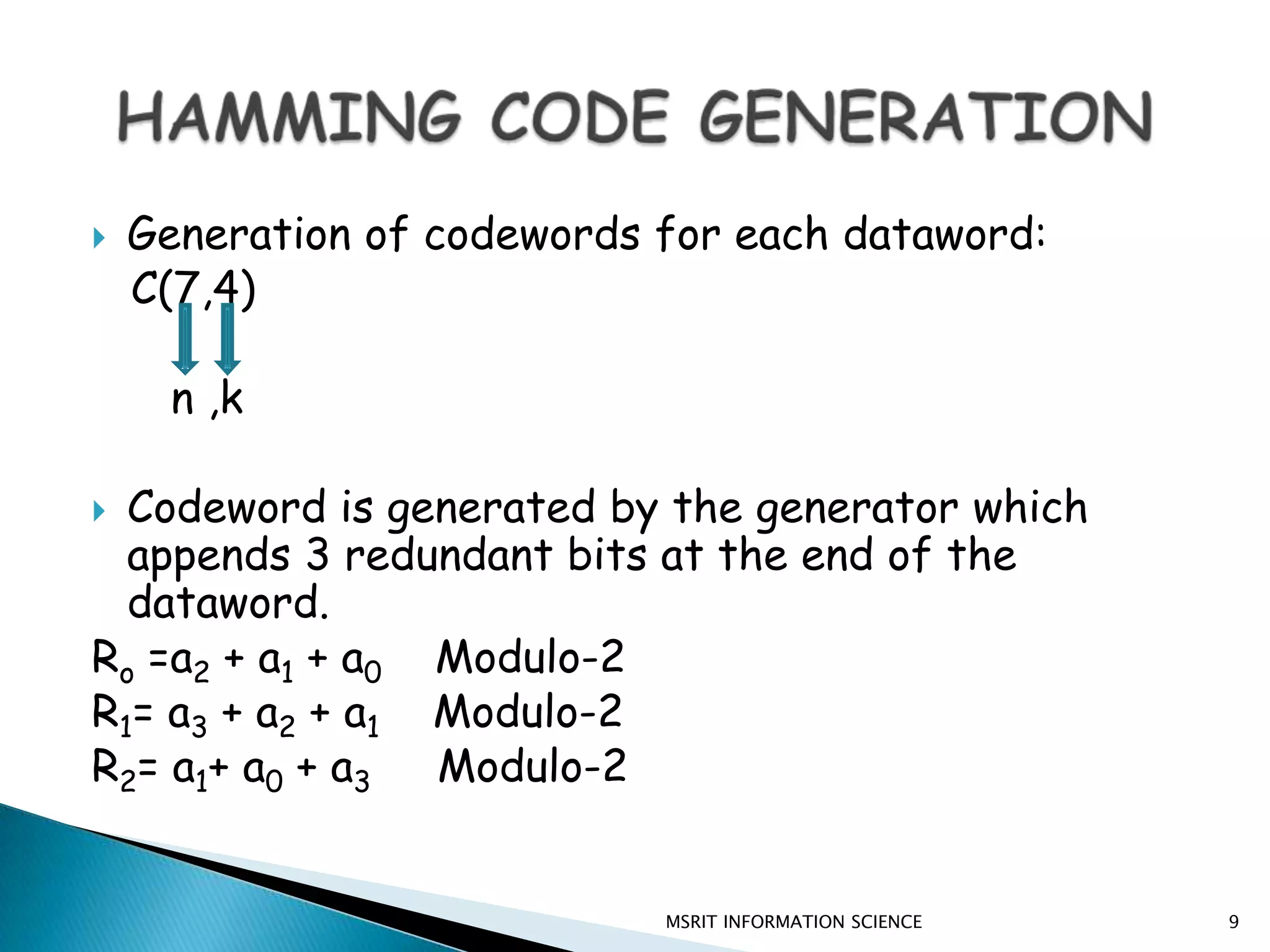
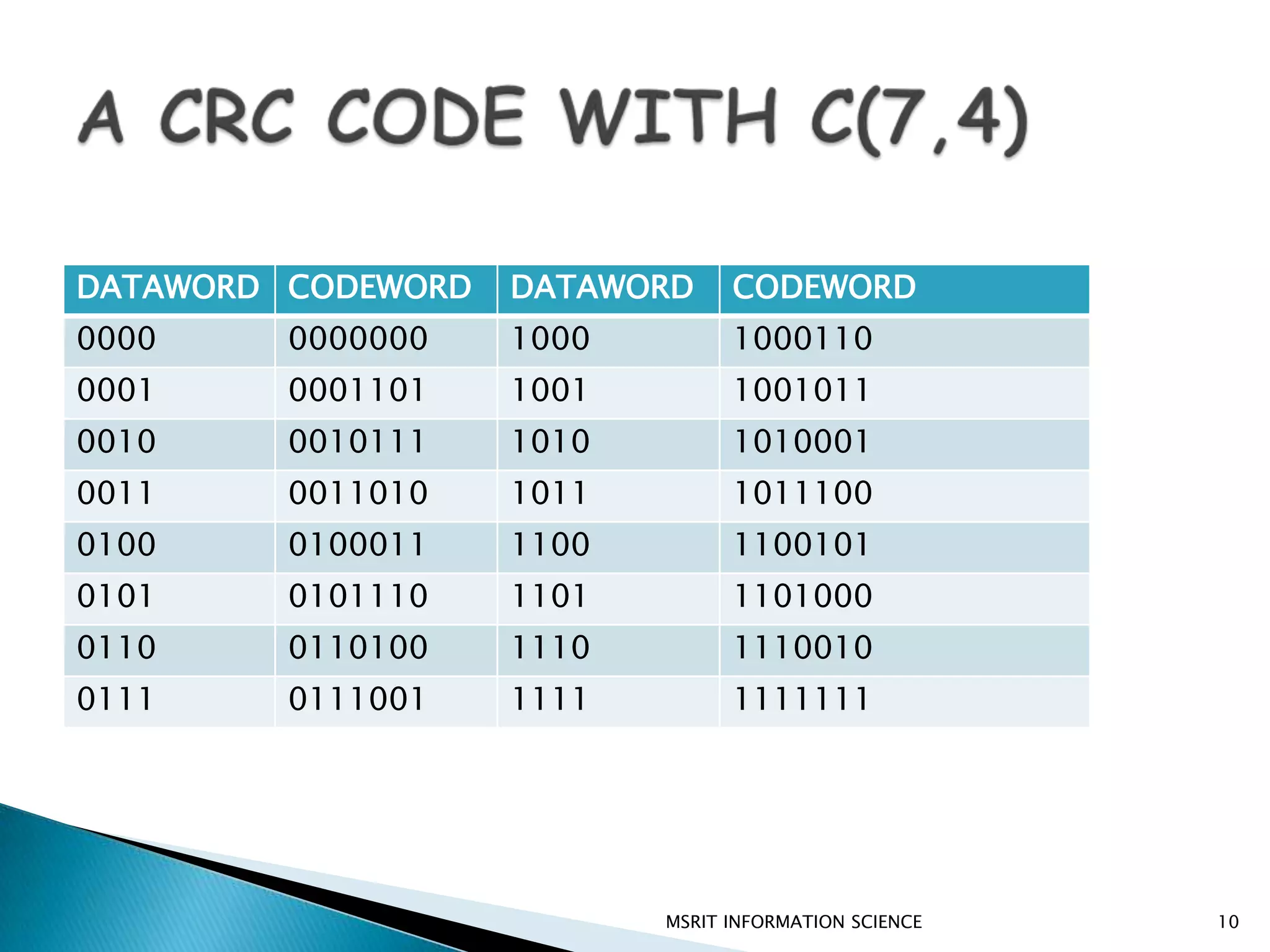
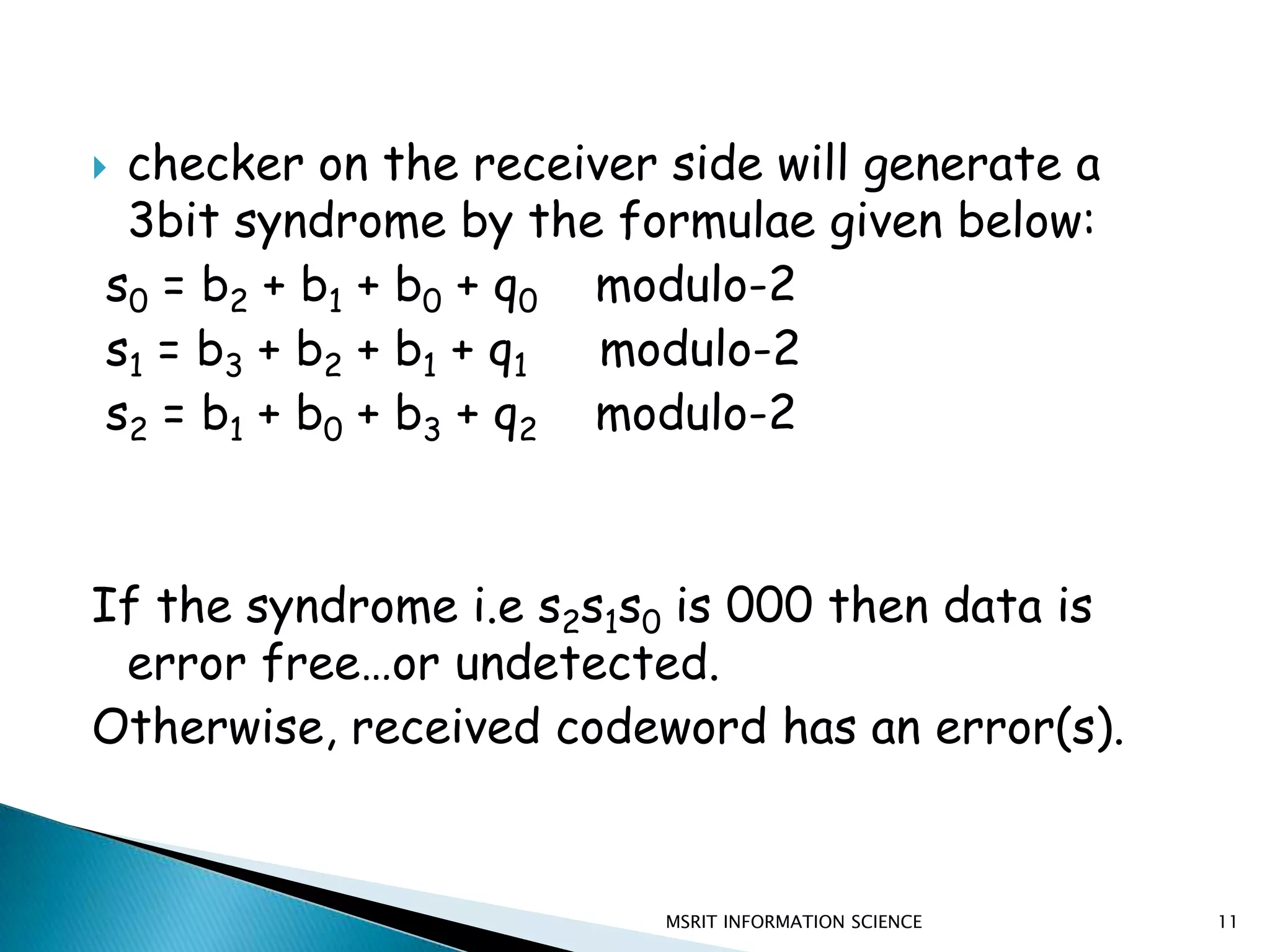
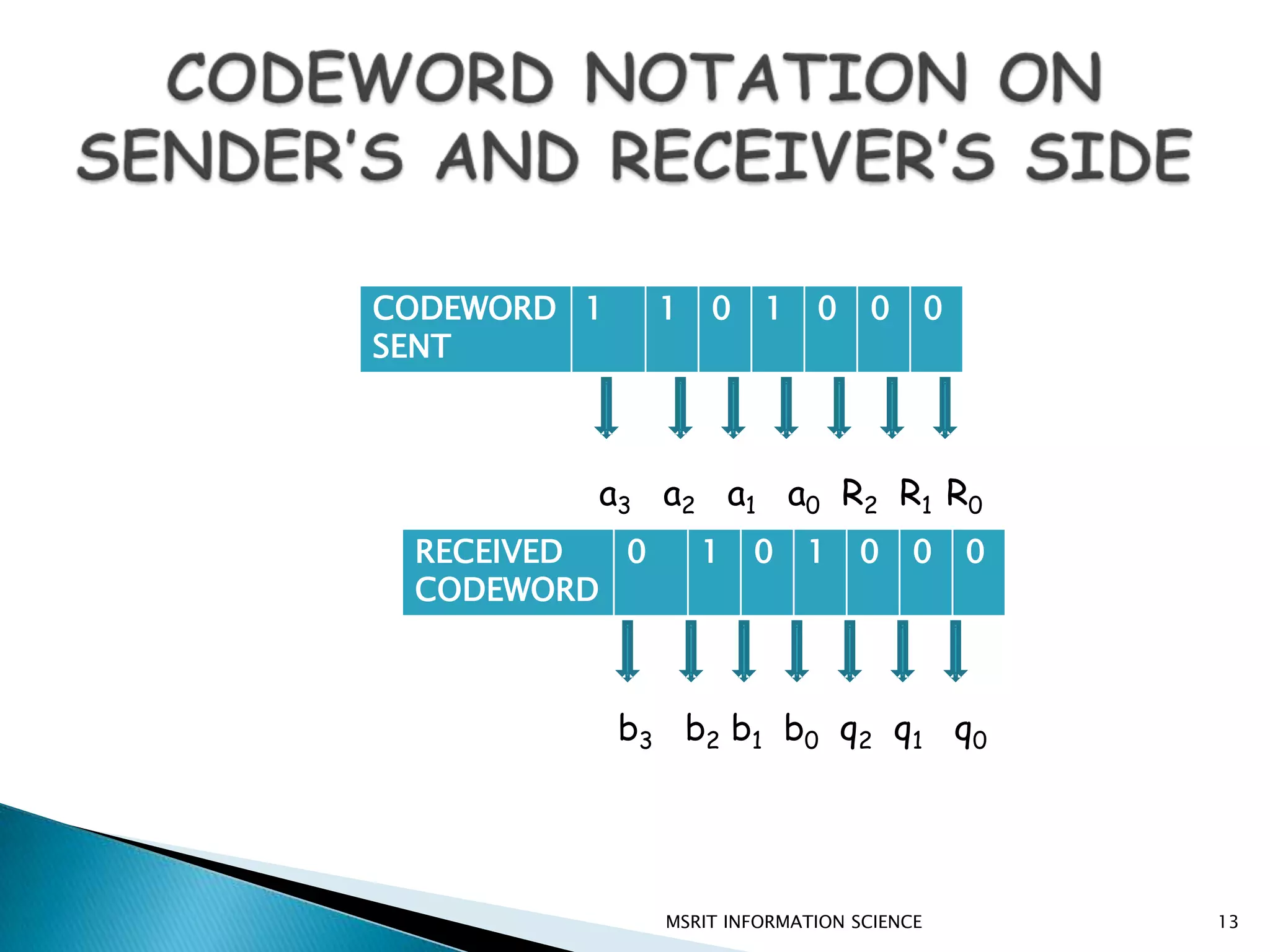
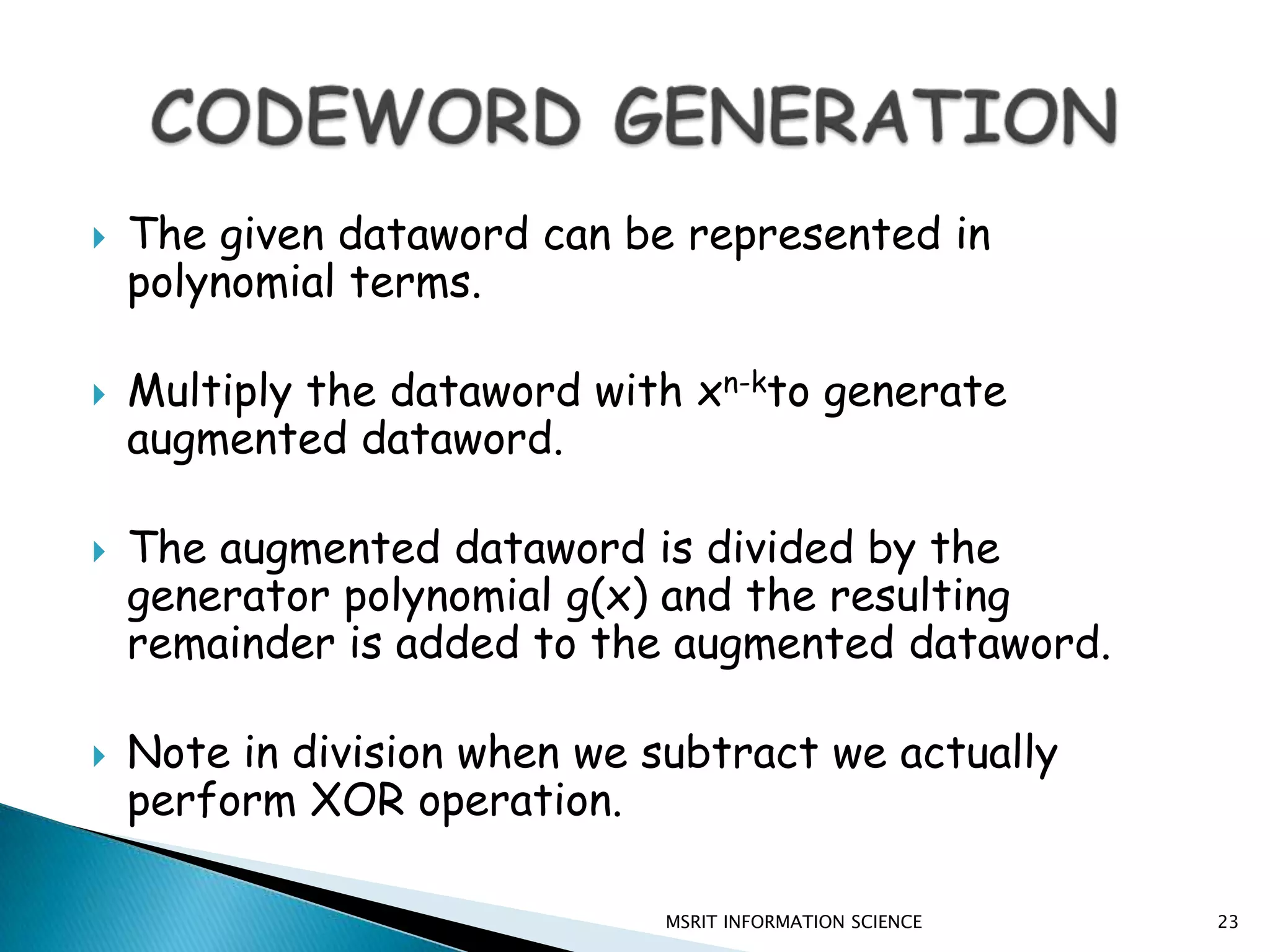
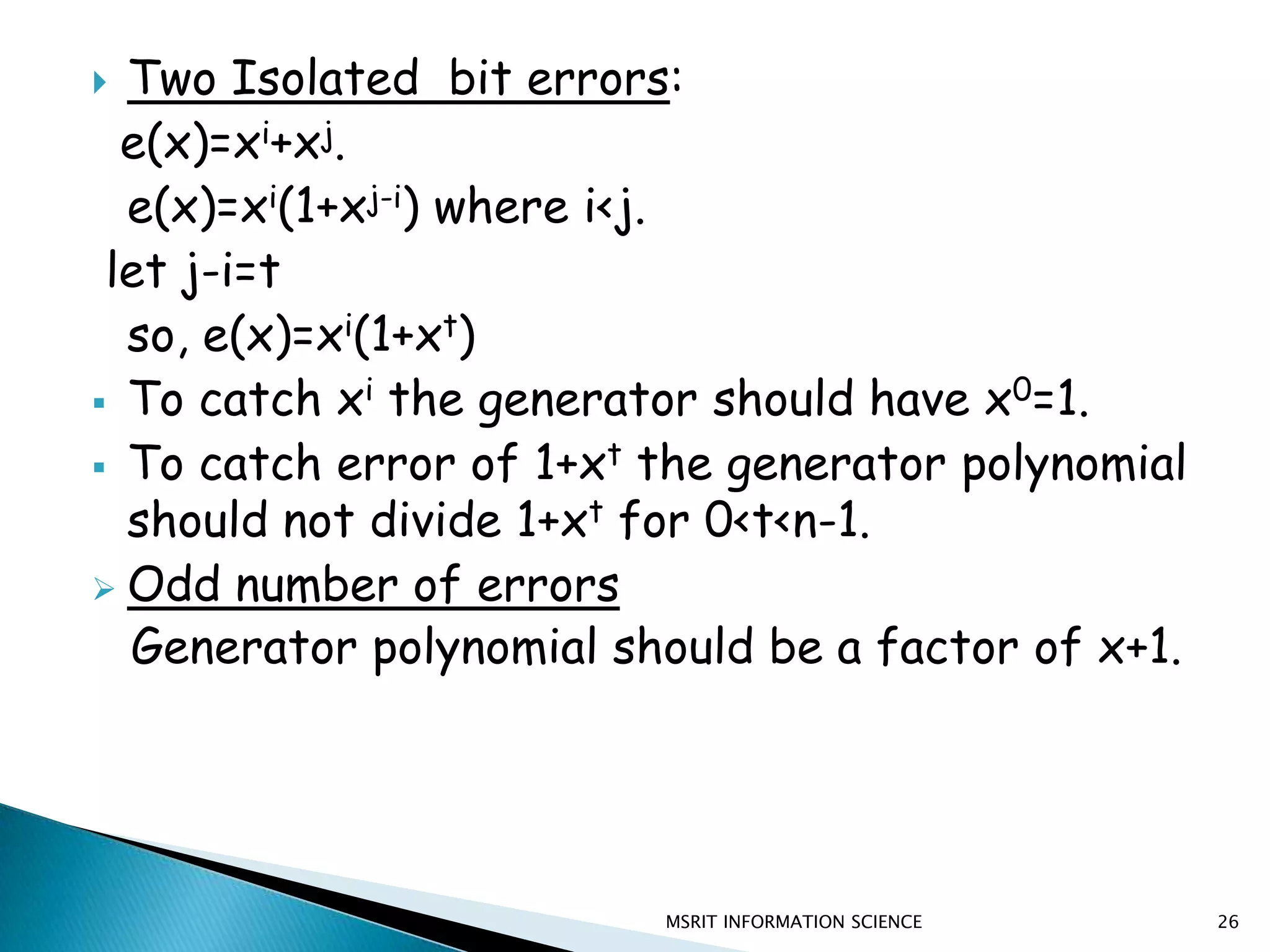
This document discusses error detection and correction techniques. It introduces concepts like redundancy, forward error correction, retransmission, linear block coding, Hamming codes, and cyclic redundancy checks (CRC). Specific error correction codes covered include Hamming codes, which use modulo-2 arithmetic to add redundant bits to detect and correct single bit errors. CRC codes are also discussed, which use cyclic codes and polynomial representations to detect errors by computing a syndrome value. The document provides information on generating and detecting errors for different codes.