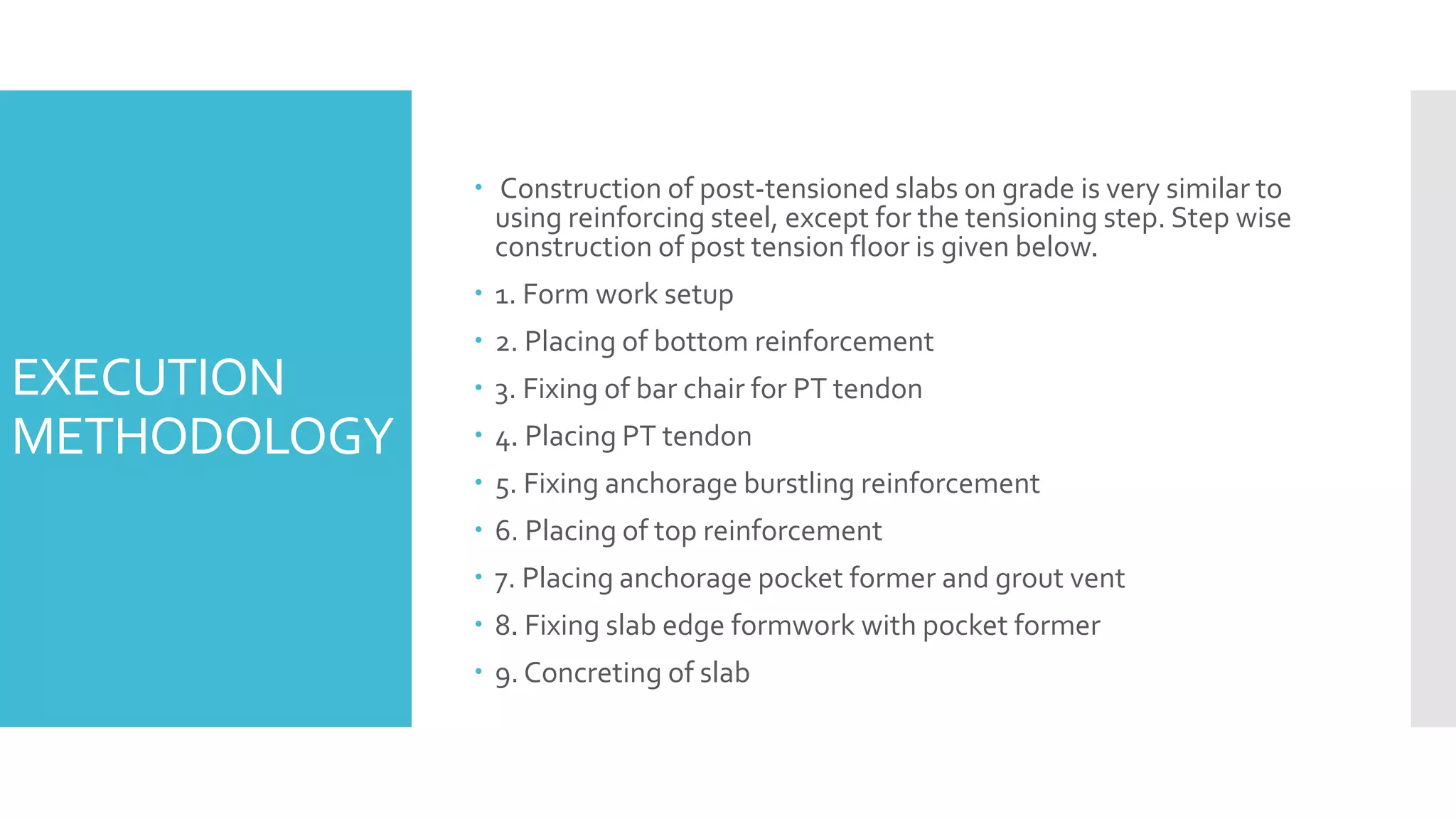
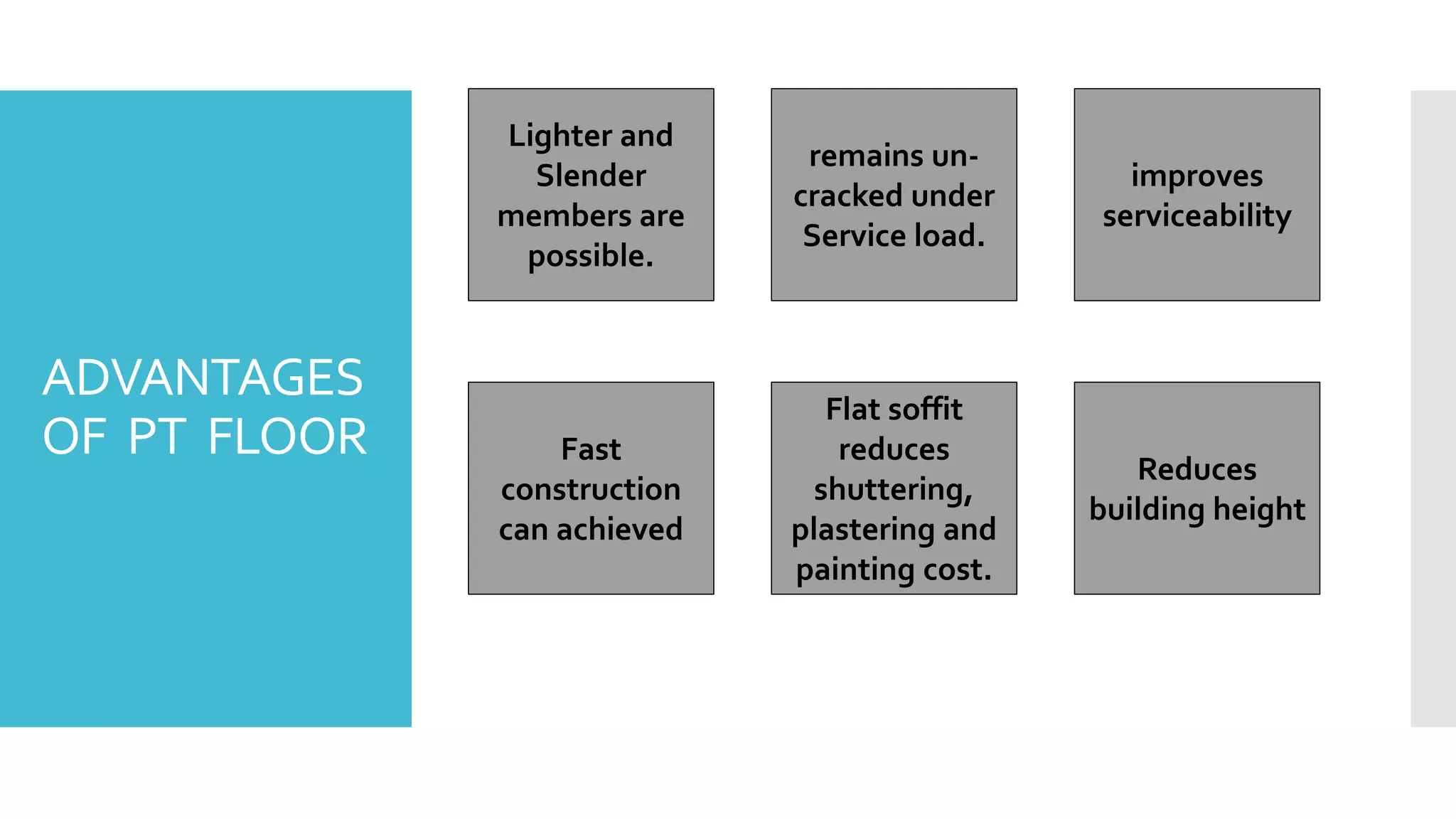
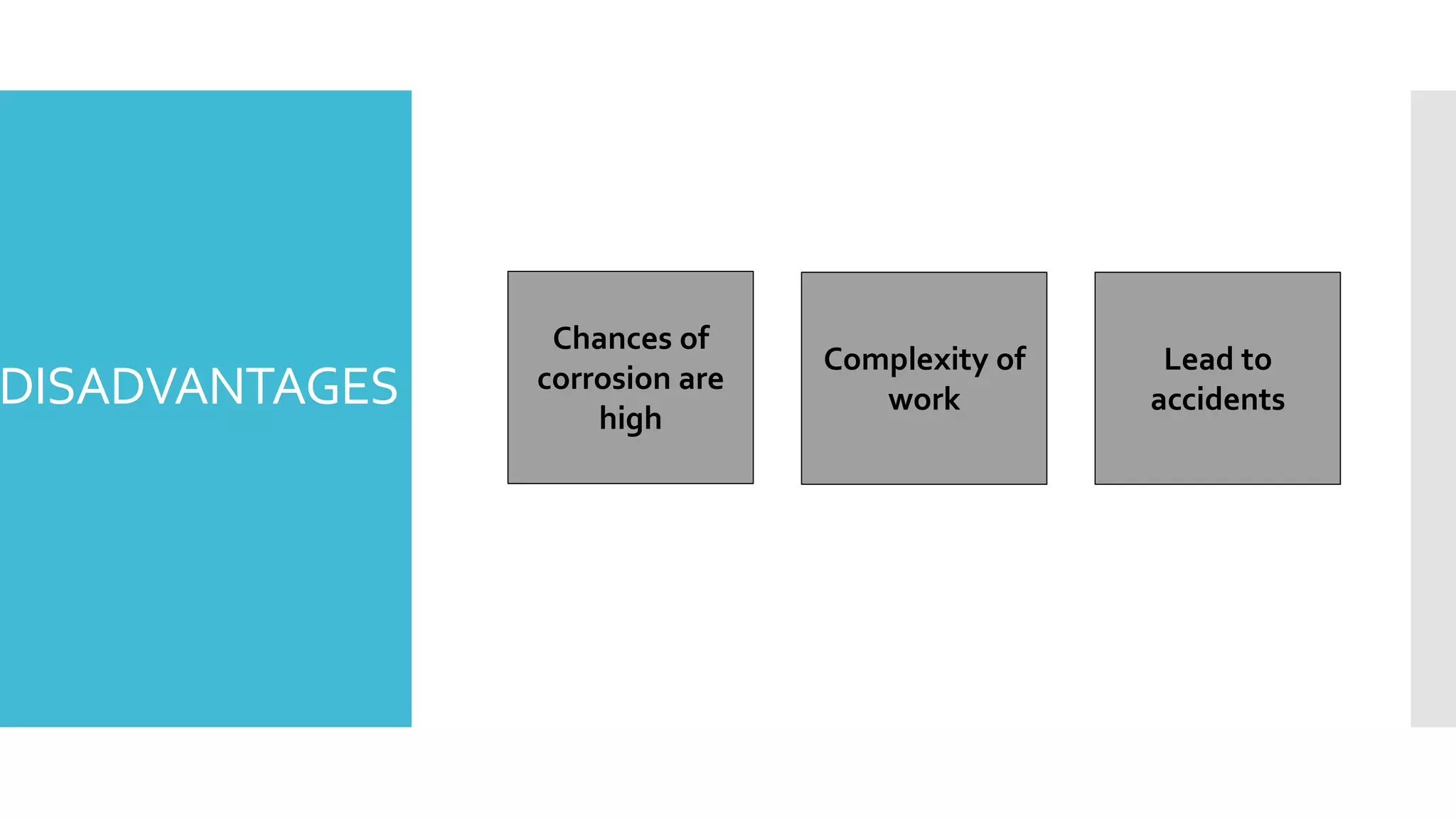
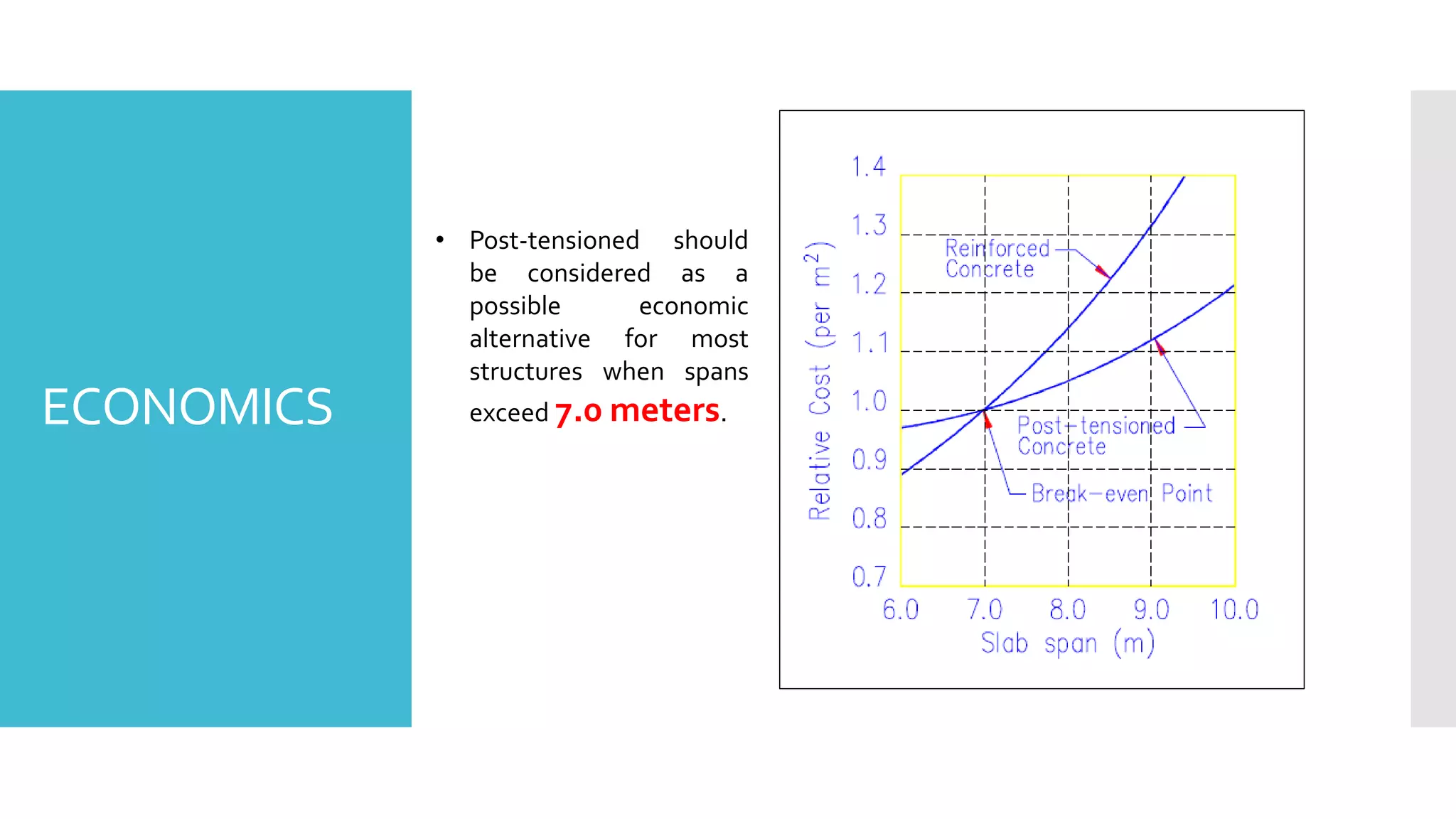
The document discusses the post-tensioned floor system, detailing its construction methodology and advantages such as lighter and un-cracked structures, faster construction, and reduced costs compared to conventional reinforced concrete. It also addresses disadvantages like high corrosion risk and complexity of work. Additionally, economic analysis shows that post-tensioned systems are more cost-effective for spans exceeding 7.0 meters, with notable time savings in construction cycles.









![REFERENCES
[1] “POST-TENSIONING IN BUILDING STRUCTURES”, Ed Cross1
BE, Grad.Dip(Tech.Mgt), MIEAust, CPEng.
[2] POST-TENSIONEDSLABS, PUBLISHED BYVSL
INTERNATIONAL LTD.
[3] Sanfield (India) LTD., PT Slab brochure.
[4] “A PROJECT-BASEDCOMPARISON BETWEEN REINFORCED
AND POST-TENSIONED STRUCTURES FROMA SUSTAINABILITY
PERSPECTIVE.”,Carol Hayek & Saleem Kalil.
[5] www.concreteconstruction.net](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ptppt-160909102502/75/Post-tension-Floor-System-15-2048.jpg)
