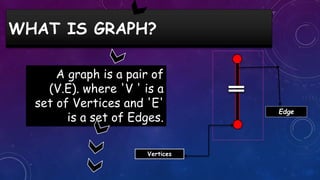
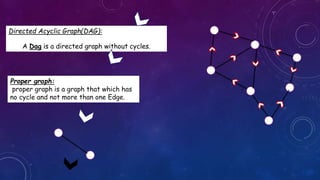
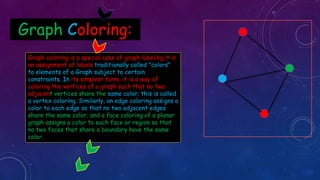
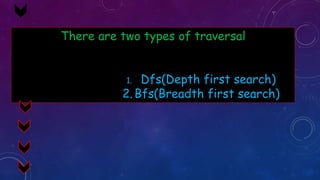
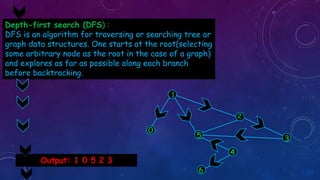
The document provides an overview of graph concepts including definitions of a graph as a pair of vertices and edges, different types of graphs such as directed/undirected graphs and cyclic/acyclic graphs. It also discusses graph coloring, adjacency matrices/lists for representing graphs, and algorithms for traversing graphs including depth-first search and breadth-first search. Examples are given for each concept to illustrate key differences and properties.