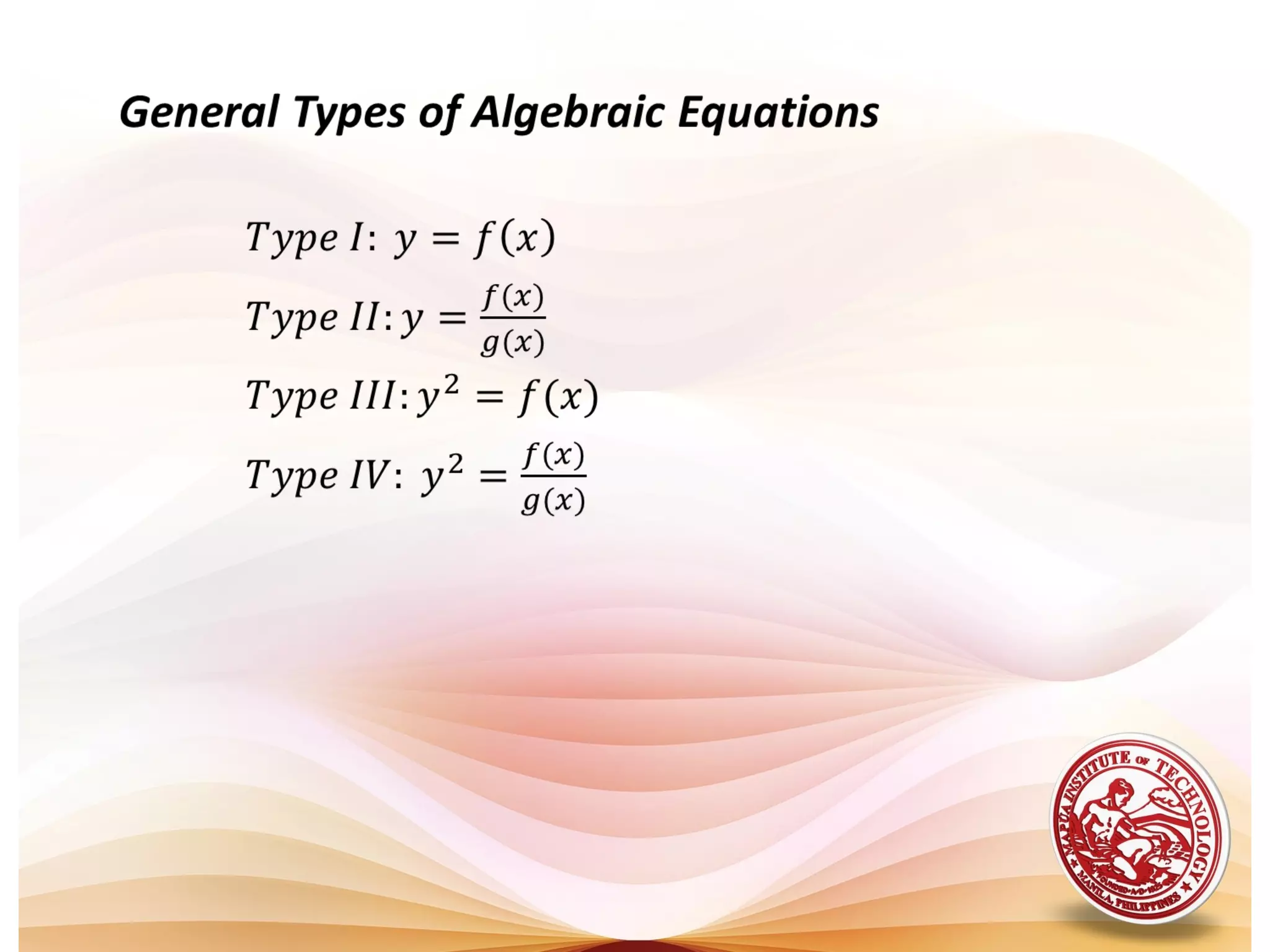
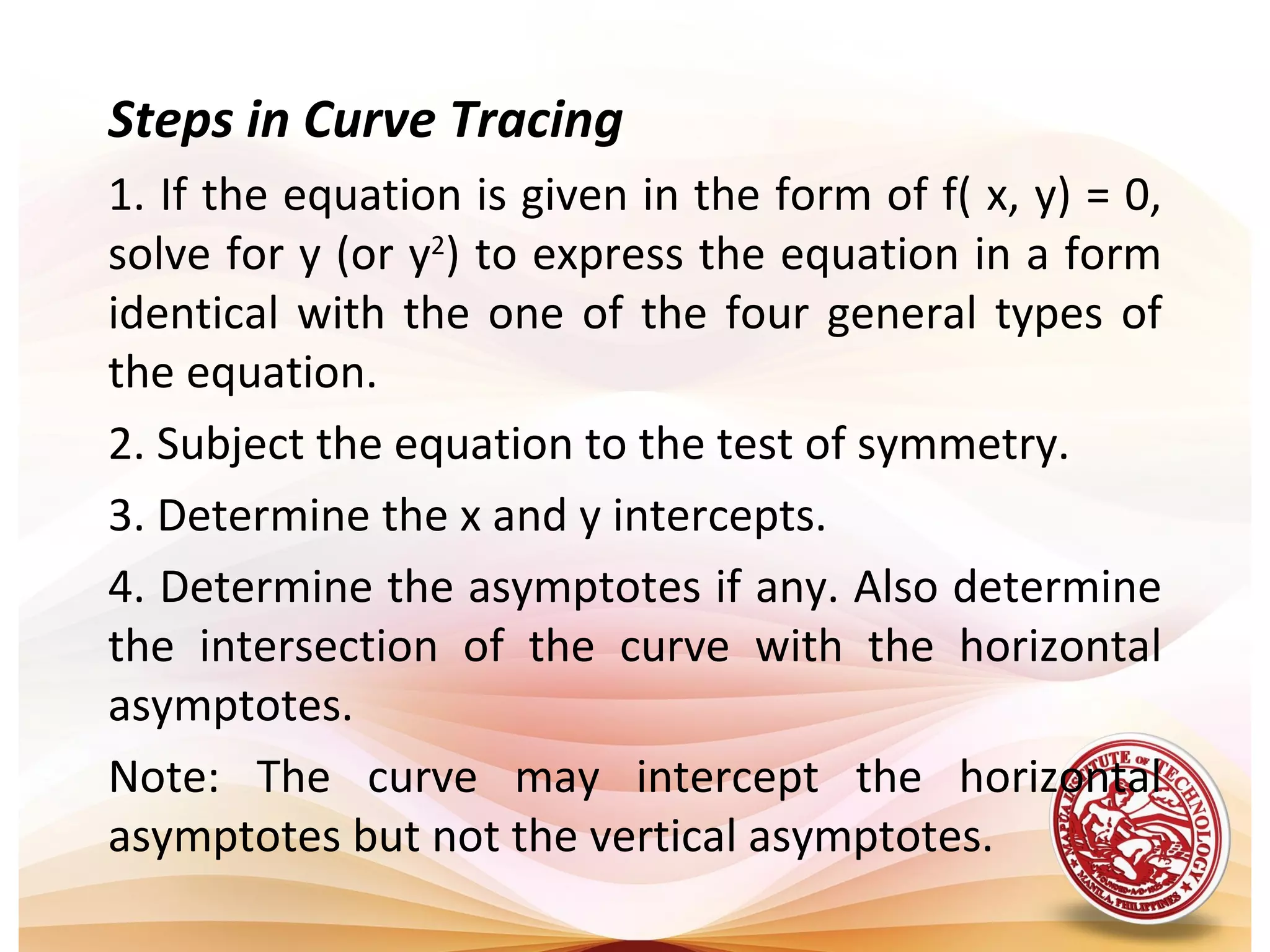
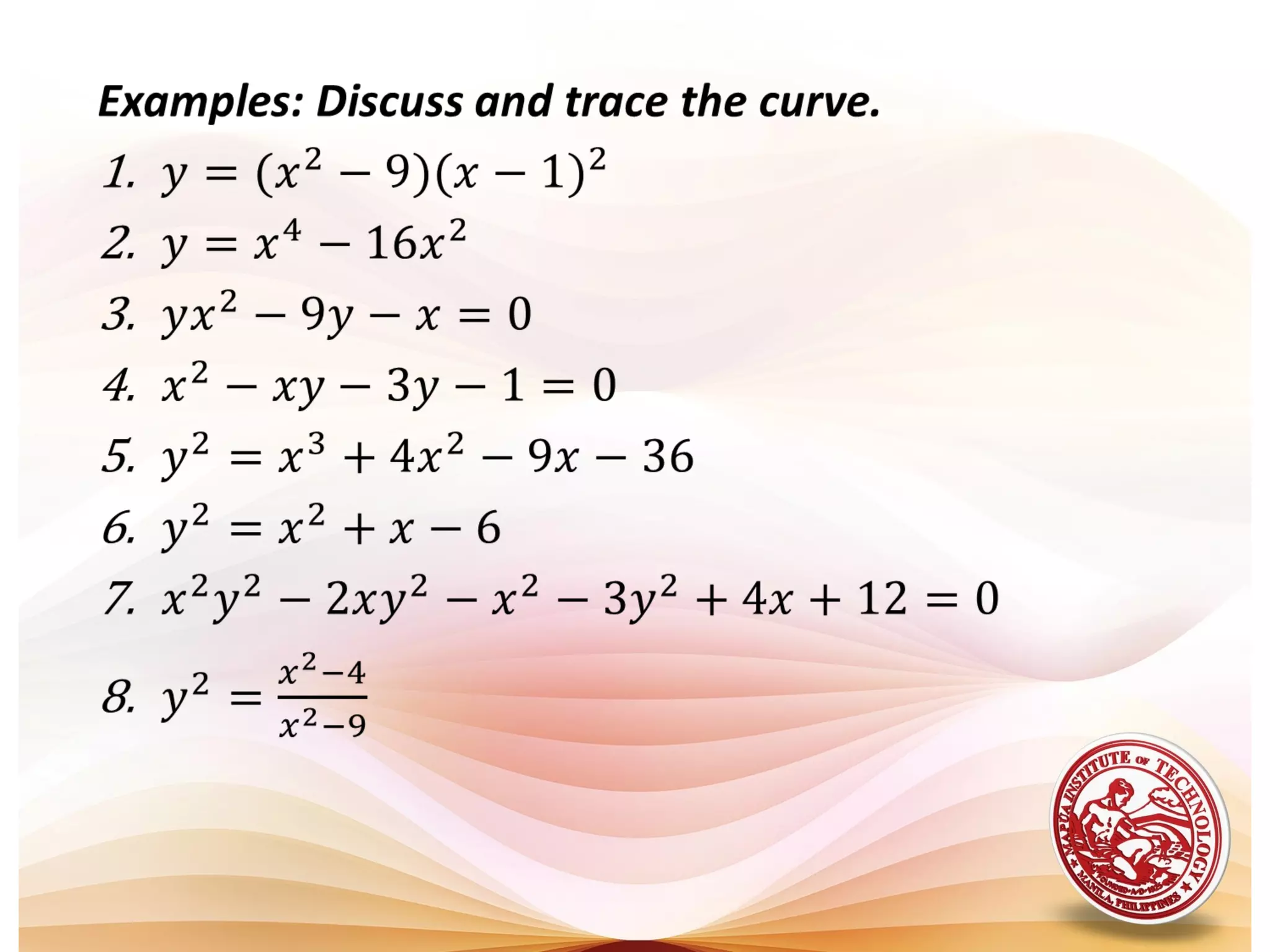
1) The document defines algebraic curves as geometric figures formed by the set of points satisfying a given equation relating x and y.
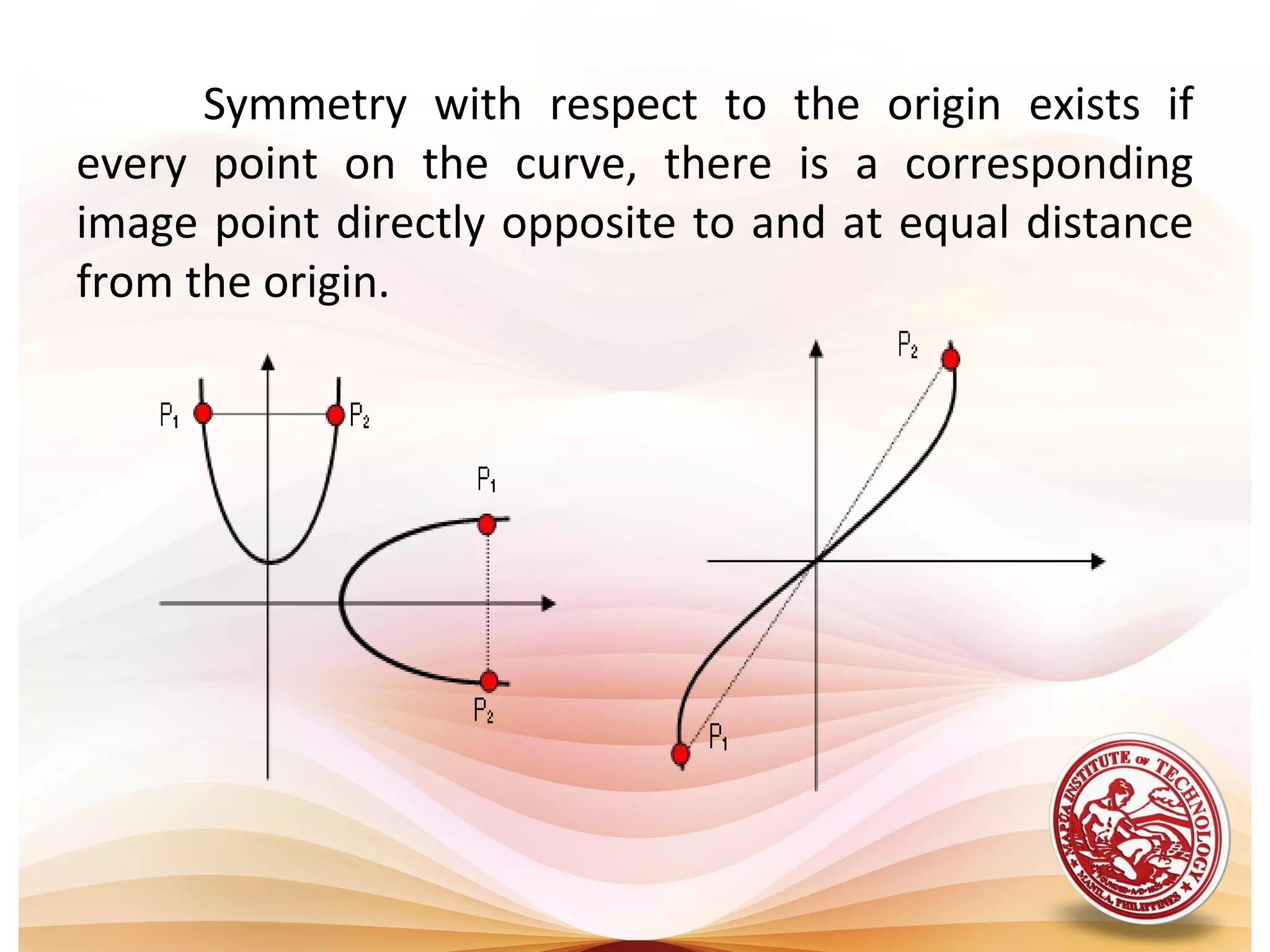
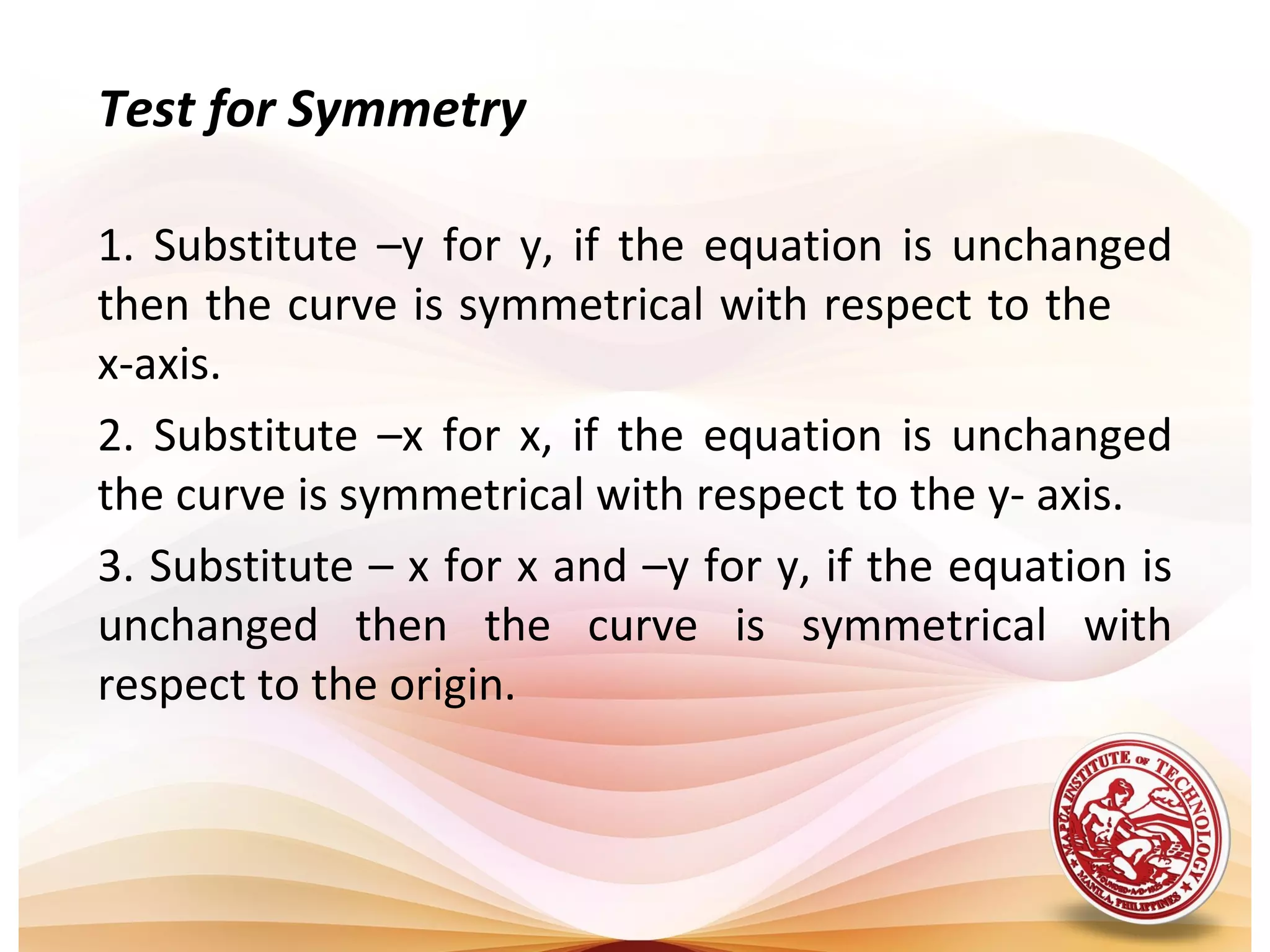
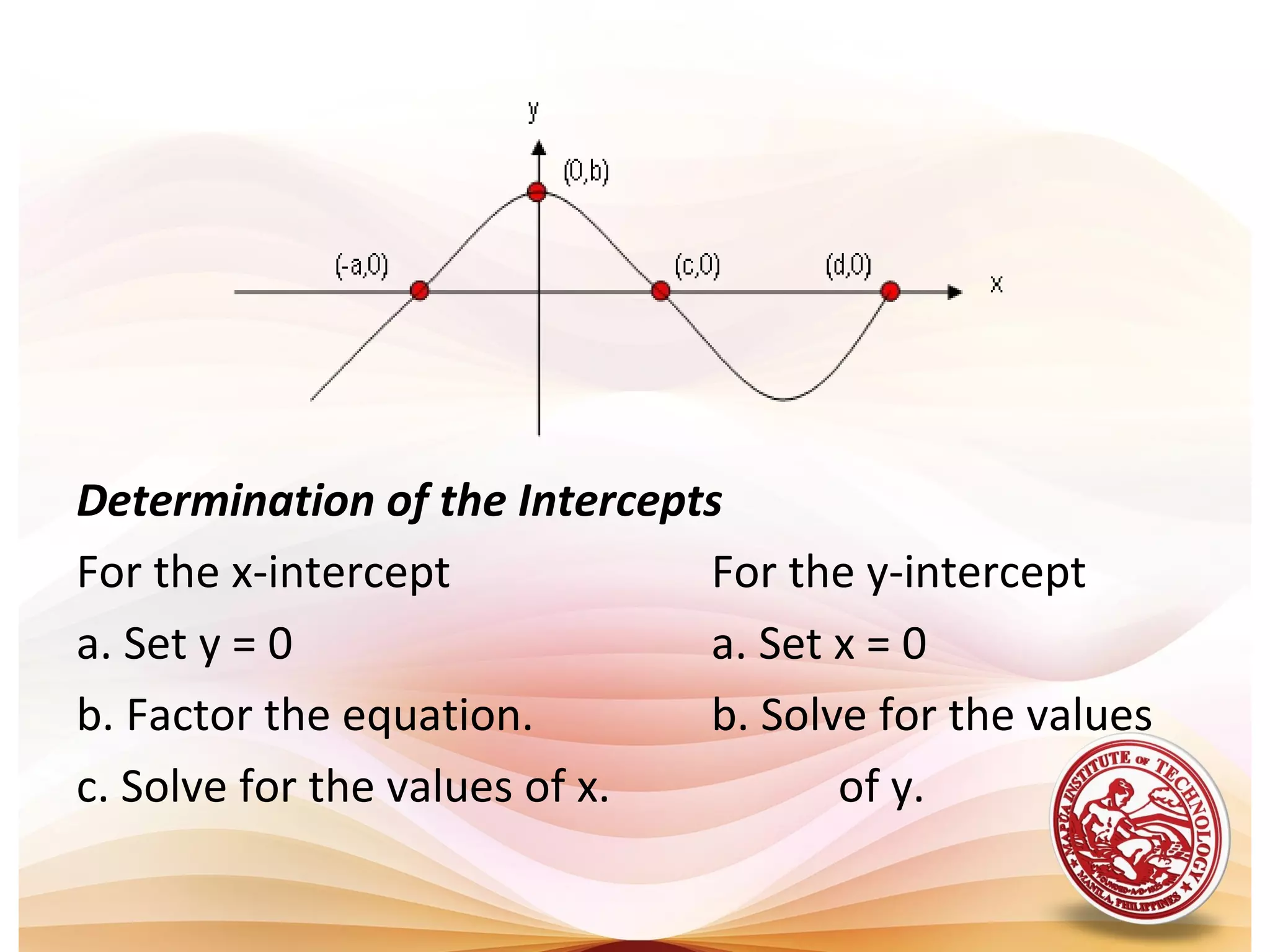
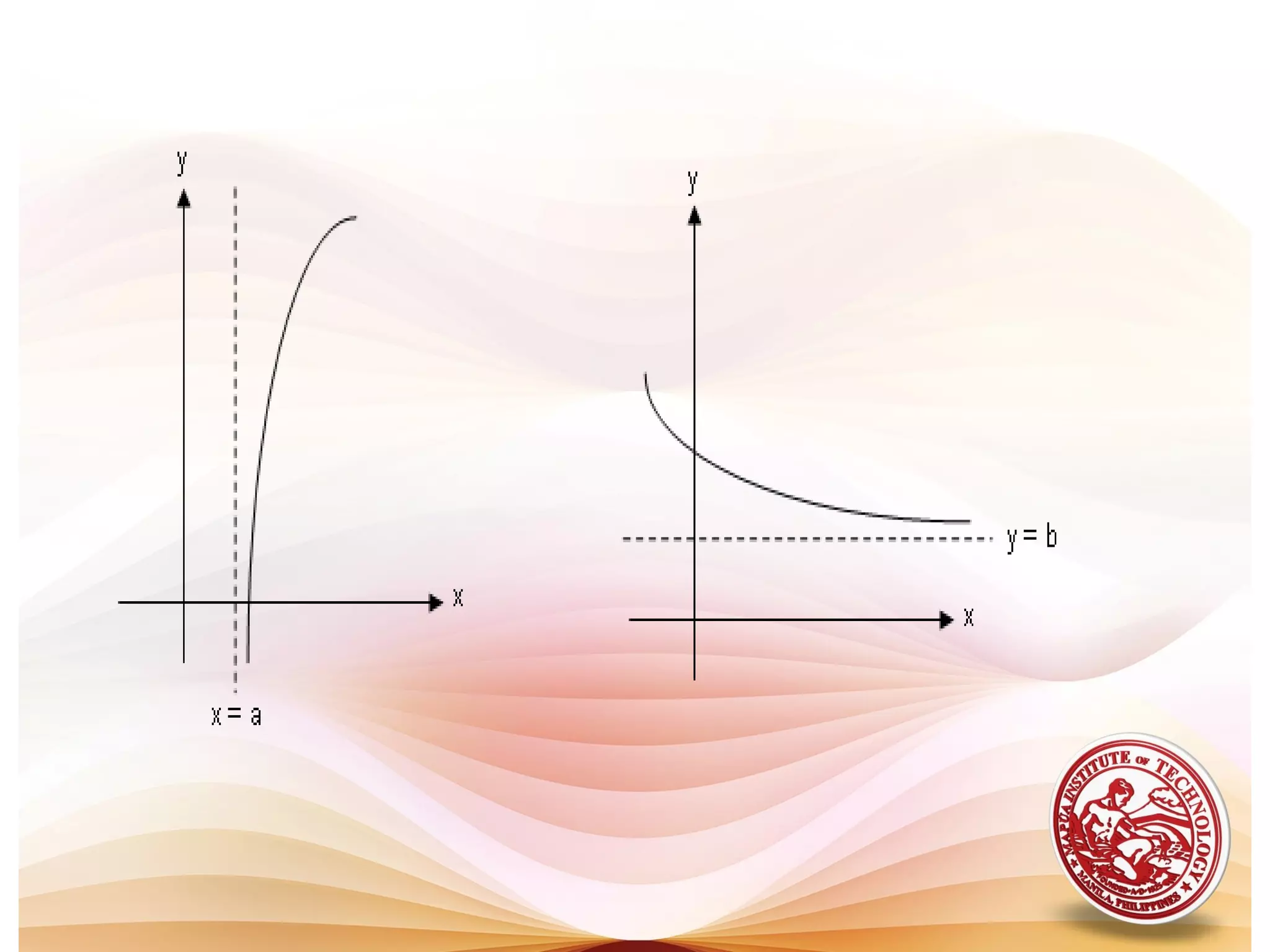
2) Key properties of algebraic curves include their extent (domain and range), symmetry, intercepts, and asymptotes. Symmetry can be tested by substituting -x or -y. Intercepts are where the curve crosses the axes. Asymptotes are lines a curve approaches but never touches.
3) Tracing a curve involves determining its region, testing for symmetry, finding intercepts and asymptotes, and plotting points to sketch the curve.