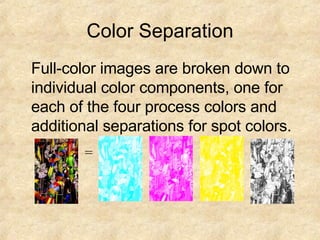
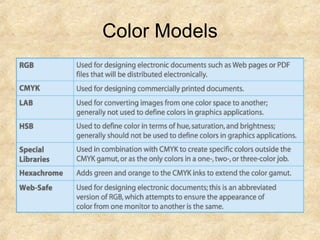
There are two main types of graphics formats - vector and raster. Vector graphics can scale infinitely and have small file sizes but raster images have fixed resolution. There are three main formats used on the web - GIF, JPG, and PNG. GIFs use lossless compression and are best for images with few colors like line art. JPGs use lossy compression and are best for photos. PNGs support transparency and compression but not animation. Pixels are the smallest element in an image and color depth refers to the number of bits used to represent each pixel, affecting the number of displayable colors. Resolution refers to pixels per inch, affecting image sharpness.