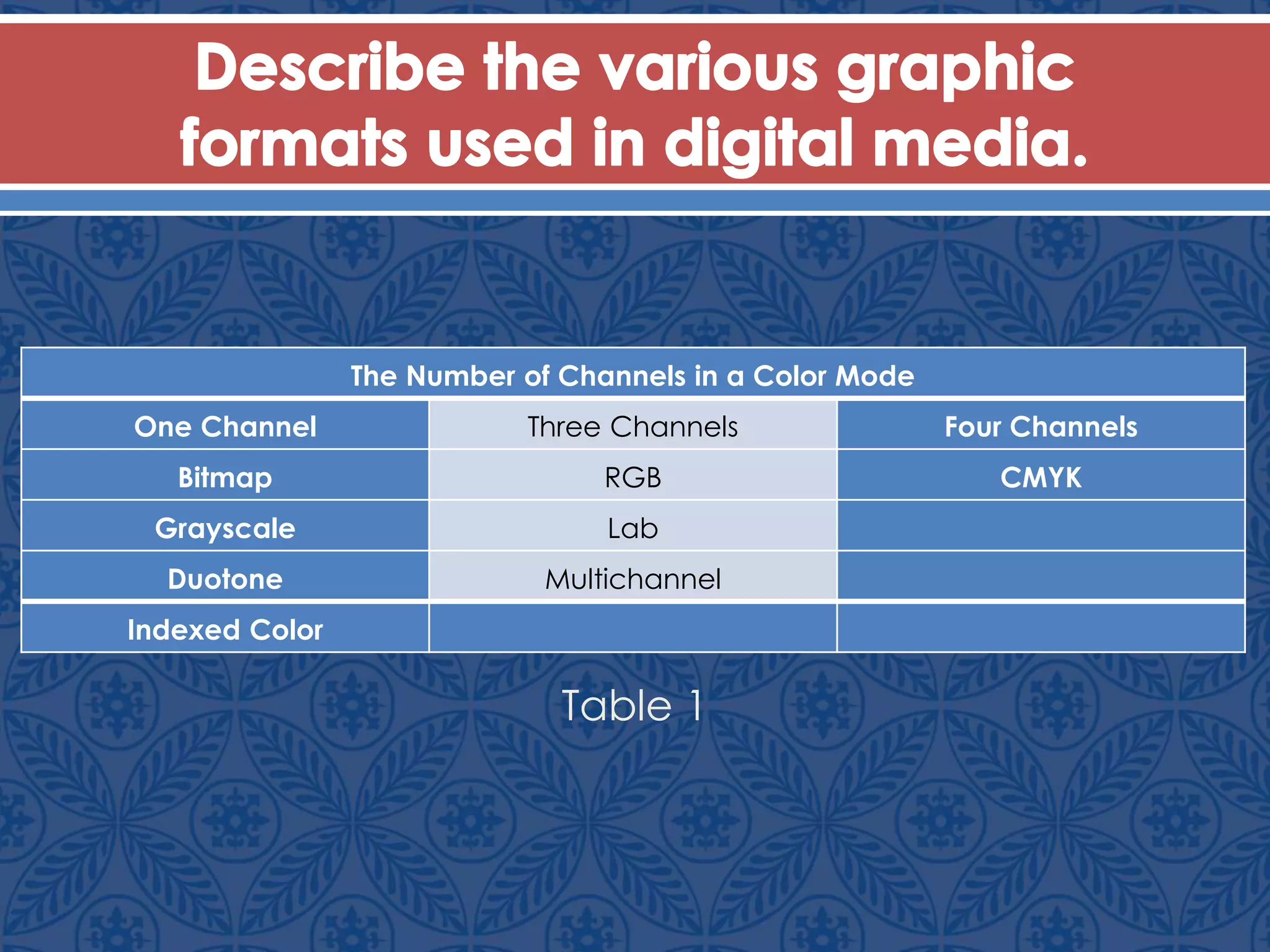
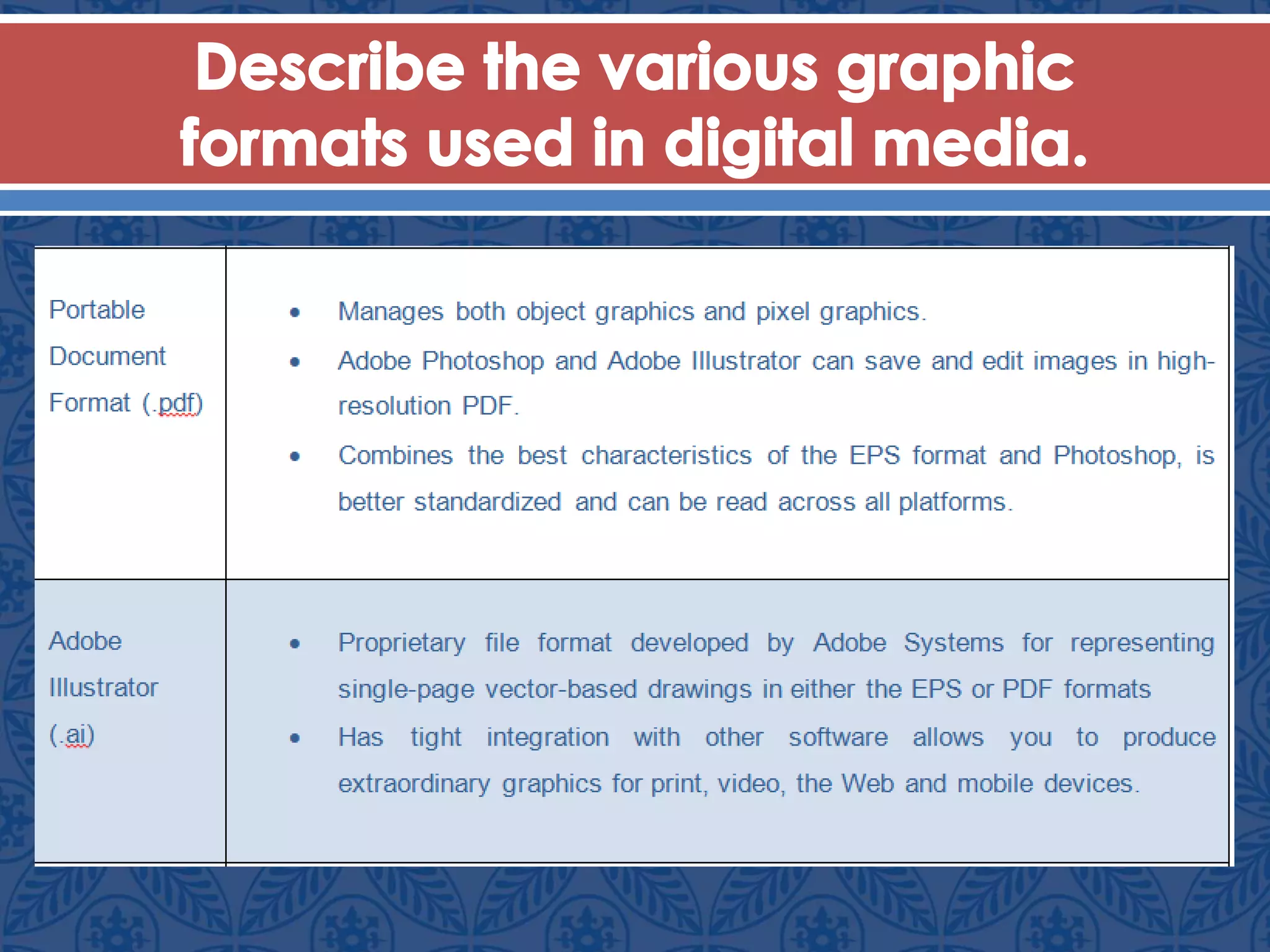
Vector graphics use mathematical formulas to define images as objects made of points and paths, allowing resolution-independent scaling. Raster graphics are composed of pixels arranged in a grid to form images. Key factors that determine raster image quality include resolution, color depth, and file format. Common file formats like JPEG, PNG, and GIF vary in their compression algorithms and support for animation and transparency.