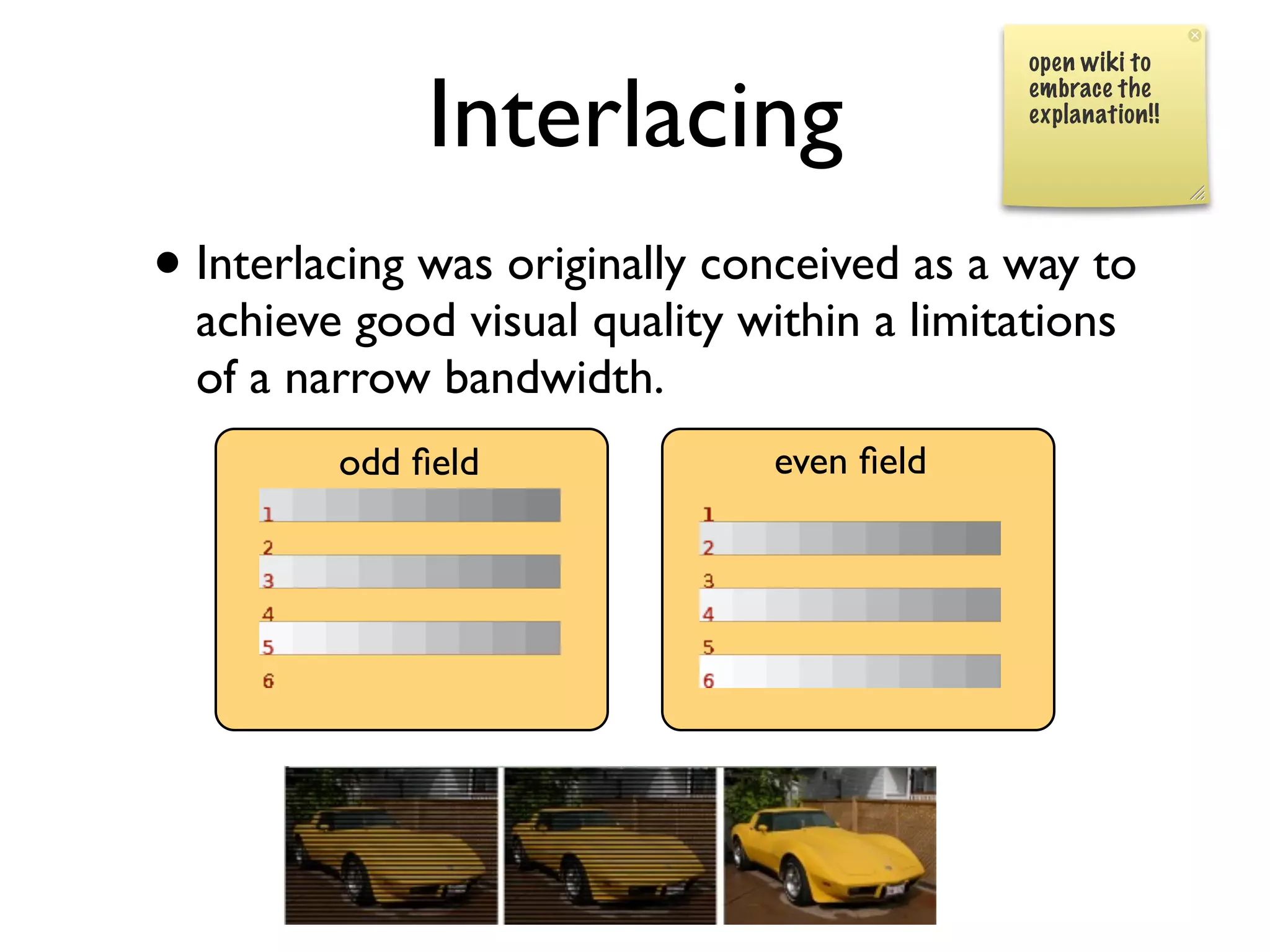
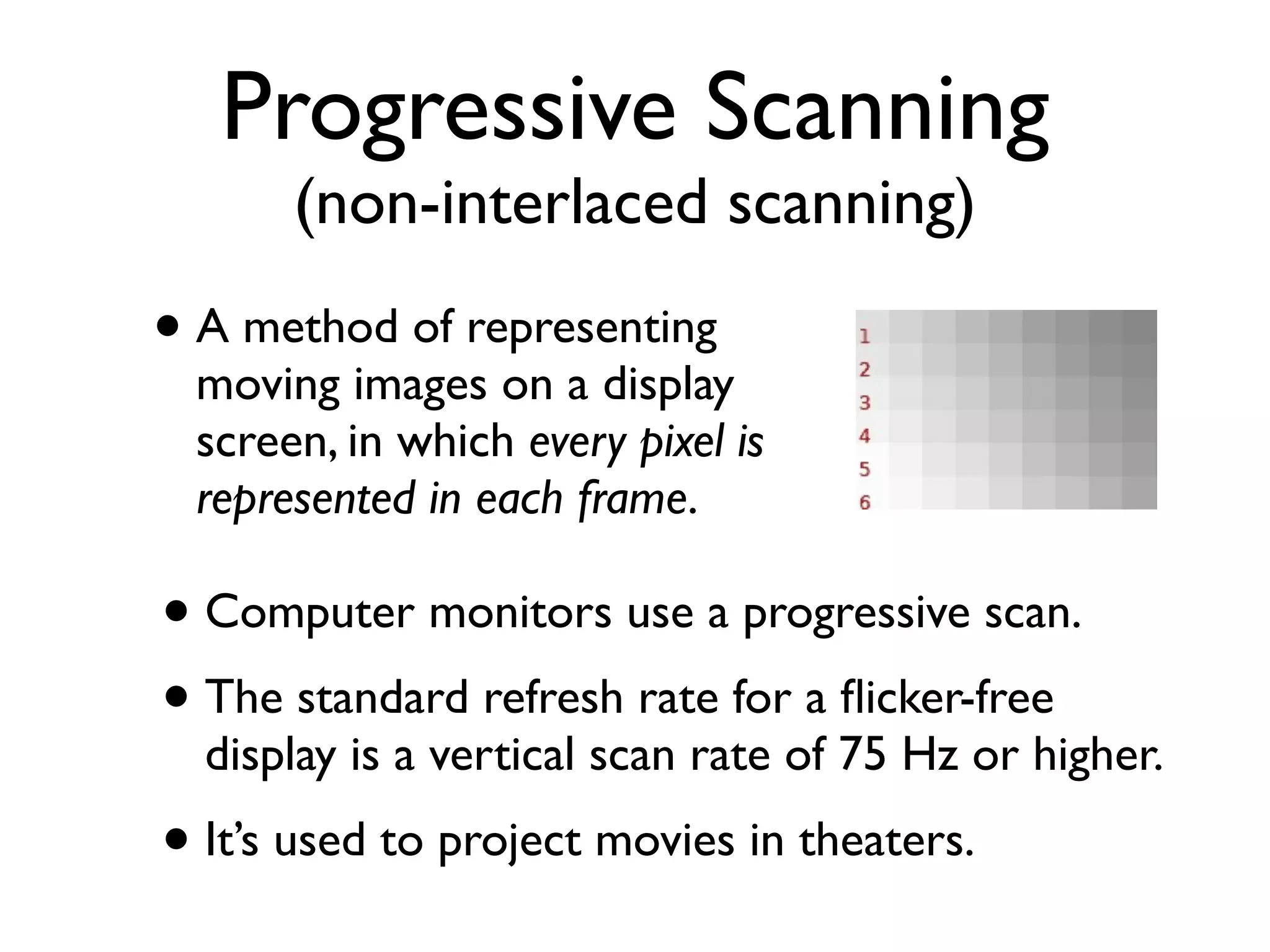
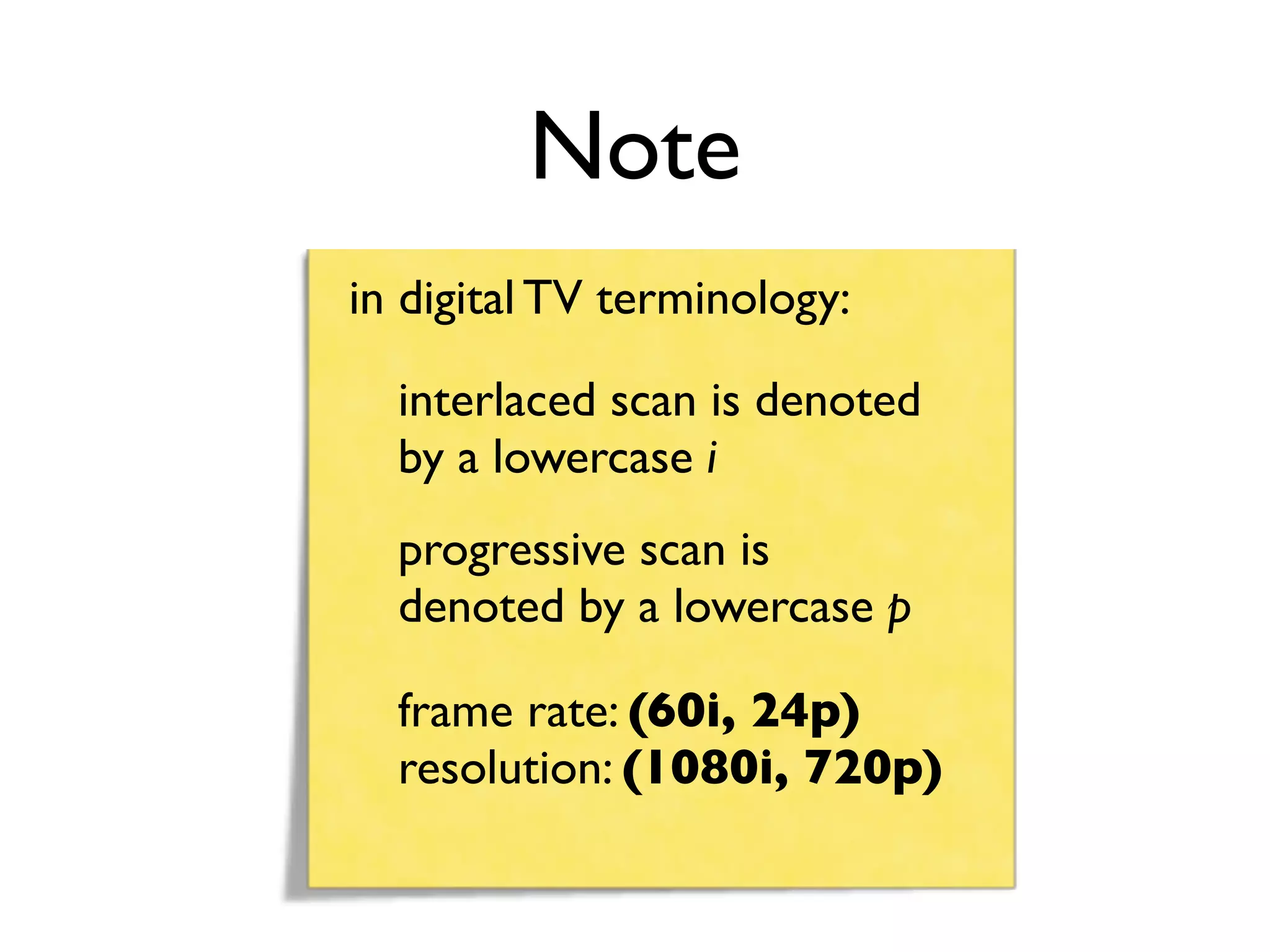
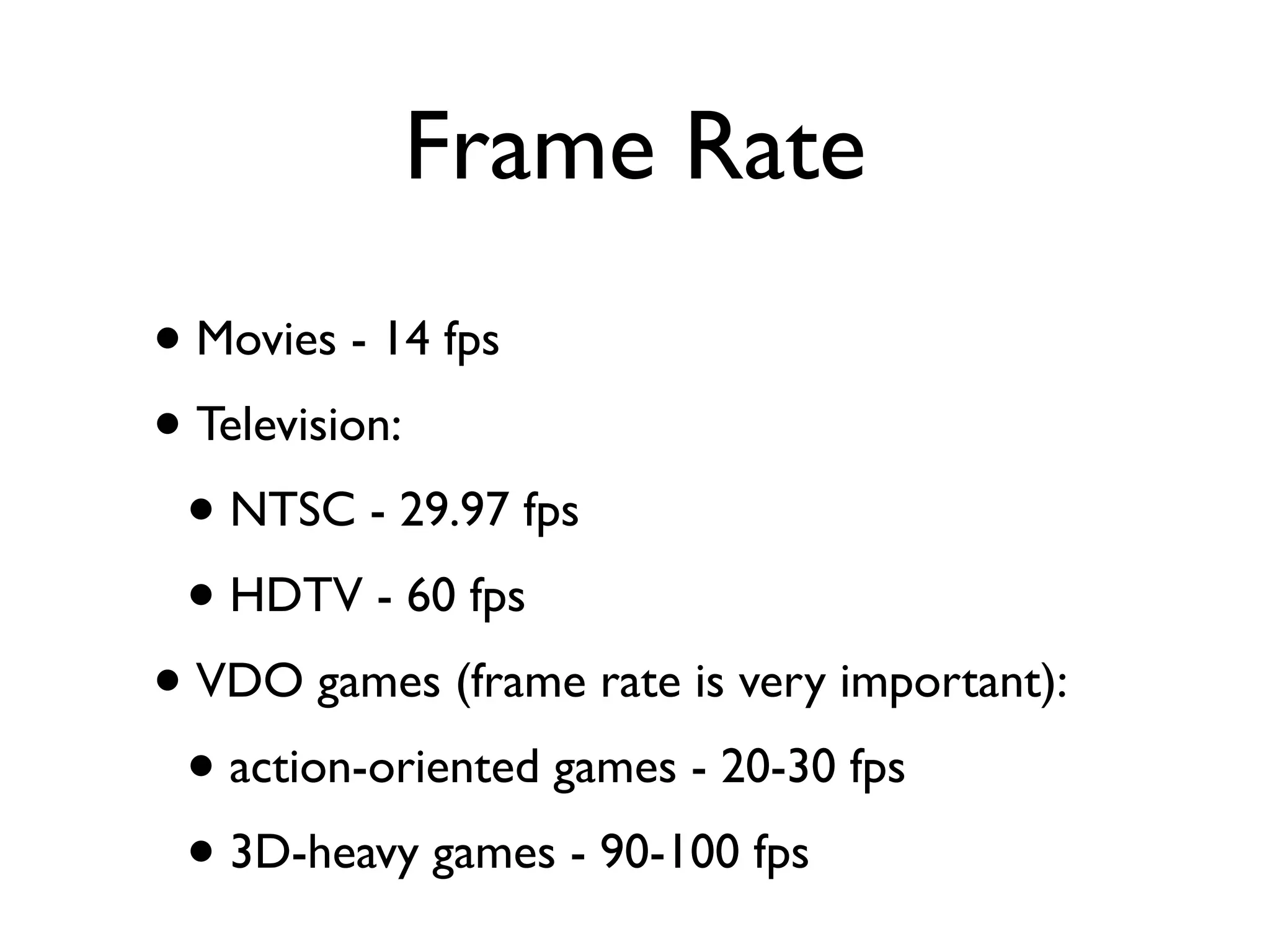
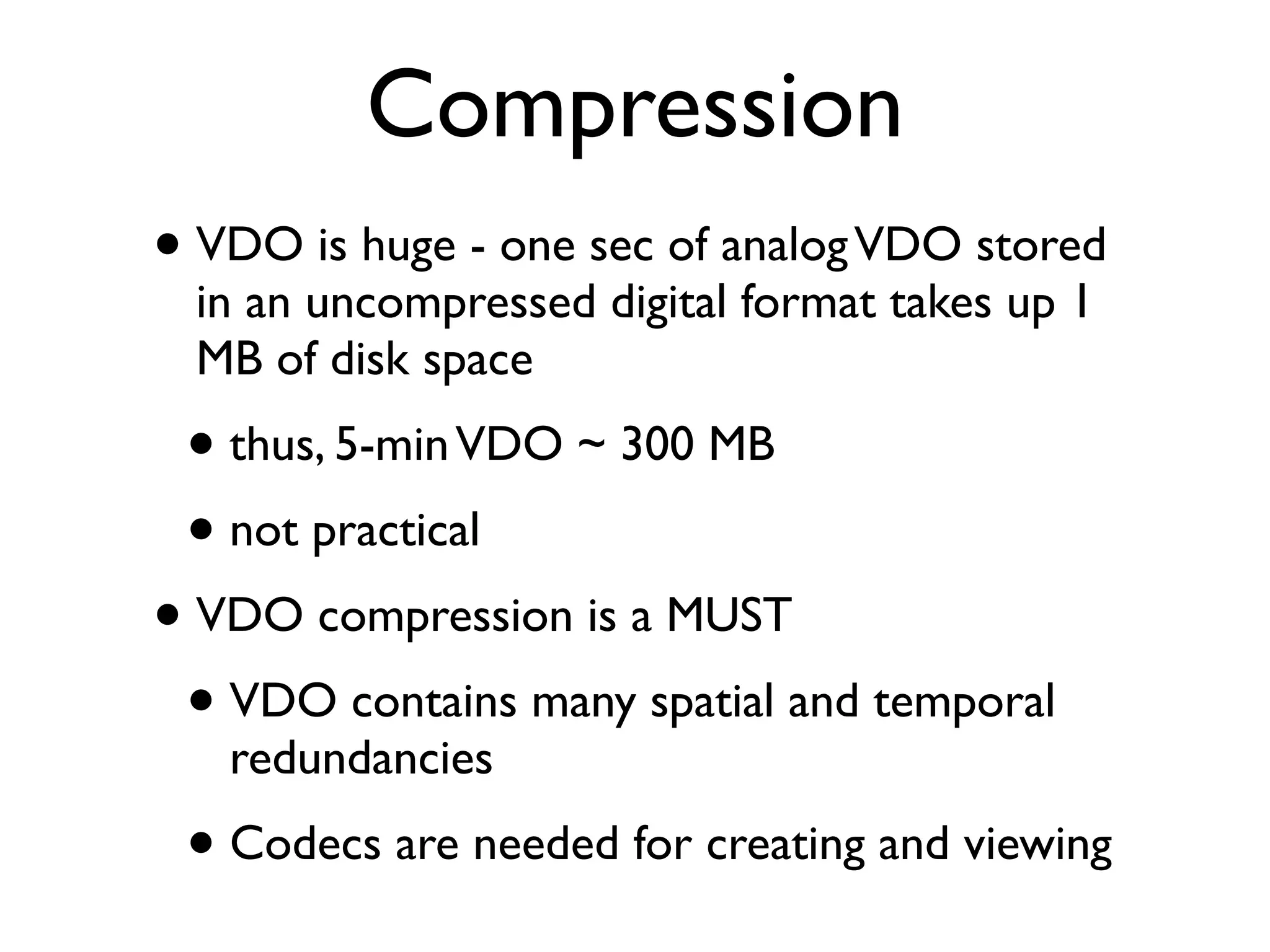
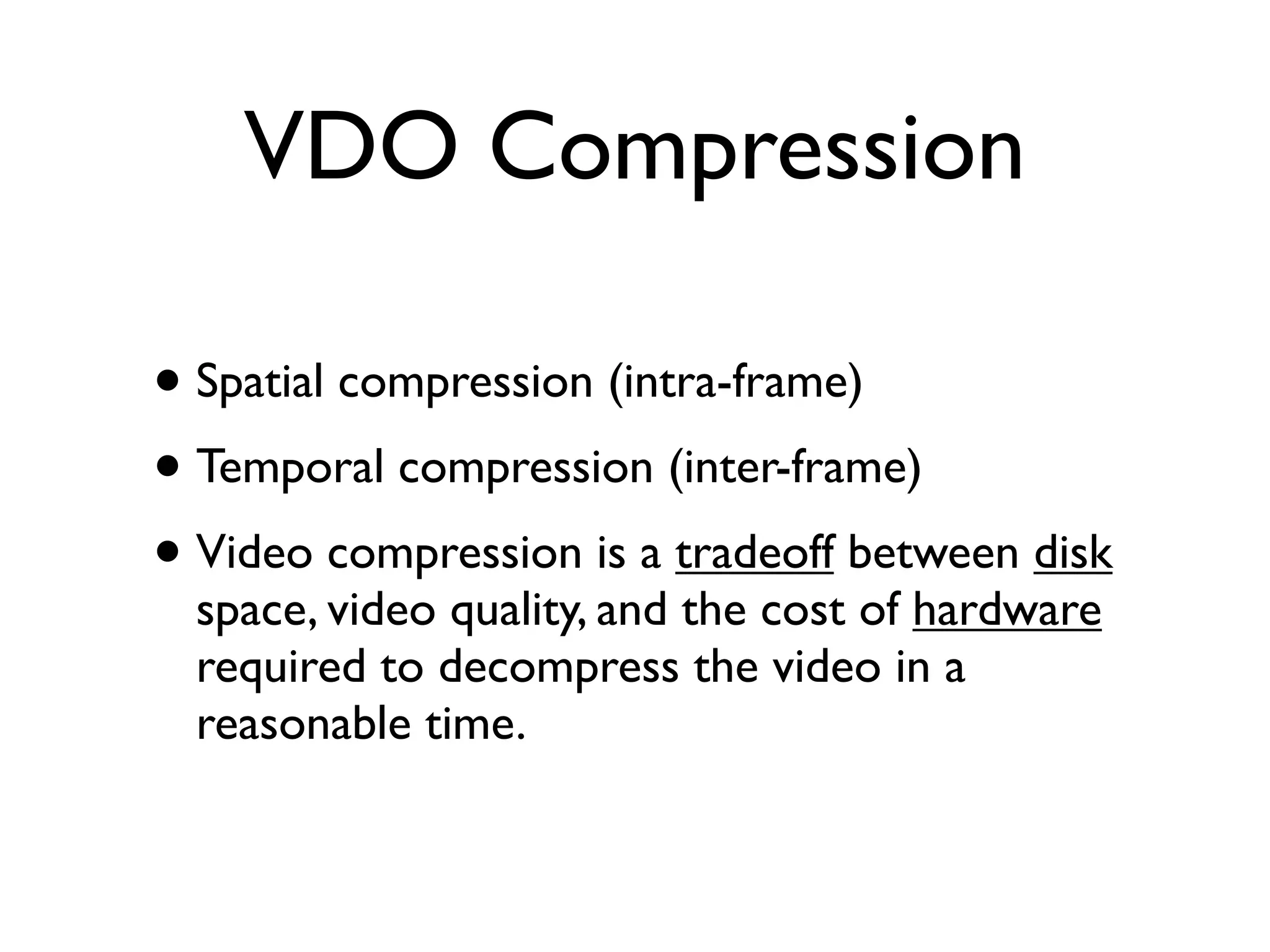
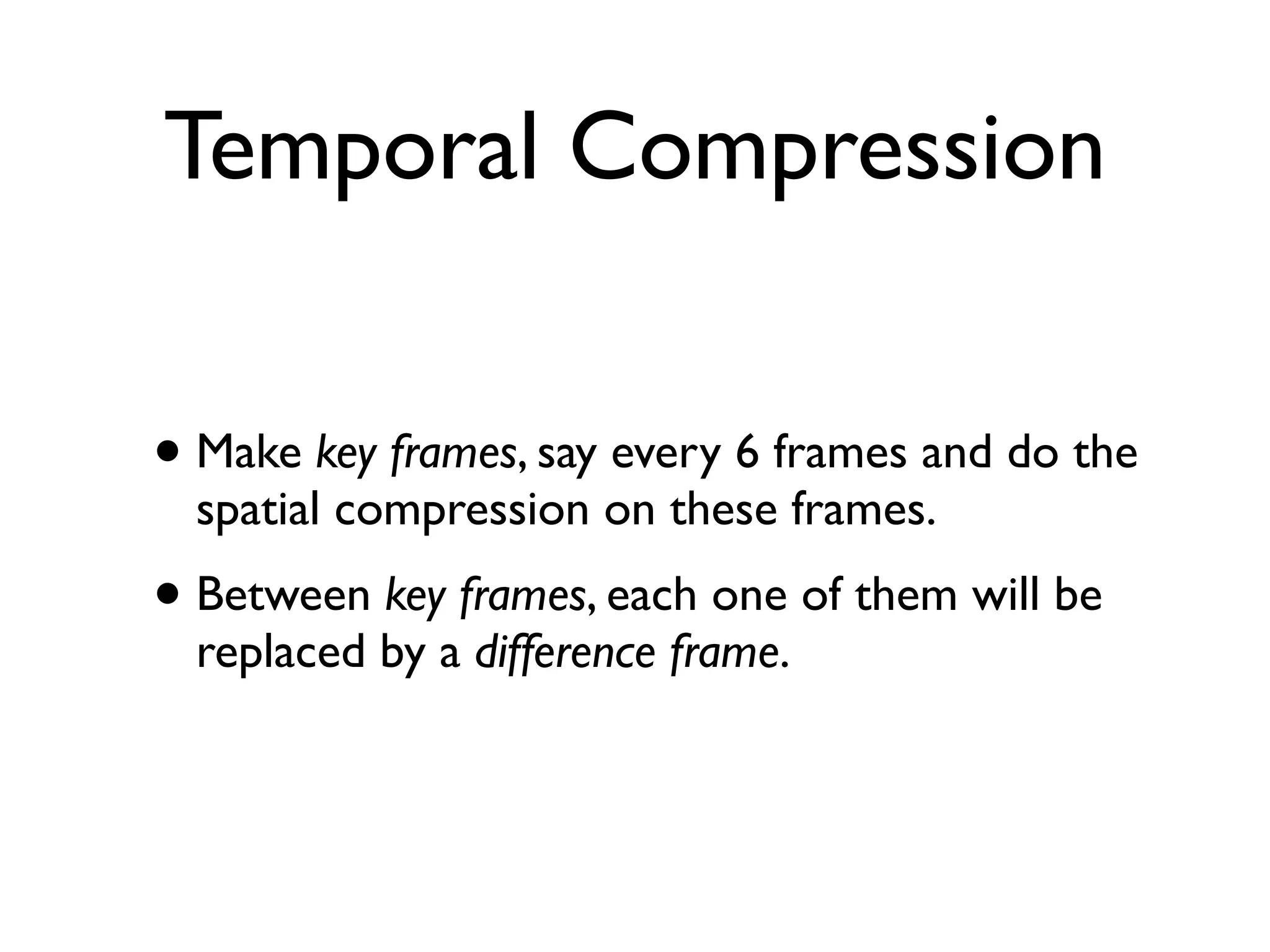
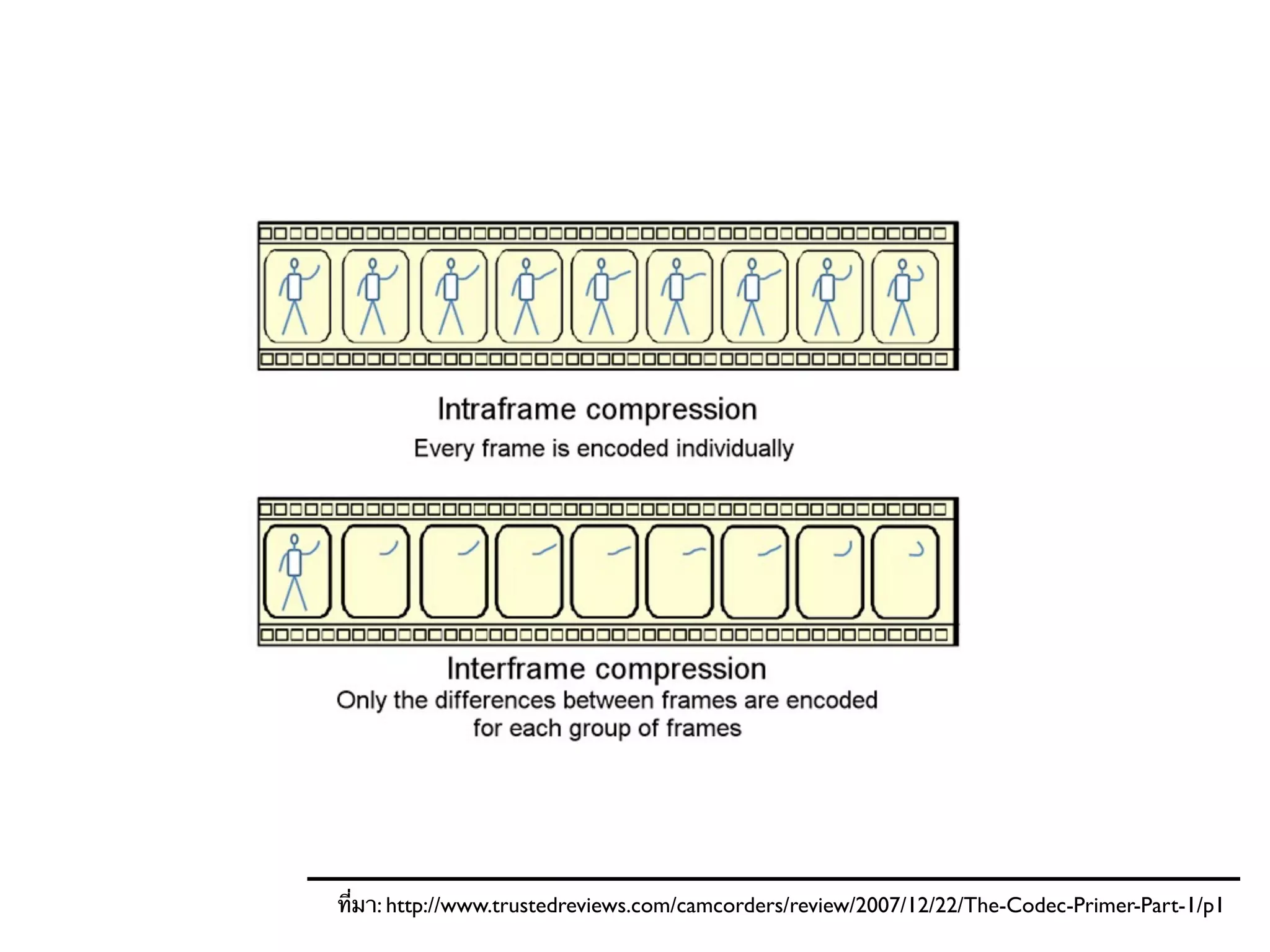
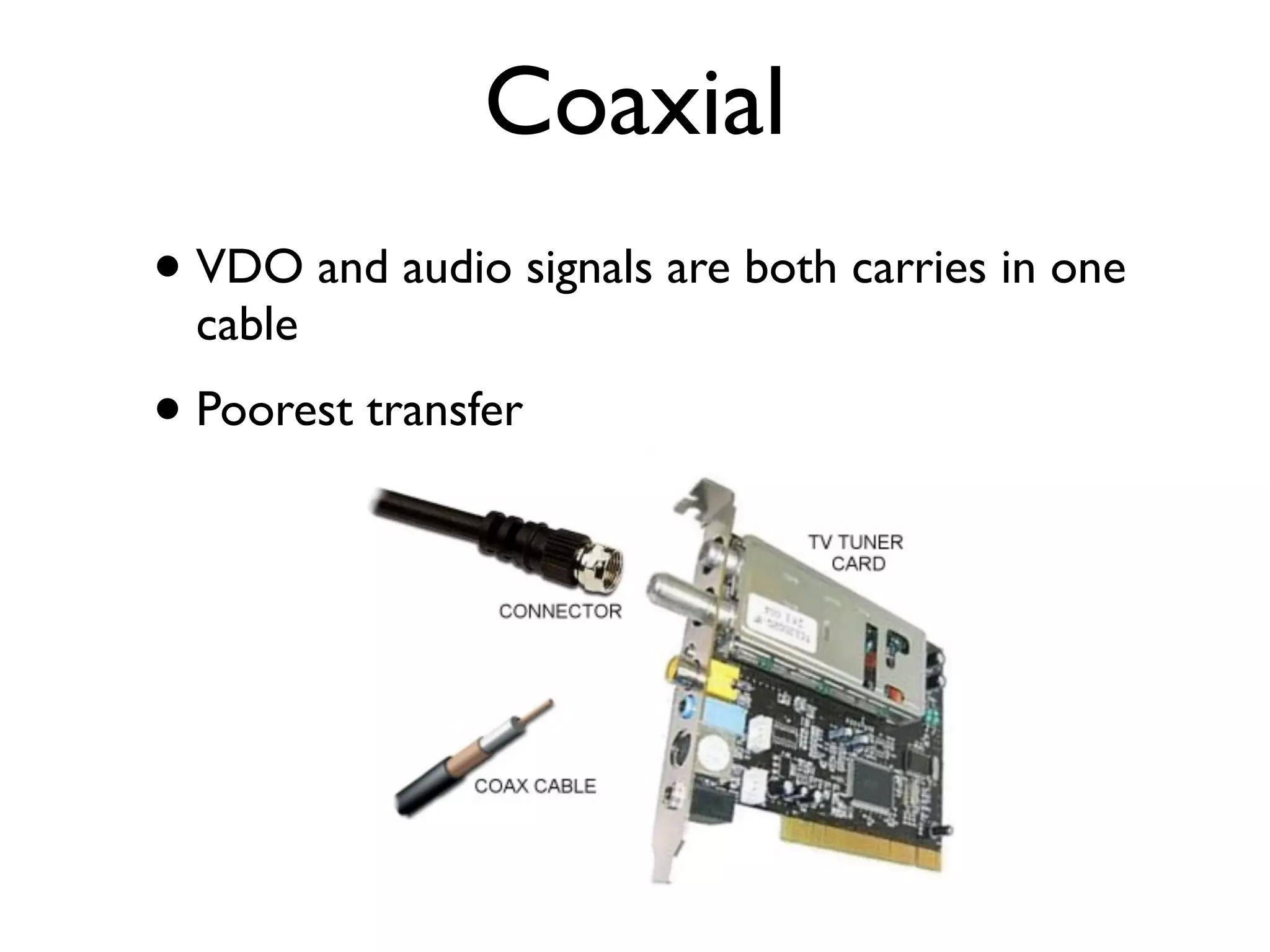
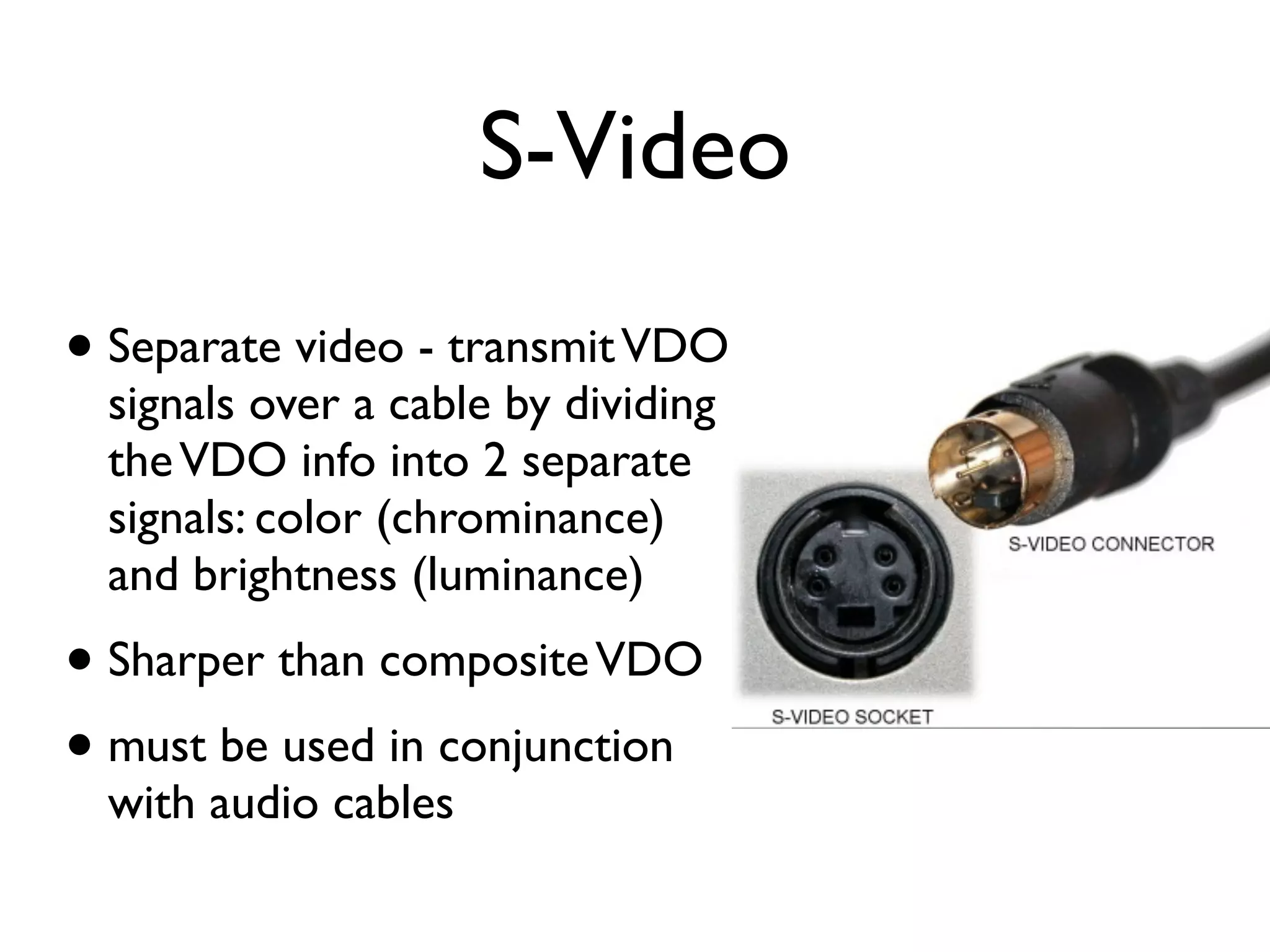
This document provides an overview of key concepts in multimedia systems including digital video formats, properties of video such as frame rate and aspect ratio, video compression techniques, and video production equipment and processes. It covers analog vs digital video, interlacing vs progressive scanning, common video file formats like AVI, MOV, and MPG, and how to transfer video from a camcorder to a computer.
![ia Systems
520251: Multimed
Êส‹‹Çว¹น»ปÃรÐะ¡กÍอºบÁมÑัÅลµตÔิÁมÕีàเ´ดÕีÂย
[ÇวÔิ´ดÕีâโÍอ]
3 ¡กÑั¹นÂยÒาÂย¹น 2555](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06-vdo-120913004730-phpapp01/75/06-vdo-1-2048.jpg)