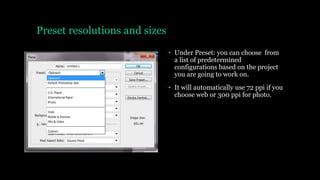
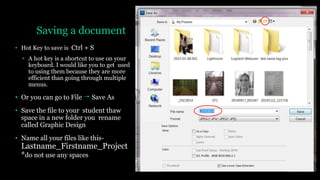
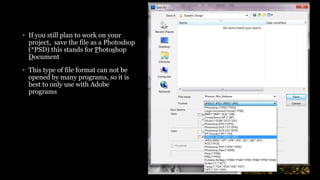
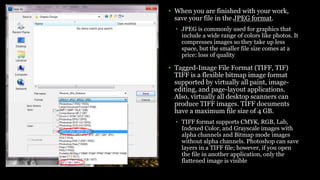
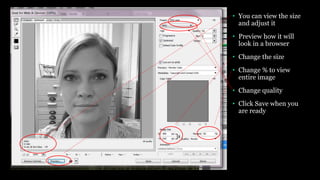
This document provides an introduction to using Photoshop including an overview of its tools and functions. It discusses opening and saving images in various formats, and setting image size and resolution for different uses such as web or print. Key terms like raster images, pixels, resolution, and bit depth are introduced. The document demonstrates how to create and save new documents and provides resources for learning more Photoshop skills.