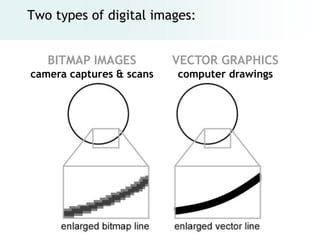
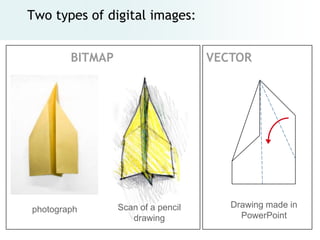
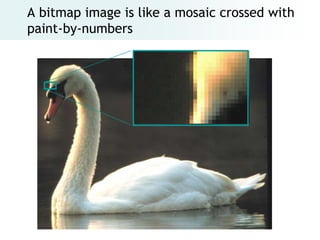
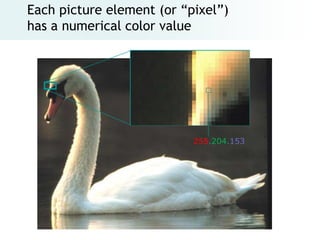
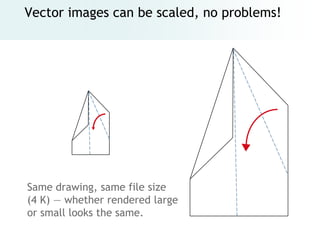
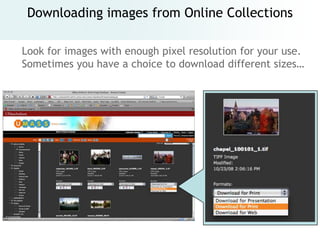
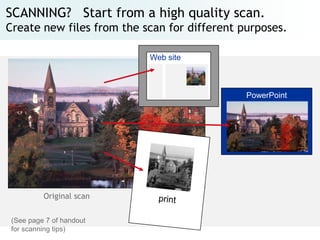
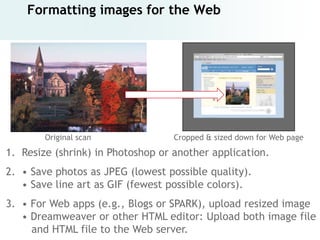
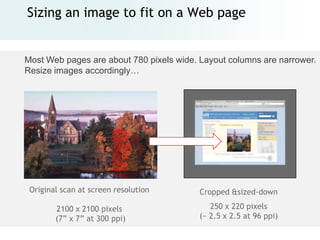
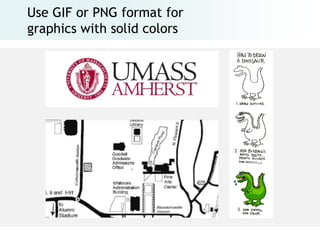
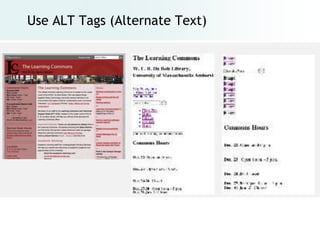
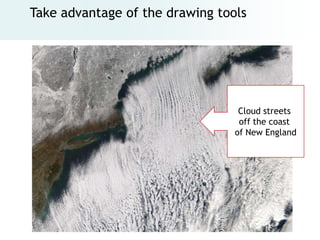
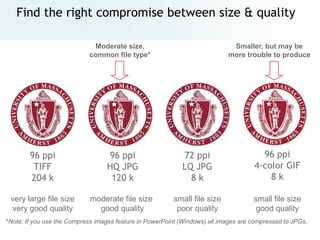
The document provides an overview of digital images, including sources for obtaining them, copyright considerations, and types of images (bitmap and vector). It discusses technical aspects such as resolution, pixel values, and color depth, as well as practical tips for formatting images for web, print, and presentations. Additionally, it covers the process of downloading, resizing, and optimizing images for various uses.