The document provides information on various Spanish grammar topics including:
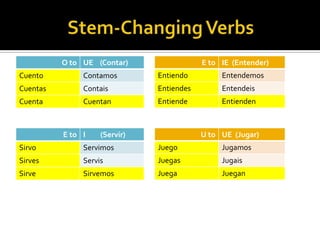
1. Nationalities and stem-changing verbs
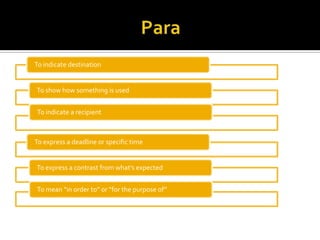
2. The uses of para, a, and de to indicate different meanings
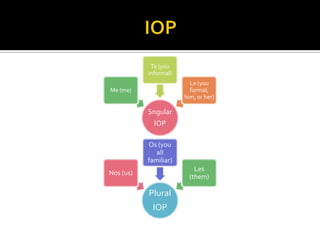
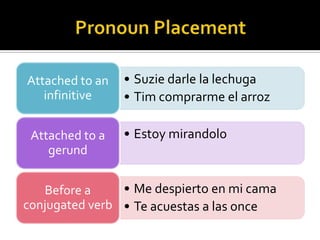
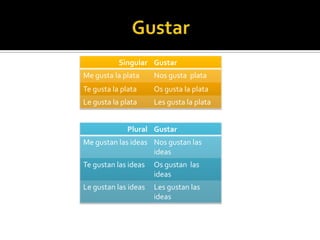
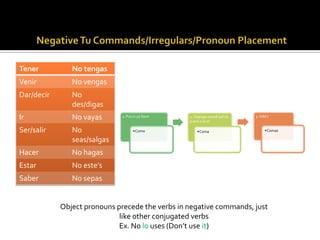
3. Different object pronouns used with singular and plural subjects
4. Forming reflexive verbs and examples of common irregular reflexive verbs
5. Ways to indicate sequencing of events in Spanish including first, then, before, after, etc.