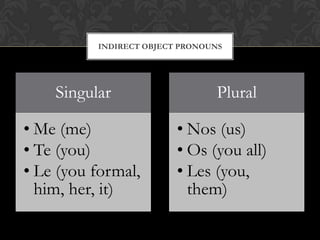
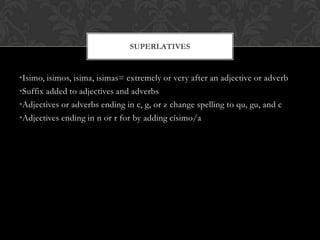
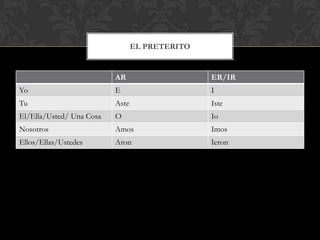
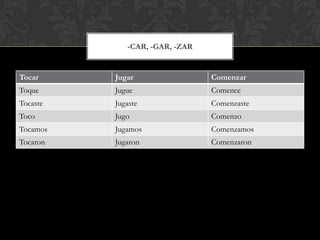
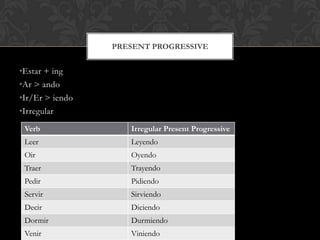
The document is a grammar book that covers topics such as: stem changing verbs, para, indirect object pronouns, pronoun placement, gustar, affirmative and negative words, superlatives, reflexives, affirmative and negative tu commands with irregular verbs and pronoun placement, sequencing events, el preterito, trigger words, verbs ending in -car, -gar, -zar, deber + infinitive, modal verbs, present progressive, and adverbs ending in mente. It provides conjugations, examples, and explanations of grammar structures in Spanish.