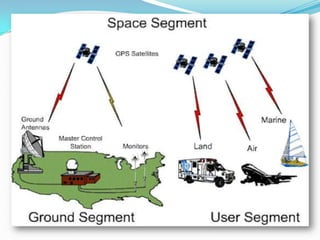
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system consisting of 24 satellites in medium Earth orbit controlled by the US Air Force. A GPS receiver can determine its position by measuring the time delay of signals received from at least 3 satellites to calculate distance via trilateration. The system consists of space, control, and user segments, with the control segment monitoring satellite health and transmitting updates. GPS is mainly used for navigation, mapping, and has military applications.