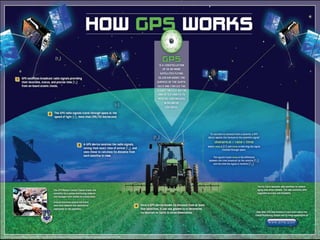
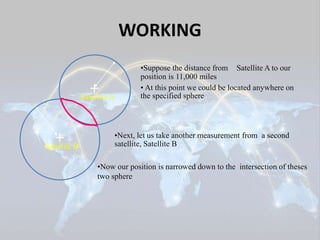
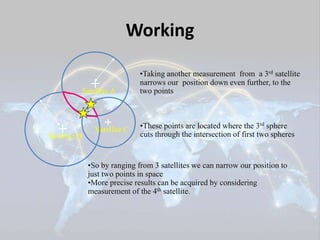
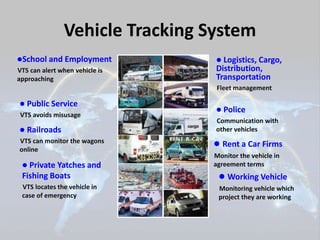
The document summarizes a seminar presentation on the Global Positioning System (GPS). It describes GPS as a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth. The presentation covers the history of GPS, how it works using satellites and receivers, its applications in navigation and tracking, and advantages like its coverage and ease of use, as well as disadvantages like potential signal interference.