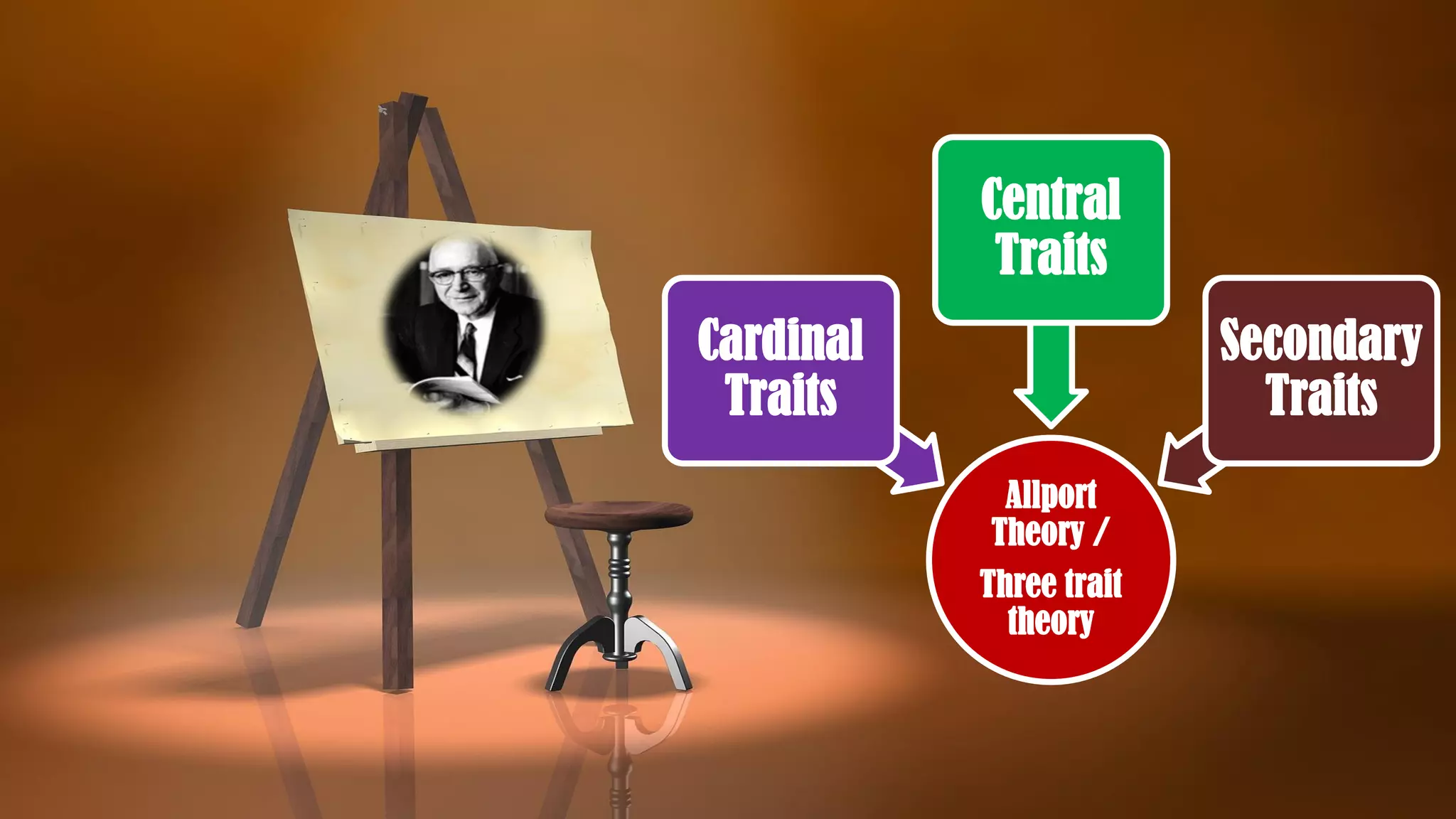
The document discusses trait theory in personality psychology, distinguishing between personality types and traits. Gordon Allport's work categorizes traits into cardinal, central, and secondary traits, each playing different roles in shaping behavior and personality. It emphasizes that traits are stable over time, vary among individuals, and influence perceptions and actions.