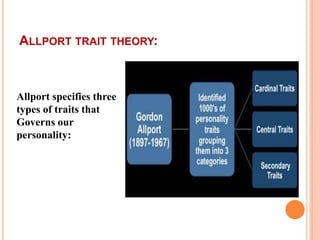
Gordon Allport's personality theory defines personality as a dynamic organization of psychophysical systems that influences individual behavior and thought. He distinguishes between cardinal, central, and secondary traits, positioning traits as fundamental to personality and highlighting six standards for mature personality. Allport's approach, rooted in common sense, emphasizes the uniqueness of individuals but is critiqued for its lack of empirical generalizability.